Abstract
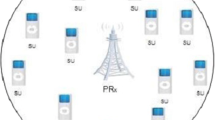
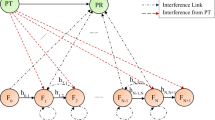
Transmit antenna selection (TAS) is most popular technique in underlay cognitive radio (CR) networks as they increase the capacity of secondary users with less hardware requirements. In this paper, a new scenario of CR ad-hoc network topology is proposed in which apart from primary users, there are multiple number of secondary users which are assumed to be distributed as homogeneous spatial Poisson point process (PPP) and are trying to use the primary spectrum in underlay mode. These multiple secondary transmitters generate the aggregate interference and can degrade the performance of secondary receiver. Here this aggregate interference is estimated and its impact on performance of secondary receiver under unconstrained mode of operation is presented. Further, to enhance the performance of secondary receivers in this scenario, single TAS technique based on maximizing the received signal to interference noise ratio by using optimum combining (OC) method is proposed. Furthermore, in this work the design of end to end Simulink based environment for secondary trans–receiver system with advancements in channel design and estimation is proposed. The bit error rate (BER) analysis is presented and verified for image data for single TAS-OC technique for unconstrained mode in underlay CR network in Rician fading channel. The BER performance is also presented for different number of secondary interference sources which are located at fixed distance in one case and they are assumed to be distributed as PPP in another case.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spectrum Policy Task Force (2002). Tech. rep. 02135, Federal Communications Commission.
Mitola, J. (1999). Cognitive radio for flexible mobile multimedia communications. In IEEE international workshop mobile multimedia communications (pp. 3–10).
Lee, W., Lee, H., & Cho, D. H. (2007). Cognition based seamless transmission by using underlay–overlay switching methods in future wireless communication system. In Wireless networks: International conference on cognitive radio oriented (pp. 374–383).
Zhang, R., & Liang, Y. C. (2008). Exploiting multi-antennas for opportunistic spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks, IEEE. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2(1), 88–102.
Ricardo, B., Jing, L., Thobaben, R., Jorswieck, E., & Skoglund, M. (2013). Multi-antenna transmission for underlay and overly cognitive radio with explicit message-learning phase. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, special issue on "Cooperative Cognitive Networks", 2013, 1–21.
Scutari, G., Palomer, D., & Barbarossa, S. (2008). Cognitive mimo radio. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25, 46–59.
Zhou, J., Li, Y., & Evans, B. (2012). Antenna selection for multiple-input and single-output cognitive radio systems. IET Communications Magazine, 6(8), 917–930.
Suraweera, H. A., & Smith, P. J. (2010). Capacity limits and performance analysis of cognitive radio with imperfect channel knowledge. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59, 1811–1822.
Zhou, J., & Thompson, J. (2008). Single antenna selection for miso cognitive radio. In Proceedings IET seminar cognitive radio software defined radio: Technologies techniques (pp. 1–5).
Zhang, N., Yemao, X., & Xiao, G. (2011). A new antenna selection algorithm in cognitive MIMO systems. Journal of Selected Areas in Telecommunications (pp. 1–6).
Wang, Y., & Coon, J. (2011). Difference antenna selection and power allocation for wireless cognitive systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 59, 3494–3503.
Sarvendranath, R., & Mehta, N. (2013). Antenna selection in interference-constrained underlay cognitive radios: Sep optimal rule and performance benchmarking. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(2), 496–506.
Sarvendranath, R., & Mehta, N. (2014). Antenna selection with power adaptation in interference-constrained cognitive radios. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 62(3), 786–796.
Zhou, X., Bai, B., & Chen, W. (2014). An iterative algorithm for joint antenna selection and power adaptation in energy efficient MIMO. In IEEE international conference on communications (pp. 3812–3816).
Yeoh, P. L., Elkashlan, M., & Duong, T. Q. (2014). Transmit antenna selection for interference management in cognitive relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(7), 3250–3262.
Deshmukh, M., Frederiksen, F. B., & Prasad, R. (2015). A closed form estimate of TVWS capacity under the impact of aggregate interference. Wireless Personal Communications, 61(2), 496–506.
Stuber, G. (2002). Principles of mobile communication. New York: Kluwer.
Winters, J. H. (1984). Optimum combining in digital mobile radio with co channel interference. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communication, 2(4), 528–539.
Chiani, M., Win, M. Z., & Zanella, A. (2003). Error probability for optimum combining of M-ary PSK signals in the presence of interference and noise. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 51(11), 1949–1957.
Hendre, V., Murugan, M., & Chandgude, A. (2015). Multiple transmit antenna selection in MIMO–OSTBC system in Nakagami-M fading channel. Procedia Computer Science, 54, 558–565.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hendre, V., Murugan, M., Deshmukh, M. et al. Transmit Antenna Selection with Optimum Combining for Aggregate Interference in Cognitive Underlay Radio Network. Wireless Pers Commun 92, 1071–1088 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3593-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3593-1