Abstract
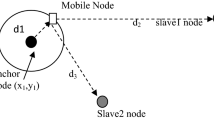
The applications of wireless senor networks (WSN) vary in diversified field, at different geographic locations. Location aware computing is the key for the success of such applications. Henceforth, there is a need of efficiently estimating the location of individual WSN nodes deployed in the remote geographic locations. Manually estimating the locations of these densely deployed nodes is impossible, therefore the WSN nodes must be able to localize themselves collecting local information from its neighboring nodes, which is called as the localization technique. The information used for localization is generally distance and bearing information obtained from the ranging techniques which are not accurate and are prone to error. Therefore there is a need for techniques which can cope up with this perturbed distance information. Rigid graphs have the property of sustaining various kind of deformations due to translation, rotation and reflection. Hence, it is more fruitful using the concepts of rigid graphs, for estimating accurate location coordinates from error prone distance measurements. In this paper we will scrutinize the sound theoretical background which defines the need of rigid graph based localization and different localization techniques, with associated algorithms which uses the concepts of rigid graphs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). A survey on sensor networks. IEEE Communications magazine, 40(8), 102–114.
Anderson, B. D., Belhumeur, P. N., Eren, T., Goldenberg, D. K., Morse, A. S., Whiteley, W., et al. (2009). Graphical properties of easily localizable sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 15(2), 177–191.
Anderson, B. D., Shames, I., Mao, G., & Fidan, B. (2010). Formal theory of noisy sensor network localization. SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 24(2), 684–698.
Aspnes, J., Eren, T., Goldenberg, D. K., Morse, A. S., Whiteley, W., Yang, Y. R., et al. (2006). A theory of network localization. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 5(12), 1663–1678.
Aspnes, J., Goldenberg, D., & Yang, Y. R. (2004). On the computational complexity of sensor network localization. In: Algorithmic aspects of wireless sensor networks (pp. 32–44). Springer
Connelly, R. (2005). Generic global rigidity. Discrete and Computational Geometry, 33(4), 549–563.
Eren, T. (2011). Cooperative localization in wireless ad hoc and sensor networks using hybrid distance and bearing (angle of arrival) measurements. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2011(1), 1–18.
Eren, T., Anderson, B. D., Morse, A. S., Whiteley, W., Belhumeur, P. N., et al. (2003). Operations on rigid formations of autonomous agents. Communications in Information and Systems, 3(4), 223–258.
Eren, T., Belhumeur, P. N., Anderson, B. D., & Morse, A. S. (2002). A framework for maintaining formations based on rigidity. In: Proceedings of the 15th IFAC world congress (pp. 2752–2757), Barcelona, Spain
Eren, T., Goldenberg, O., Whiteley, W., Yang, Y. R., Morse, A. S., & Anderson, B. D., et al. (2004). Rigidity, computation, and randomization in network localization. In: INFOCOM 2004. Twenty-third annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies (Vol. 4, pp. 2673–2684). IEEE
Fang, J., & Morse, A. S. (2009). Merging globally rigid graphs and sensor network localization. In: Proceedings of the 48th IEEE conference on decision and control, 2009 held jointly with the 2009 28th Chinese control conference, CDC/CCC 2009 (pp. 1074–1079). IEEE
Goldenberg, D. K., Bihler, P., Cao, M., Fang, J., Anderson, B., & Morse, A. S., et al. (2006). Localization in sparse networks using sweeps. In: Proceedings of the 12th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking (pp. 110–121). ACM
Goldenberg, D. K., Krishnamurthy, A., Maness, W. C., Yang, Y. R., Young, A., & Morse, A. S., et al. (2005). Network localization in partially localizable networks. In: Proceedings IEEE, 24th annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies INFOCOM 2005 (Vol. 1, pp. 313–326). IEEE
Gortler, S. J., Healy, A. D., & Thurston, D. P. (2010). Characterizing generic global rigidity. American Journal of Mathematics, 132(4), 897–939.
Hendrickson, B. (1992). Conditions for unique graph realizations. SIAM Journal on Computing, 21(1), 65–84.
Kuhn, F., Moscibroda, T., & Wattenhofer, R. (2004). Unit disk graph approximation. In: Proceedings of the 2004 joint workshop on foundations of mobile computing (pp. 17–23). ACM
Laman, G. (1970). On graphs and rigidity of plane skeletal structures. Journal of Engineering mathematics, 4(4), 331–340.
Liu, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, X., & Jian, L. (2010). Location, localization, and localizability. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 25(2), 274–297.
Mao, G., Fidan, B., & Anderson, B. (2007). Wireless sensor network localization techniques. Computer Networks, 51(10), 2529–2553.
Moore, D., Leonard, J., Rus, D., & Teller, S. (2004). Robust distributed network localization with noisy range measurements. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on embedded networked sensor systems (pp. 50–61). ACM
Wang, X., Liu, Y., Yang, Z., Lu, K., & Luo, J. (2014). Robust component based localizationin sparse networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 25(5), 1317–1327.
Wang, X., Luo, J., Liu, Y., Li, S., & Dong, D. (2011). Component-based localization in sparse wireless networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (ToN), 19(2), 540–548.
Xiao, Q., Bu, K., Wang, Z., & Xiao, B. (2013). Robust localization against outliers in wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 9(2), 24.
Yang, Z., Jian, L., Wu, C., & Liu, Y. (2013). Beyond triangle inequality: Sifting noisy and outlier distance m for localization. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 9(2), 26.
Yang, Z., & Liu, Y. (2012). Understanding node localizability of wireless ad hoc and sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 11(8), 1249–1260.
Yang, Z., Liu, Y., & Li, X. Y. (2010). Beyond trilateration: On the localizability of wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (ToN), 18(6), 1806–1814.
Yang, Z., Wu, C., Chen, T., Zhao, Y., Gong, W., & Liu, Y. (2013). Detecting outlier measurements based on graph rigidity for wireless sensor network localization. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(1), 374–383.
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., & Liu, Y. (2012). Towards unique and anchor-free localization for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 63(1), 261–278.
Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Zhao, X., & Jia, Z. (2012). Theoretic analysis of unique localization for wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 10(3), 623–634.
Zhu, Y., Gortler, S., & Thurston, D. (2009). Sensor network localization using sensor perturbation. In: INFOCOM 2009, IEEE (pp. 2796–2800). doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2009.5062234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, S., Varma, S. Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Rigid Graphs: A Review. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 4467–4484 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4397-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4397-7