Abstract
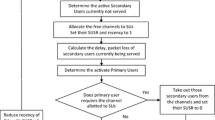
Cognitive radio is an intelligent radio which will run the cognitive cycle of observing, understand, create knowledge, make a decision and modifies the radio parameters for the given objective. Cognitive radio designed with single purpose may not be suitable for the next generation of heterogeneous network, where there are multiple QoS requirements on application/user side, experiences a different kind of channel condition and must support different frequency band of transmission. So, there is a need for cognitive radio that will meet the multi-scenario requirements or context aware cognitive radio communication system for the heterogeneous network. This work presents five transmission mode cognitive waveforms for handle five different contexts. The five transmission waveforms are (1) Energy efficient QoS CR waveform using Genetic algorithm. (2) Low data rate FBMC based subcarrier level interleave CR waveform. (3) Emergency communication support underlay spatial coder waveform. (4) Hardware impairment handling waveform using prewhitened precoding. (5) Imperfect channel state handling adaptive training sequence design based interleave CR waveform. Optimal decision making based on observed values and receiver feedback relies on the accuracy level of observed values which is not a precise one. The fuzzy logic is tolerant of such impreciseness of data. So a cognitive engine deigns with fuzzy based decision system to select optimal waveform for the given context is presented. The system is designed to take input from spectrum hole from detecting unit and database, inputs from receiver feedback like BER, data rate, channel gain, channel imperfection, SINR from PR receiver, input from the transmitter about hardware impairment and finally input from user application about the QoS requirement.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reggiani, L., Fiorina, J., Gezici, S., Morosi, S., & Najar, M. (2013). Radio context awareness and applications. Journal of Sensors, 2013, 1–12.
Kliks, A., Triantafyllopoulou, D., De Nardis, L., Holland, O., Gavrilovska, L., & Bantouna, A. (2015). Cross-layer analysis in cognitive radio—Context identification and decision making aspects. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 1(4), 450–463.
Mitran, P., Le, L. B., & Rosenberg, C. (2010). Queue-aware resource allocation for downlink OFDMA cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(10), 3100–3111.
Yau, K. L. A., Komisarczuk, P., & Teal, P. D. (2011). Achieving context awareness and intelligence in distributed cognitive radio networks: A payoff propagation approach, 2011. In Workshops of International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (pp. 210–215).
Pang, Y. C., Lin, G. Y., & Wei, H. Y. (2016). Context-aware dynamic resource allocation for cellular M2M Communications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(3), 318–326.
Huynh, C. K., & Lee, W. C. (2013). An interference avoidance method using two dimensional genetic algorithm for multicarrier communication systems. Journal of Communications and Networks, 15(5), 486–495.
Doost-Mohammady, R. (2009). Cognitive radio design: An SDR approach. Master of Science Thesis.
Zhao, N., Li, S., & Wu, Z. (2012). Cognitive radio engine design based on ant colony optimization. Wireless Personal Communications, 65, 15–24.
Giarratano, J. C., & Riley, G. D. (2006). Expert system: Principles and programming (4th ed.). Stamford: Thomson Learning.
Newman, T. R. (2008). Multiple objective fitness functions for cognitive radio adaptation. Doctorial dissertation. Kansas: University of Kansas.
He, A., Bae, K. K., Newman, T. R., & et al. (2010). A survey of artificial intelligence for cognitive radios. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59, 1578–1592.
MacKenzie, A. B., Athanas, P., Buehrer, R. M., & et al. (2009). Cognitive radio and networking research at Virginia Tech. Proceedings of the IEEE, 97, 660–688.
He, A., Gaeddert, J., Bae, K., Newman, T. R., Reed, J. H., Morales, L., & et al. (2009). Development of a case-based reasoning cognitive engine for IEEE 802.22 WRAN applications. Mobile Computing Communication Review, 13, 37–48. doi:10.1145/1621076.1621081.
Kolodner, J. L., & Leake, D. (1996). A tutorial introduction to case-based reasoning. In Case-based reasoning: Experiences, lessons and future directions. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Rieser, C. J. (2004). Biologically inspired cognitive radio engine model utilizing distributed genetic algorithes for secure and robust wireless communications and networking. Blacksburg: Virginia Tech.
Rieser, C. J., Rondeau, T. W., & Bostian, C. W. (2004). Cognitive radio testbed: Further details and testing of a distributed genetic algorithm based cognitive engine for programmable radios. In Proceedings of the Military Communications Conference (MILCOM 04), October 2004 (pp. 1437–1443). doi:10.1109/MILCOM.2004.1495152.
Rondeau, T., Le, B., Rieser, C., & Bostian, C. (2004). Cognitive radios with genetic algorithms: Intelligent control of software defined radios. In Proceedings of the Software Defined Radio Forum Technical Conference (SDR 04) (pp. 3–8).
Baldo, N., Tamma, B. R., Manoj, B. S., & et al. (2009) A neural network based cognitive controller for dynamic channel selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2009 (pp. 1–5). Dresden: Washington, DC.
Zhu, X., Liu, Y., Weng, W., & et al. (2008). Channel sensing algorithm based on neural network for cognitive wireless mesh network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, 2008 (pp. 1–4). Dalian: Washington, DC.
Tumuluru, V. K., Wang, P., & Niyato, D. (2010). A neural network based spectrum prediction for cognitive radio. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2010, Cape Town, South Africa (pp. 1–5). Washington, DC.
Baldo, N., & Zorzi, M. (2008) Learning and adaptation in cognitive radios using neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, 2008 (pp. 998–1003). Las Vegas: Washington, DC.
Bchini, T., Tabbane, N., Tabbane, S., Chaput, E., & Beylot, A. (2010). Fuzzy logic based layers 2 and 3 handovers in IEEE 802.16e network. Journal on Computer Communications, 33(18), 2224–2245.
Kustiawan, I., & Chi, K. H. (2015). Handoff decision using a Kalman filter and fuzzy logic in heterogeneous wireless networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(12), 2258–2261.
el mouna Zhioua, G., Tabbane, N., Labiod, H., & Tabbane, S. (2015). A fuzzy multi-metric QoS-balancing gateway selection algorithm in a clustered VANET to LTE advanced hybrid cellular network. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(2), 804–817.
Matinmikko, M., Del Ser, J., Rauma, T., & Mustonen, M. (2013). Fuzzy-logic based framework for spectrum availability assessment in cognitive radio systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(11), 2173–2184.
Vijayakumar, P., & Malarvizhi, S. (2016). Reconfigurable filter bank multicarrier modulation for cognitive radio spectrum sharing—A SDR implementation. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 9(6), 1–6.
Vijayakumar, P., & Malarvizhi, S. (2016). MIMO cognitive radio spectrum sharing using spatial coding and user scheduling for fading channels. International Journal of Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering, 11(3), 103–114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vijayakumar, P., Malarvizhi, S. Fuzzy Logic Based Decision System for Context Aware Cognitive Waveform Generation. Wireless Pers Commun 94, 2681–2703 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3879-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3879-3