Abstract
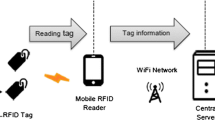
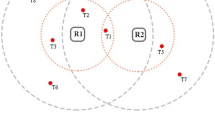
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is considered as one of the most applicable wireless technologies in the present era. Readers and tags are two main components of this technology. Several adjacent readers are used in most cases of implementing RFID systems for commercial, industrial and medicinal applications. Collisions which come from readers’ simultaneous activities lead to a decrease in the performance of RFID systems. Therefore, a suitable solution to avoid collisions and minimize them in order to enhance the performance of these systems is necessary. Nowadays, several researches are done in this field, but most of them do not follow the rules and standards of RFID systems; and don’t use network resources proficiently. In this paper, a solution is provided to avoid collisions and readers’ simultaneous activities in dense passive RFID networks through the use of time division, CSMA techniques and measuring received signal power. The new anti-collision protocol provides higher throughput than other protocols without extra hardware in dense reader environment; in addition, the suggested method conforms to the European standards and rules.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheng, Q. Z., Li, X., & Zeadally, S. (2008). Enabling next-generation RFID applications: Solutions and challenges. IEEE Computer, 41(9), 21–28.
Want, R. (2004). Enabling ubiquitous sensing with RFID. Computer, 37(4), 84–86.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., Egea-Lopez, E., Vales-Alonso, J., & Garcia-Haro, J. (2009). Radio-frequency identification technology. In Handbook of enterprise integration (pp. 429–466).
Klair, D. K., Chin, K.-W., & Raad, R. (2010). A survey and tutorial of RFID anti-collision protocols. Communications Surveys and Tutorials, IEEE, 12(3), 400–421.
Prodanoff, Z. G. (2010). Optimal frame size analysis for framed slotted ALOHA based RFID networks. Computer Communications, 33(5), 648–653.
Gandino, F., et al. (2009). Introducing probability in RFID reader-to-reader anti-collision. In 8th IEEE international symposium on network computing and applications. NCA 2009. IEEE.
ETSI, EN. (2011). 302 208-1 version 1.4. 1. Available: http://www.etsi.org. Jan 2015.
Joshi, G. P., & Kim, S. W. (2008). Survey, nomenclature and comparison of reader anti-collision protocols in RFID. IETE Technical Review, 25(5), 285.
EPC Radio-Frequency Identify Protocols Class-1 Generation-2 UHF RFID EPC Global (2008). Online. Available: http://www.epcglobalinc.org. Jan 2015.
Ferrero, R., et al. (2014). Improving colorwave with the probabilistic approach for reader-to-reader anti-collision TDMA protocols. Wireless Networks, 20(3), 397–409.
Leong, K. S., Ng, M. L., & Cole, P. H. (2005). The reader collision problem in RFID systems. In 2005. MAPE 2005. IEEE international symposium on microwave, antenna, propagation and EMC technologies for wireless communications. Vol. 1. IEEE.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., et al. (2010). A comparative study of RFID schedulers in dense reader environments. In 2010 IEEE international conference on industrial technology (ICIT), IEEE.
Waldrop, J., Engels, D. W., & Sarma, S. E. (2003). Colorwave: An anticollision algorithm for the reader collision problem. In IEEE international conference on communications, 2003. ICC’03. Vol. 2. IEEE.
Gandino, F., et al. (2011). Probabilistic DCS: An RFID reader-to-reader anti-collision protocol. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 34(3), 821–832.
Waldrop, J., Engels, D. W., & Sarma, S. E. (2003). Colorwave: A MAC for RFID reader networks. In Wireless communications and networking, 2003. WCNC 2003. IEEE. Vol. 3. IEEE.
Yu, J., Lee, W., & Du, D.-Z. (2011). Reducing reader collision for mobile RFID. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 57(2), 574–582.
Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., Hosseinzadeh, M., Reshadi, M., & Rahmani, A. M. (2015). A Reader Anti-collision Protocol for RFID-Enhanced Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 81(2), 893–905.
Eom, J. B., Yim, S. B., & Lee, T.-J. (2009). An efficient reader anticollision algorithm in dense RFID networks with mobile RFID readers. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 56(7), 2326–2336.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., et al. (2013). A geometric distribution reader anti-collision protocol for RFID dense reader environments. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 10(2), 296–306.
Tay, Y. C., Jamieson, K., & Balakrishnan, H. (2004). Collision-minimizing CSMA and its applications to wireless sensor networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 22(6), 1048–1057.
Drodi, R. (2005). RFID white paper (online). Available: http://www.mtiwe.com. Jan 2015.
Zhang, L., et al. (2013). Simulation and evaluation of the interference models for RFID reader-to-reader collisions. In Proceedings of international conference on advances in mobile computing & multimedia. ACM.
Yoon, W., & Vaidya, N. H. (2012). RFID reader collision problem: Performance analysis and medium access. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 12(5), 420–430.
Ferrero, R., et al. (2013). Simulating reader-to-reader interference in RFID systems. In 2013 27th international conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops (WAINA). IEEE.
Ko, D., Kim, B., & An, S. (2010). Research on anti-reader collision protocols for integrated RFID–WSNs. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems (TIIS), 4(5), 776–796.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., & Vales-Alonso, J. (2011). On the optimal frame-length configuration on real passive RFID systems. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 34(3), 864–876.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., Issazadehkojidi, N. A Distance Based RFID Reader Collision Avoidance Protocol for Dense Reader Environments. Wireless Pers Commun 95, 1781–1798 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3918-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3918-0