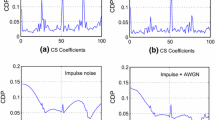
Abstract
Automatic modulation classification plays a key role in cognitive radio for recognizing the modulation scheme. In this paper, we propose a new classifier based on sparse signal decomposition using an overcomplete composite dictionary (constructed using cyclostationary coefficients) for the classification of modulation format of primary user or to identify noise. The basic principle of the classifier is to classify the received signal modulation format based on reconstructed sparse coefficients after solving \(l_1\) norm minimization using the overcomplete dictionary. Then, relative energies of reconstructed sparse coefficients are compared for recognition of modulation format of the received signal. It is a promising candidate for the cognitive radio due to its robust classification ability. The performance of the proposed classifier is compared with other well known classifiers available in literature. Results show the superiority of the proposed classifier over other classifiers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobre, O. A., Abdi, A., Bar-Ness, Y., & Su, W. (2007). Survey of automatic modulation classification techniques: Classical approaches and new trends. IET Communications, 1(2), 137–156.
Hazza, A., Shoaib, M., Alshebeili, S. A., & Fahad, A. (2013). An overview of feature-based methods for digital modulation classification. In Proceedings of 1st international conference on communication signal process. Applicat. IEEE ICCSPA, pp. 1–6.
Orlic, V. D., & Dukic, M. L. (2010). Multipath channel estimation algorithm for automatic modulation classification using sixth-order cumulants. Electronics Letters, 46(19), 1348–1349.
Orlic, V., & Dukic, M. L. (2009). Algorithm for automatic modulation classification in multipath channel based on sixth-order cumulants. In Proceedings of 9th international conference on IEEE telecommunication modern satellite, cable, and broadcast. Services (TELSIKS 09).
Orlic, V. D., & Dukic, M. L. (2009). Automatic modulation classification algorithm using higher-order cumulants under real-world channel conditions. IEEE Communications Letters, 13(12), 917–919.
Wu, H.-C., Saquib, M., & Yun, Z. (2008). Novel automatic modulation classification using cumulant features for communications via multipath channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(8), 3098–3105.
Le Martret, C., & Boiteau, D. M. (1997). Modulation classification by means of different orders statistical moments. Proceedings of IEEE MILCOM ’97, 3, 1387–1391.
Marchand, P., Le Martret, C. & Lacoume, J.-L. (1997). Classification of linear modulations by combination of different orders cyclic cumulants. In Proceedings of the IEEE signal process. Workshop on higher-order statistics, pp. 47–51.
Bao, F., Wang, X., Tao, Z., Wang, Q., & Du, S. (2009). Adaptive extraction of modulation for cavitation noise. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 126(6), 3106–3113.
Mobasseri, B. G. (1999). Constellation shape as a robust signature for digital modulation recognition. Proceedings of IEEE MILCOM, 1, 442–446.
Xu, J. L., Su, W., & Zhou, M. (2011). Likelihood-ratio approaches to automatic modulation classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, 41, 455–469.
Xu, J. L., Su, W., & Zhou, M. (2010). Likelihood function-based modulation classification in bandwidth-constrained sensor networks. In Proceedings of international conference on net., sensing and control (ICNSC), pp. 530–533.
Xu, J. L., Su, W., & Zhou, M. (2010). Software-defined radio equipped with rapid modulation recognition. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(4), 1659–1667.
Liu, J., & Luo, Q. (2012). A novel modulation classification algorithm based on daubechies5 wavelet and fractional Fourier transform in cognitive radio. In Proceedings of IEEE 14th international conference on communication technology (ICCT), pp. 115–120.
Reichert, J. (1992). Automatic classification of communication signals using higher order statistics. Proceedings of of ICASSP ’92, 5, 221–224.
Ho, K. C., Prokopiw, W., & Chan, Y. T. (2000). Modulation identification of digital signals by the wavelet transform. IEE Proceedings—Radar Sonar and Navigation, 147(4), 169–176.
Satija, U., Mohanty, M., & Ramkumar, B. (2015). Automatic modulation classification using S-transform based features. In IEEE conference on signal process, integrated net (SPIN).
Lim, C. W., & Wakin, M. B. (2012). Automatic modulation recognition for spectrum sensing using nonuniform compressive samples. In IEEE international conference on communication (ICC).
Chen, Y., Liu, J., & Lv, S. (2011). Modulation classification based on bispectrum and sparse representation in cognitive radio. In IEEE 13th international conference on communication technology (ICCT).
Chung, C.-D., & Polydoros, A. (1994). Envelope-based classification schemes for continuous-phase binary frequency-shift-keyed modulations. Proceedings of of IEEE MILCOM ’94, 3, 796–800.
Nandi, A. K., & Azzouz, E. E. (1998). Algorithms for automatic modulation recognition of communication signals. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 46(4), 431–436.
