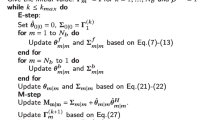Abstract
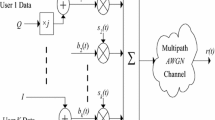
In this paper a sequential algorithm is proposed for joint blind channel equalization and decoding for orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) in frequency selective channels. This algorithm offers a recursive method to sequentially calculate the posterior probability for maximum a posteriori detection. Recursive calculations are done along the indexes in each OFDM symbol using a particle filter. By defining an appropriate importance function, and a proper prior probability distribution function for the channel tap coefficients (and marginalizing it), an efficient method is presented for joint equalization and channel decoding in OFDM based systems. Performance of the proposed detector is evaluated using computer simulations and its bit error rate is compared with the trained turbo equalizer and a conventional particle filter-based method. The results show that the proposed method outperforms the previously presented particle filter-based method without a need for training data.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Y., & Stuber, G. L. (2006). Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing for wireless communications. New york: Springer.
Proakis, J. G., & Salehi, M. (2007). Digital communications. New york: McGraw-Hill.
John, T. S., Nallanathan, A., & Armand, M. A. (2006). A non-resampling sequential Monte Carlo detector for coded OFDM systems based on periodic termination of differential phase trellis. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(7), 1846–1856.
Barhumi, I. (2012). Soft-output decision feedback equalization for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing over doubly selective channels. IET Communications, 6(13), 1890–1897.
Liu, D. N., & Fitz, M. P. (2009). Iterative MAP equalization and decoding in wireless mobile coded OFDM. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 57(7), 2042–2051.
Fang, K., Rugini, L., & Leus, G. (2008). Low complexity block turbo equalization for OFDM systems in time varying channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(11), 5555–5566.
Myburgh, H. C., & Olivier, J. C. (2013). A primer equalization, decoding and non-iterative joint equalization and decoding. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 79, 1–23.
Aerts, N., Avram, I., & Moeneclaey, M. (2014). Low-complexity a posteriori probability approximation in EM-based channel estimation for trellis-coded systems. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2014, 153.
Zhao, L. & Ge, J. (2010). Joint iterative equalization and decoding for underwater acoustic communication. In Proceedings of the Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), (pp. 1074–1078).
Al-Naffouri, T. Y., Dahman, A. A., Sohail, M. S., Weiyu, X., & Hassibi, B. (2012). Low-complexity blind equalization for OFDM systems with general constellations. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 60(12), 6395–6407.
Özen, A., Kaya, I., & Soysal, B. (2012). A Supervised constant modulus algorithm for blind equalization. Wireless Personal Communications, 62(1), 151–166.
Gupta, P., & Mehra, D. K. (2008). Kalman filter-based channel estimation and ICI suppression for high-mobility OFDM systems. International Journal of Communication Systems, 21(10), 1075–1090.
Wang, S., & Hu, J. (2013). Blind channel estimation for single-input multiple-output OFDM systems: Zero padding based or cyclic prefix based. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 13(2), 204–210.
Xu, D., Yan, K., & Wu, H. C. (2009). Blind channel equalization using expectation maximization of auxiliary objective function for complex constellations. In Proceedings of GLOBECOM’09. Conference. (pp. 5012–5017).
Jagannatham, A. K., & Rao, B. D. (2014). Cramer–Rao bound based mean-squared error and throughput analysis of superimposed pilots for semi-blind multiple-input multiple-output wireless channel estimation. International Journal of Communication Systems, 27(10), 1393–1415.
Abrar, S., & Nandi, A. K. (2010). Adaptive minimum entropy equalization algorithm. IEEE Communications Letters, 14(10), 966–968.
Yu, J. L., Wu, C. H., & Lee, M. F. (2012). MC-CDMA MIMO systems with quasi-orthogonal space–time block codes: Channel estimation and multiuser detection. International Journal of Communication Systems, 25(3), 294–313.
Bordin, C. J., & Bruno, M. G. S. (2008). Particle filters for joint blind equalization and decoding in frequency-selective channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(6), 2395–2405.
Yang, Z., & Wang, X. D. (2002). A sequential Monte Carlo blind receiver for OFDM systems in frequency-selective fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 50(2), 271–280.
Derek, Y., Reilly, J. P., & Kirubarajan, T. (2007). A blind sequential Monte Carlo detector for OFDM systems in the presence of phase noise, multipath fading, and channel order uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(9), 4581–4598.
Doucet, A., Godsill, S., & Andrieu, C. (2000). On sequential Monte Carlo sampling methods for Bayesian filtering. Statistics and Computing, 10, 197–208.
Hopgood, J. R., & Rayner, P. J. W. (2003). Blind single channel deconvolution using non-stationary signal processing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 11(5), 476–488.
Song, S., Singer, A. C., & Sung, K. M. (2004). Soft input channel estimation for turbo equalization. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(10), 2885–2894.
Liu, J. S., & Chen, R. (1995). Blind deconvolution via sequential imputations. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 90(430), 567–576.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Amir R. Forouzan. He kindly read our paper and offered very useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabahi, M.F., Ghasemi, N. Joint Blind Equalization and Decoding in OFDM Systems Using Particle Filtering. Wireless Pers Commun 97, 3875–3889 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4704-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4704-3