Azzouz, E. E., & Nandi, A. K. (1996). Procedure for automatic recognition of analogue and digital modulations. IEE Proceedings Communications, 143(5), 259–266.
Nandi, A. K., & Azzouz, E. E. (1995). Automatic analogue modulation recognition. Signal Processing, 46(2), 211–222.
Azzouz, E. E., & Nandi, A. K. (1995). Automatic identification of digital modulation types. Signal Processing, 47(1), 55–69.
Hsue, S.-Z., & Soliman, S. S. (1990). Automatic modulation classification using zero crossing. IEE Proceedings. F, Radar and Signal Processing, 137(6), 459–464.
Haring, L., Chen, Y., & Czylwik, A. (2010). Automatic modulation classification methods for wireless OFDM systems in TDD mode. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58, 2480–2485.
Zhou, X., Wu, Y., & Yang, G. (2009). Modulation classification of MPSK signals based on relevance vector machines. In International conference IEEE information engineering and computer science (ICIECS).
Aslam, M. W., Zhu, Z., & Nandi, A. K. (2012). Automatic modulation classification using combination of genetic programming and KNN. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(8), 2742–2750.
Soltanmohammadi, E., & Naraghi-Pour, M. (2013). Blind modulation classification over fading channels using expectation-maximization. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 17(9), 1692–1695.
Urriza, P., Rebeiz, E., & Cabric, D. (2013). Optimal discriminant functions based on sampled distribution distance for modulation classification. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(10), 1885–1888.
Urriza, P., Rebeiz, E., Pawelczak, P., & Cabric, D. (2011). Computationally efficient modulation level classification based on probability distribution distance functions. IEEE Communications Letters, 15(5), 476–478.
Wang, F., & Wang, X. (2010). Fast and robust modulation classification via kolmogorov–smirnov test. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(8), 2324–2332.
Valipour, M. H., Homayounpour, M. M., & Mehralian, M. A. (2012). Automatic digital modulation recognition in presence of noise using SVM and PSO. In Proceedings of 6th international telecommunications symposium (IST), pp. 378–382.
Ramkumar, B. (2009). Automatic modulation classification for cognitive radios using cyclic feature detection. The IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 9(2), 27–45.
Sobolewski, S., Adams, W. L., & Sankar, R. (2012). Automatic modulation recognition techniques based on cyclostationary and multifractal features for distinguishing LFM, PWM and PPM waveforms used in radar systems as example of artificial intelligence implementation in test. IEEE Autotestcon, 335–340.
Liu, G., Zhang, Z., & Yang, Y. (2012). Recognition of cyclostationary signals smoothed. In International conference on information technology and computer science, pp. 165–169.
Headley, W. C., Reed, J. D., & Silva, C. R. (2008). Distributed cyclic spectrum feature-based modulation classification. In Wireless communication and networking conference (WCNC), pp. 1200–1204.
Ming, L., Shaoquan, Y., & Qing, W. (2006). Algorithm for modulation classification of MPSK signals based on cyclostationary. Signal Process, 22(3), 28.
Aharon, M., Elad, M., & Bruckstein, A. (2006). K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 54(11), 4311–4322.
Manikandan, M. Sabarimalai, & Ramkumar, B. (2014). Straightforward and robust QRS detection algorithm for wearable cardiac monitor. Healthcare Technology Letters, 1(1), 40–44.
Manikandan, M. S., Samantaray, S. R., & Kamwa, I. (2015). Detection and classification of power quality disturbances using sparse signal decomposition on hybrid dictionaries. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 64(1), 27–38.
Mohanty, M., Satija, U., Ramkumar, B., & Manikandan, M. S. (2015). Digital modulation classification under non-Gaussian noise using sparse signal decomposition and maximum likelihood. In 21st national conference on communication (NCC), pp. 1–6.
Donoho, D. L., & Elad, M. (2002). Optimally sparse representation from overcomplete dictionaries vial L1-norm minimization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(5), 2197–3002.
Beidas, B. F., & Weber, C. L. (1998). Asynchronous classification of MFSK signals using the higher order correlation domain. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 46(4), 480–493.
Su, W., Xu, J. L., & Zhou, M. (2008). Real-time modulation classification based on maximum likelihood. IEEE Communications Letters, 12, 801–803.
Fehske, A., Gaeddert, J., & Reed, J. H. (2005). A new approach to signal classification using spectral correlation and neural networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on dynamic spectrum access network, pp. 144–145.
Satija, U., Manikandan, M. S., & Ramkumar, B. (2014). Performance study of cyclostationary based digital modulation classification schemes. In 9th IEEE international conference on industrial information system (ICIIS2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satija, U., Ramkumar, B. & Manikandan, M.S. A Novel Sparse Classifier for Automatic Modulation Classification using Cyclostationary Features. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 4895–4917 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4435-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4435-5