Abstract
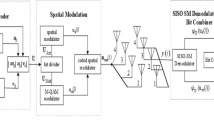
In this paper, a new variant of Spatial Modulation (SM) Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) transmission technique, designated as Redesigned Spatial Modulation (ReSM) has been proposed. In ReSM scheme, a dynamic mapping for antenna selection is adopted. This scheme employs both single antenna as well as double antenna combinations depending upon channel conditions to combat the effect of spatial correlation. When evaluated over spatially correlated channel conditions, for a fixed spectral efficiency and number of transmit antennas, ReSM exhibits performance improvement of at least 3 dB over all the conventional SM schemes including Trellis Coded Spatial Modulation (TCSM) scheme. Furthermore, a closed form expression for the upper bound on Pairwise Error Probability (PEP) for ReSM has been derived. This has been used to calculate the upper bound for the Average Bit Error Probability (ABEP) for spatially correlated channels. The results of Monte Carlo simulations are in good agreement with the predictions made by analytical results. The relative gains of all the comparison plots in the paper are specified at an ABER of 10−4.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mesleh, R. Y., Haas, H., Sinanovic, S., Ahn, C. W., & Yun, S. (2008). Spatial modulation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(4), 2228–2241.
Di Renzo, M., Haas, H., Ghrayeb, A., Sugiura, S., & Hanzo, L. (2014). Spatial modulation genelaralized for MIMO: Opportunities challenges and implementation. Proceedings of the IEEE, 102(1), 56–103.
Younis, A. (2013). Spatial modulation: Theory to practice. (Ph.D thesis, The University of Edinburgh).
Luna-Rivera, J. M & Gonzalez-Perez, M. G. (2012). An improved spatial modulation scheme for MIMO channels. EuCAP.
Luna-Rivera, J. M., Campos-Delgado, D. U., Gonzalez-Perez, M. G. (2013). Constellation design for spatial modulation. In The 2013 iberoamerican conference on electronics engineering and computer science, Elsevier.
Cheng, C. C., Sari, H., Sezginert, S., Su, Y. T. (2014). Enhanced spatial modulation with multiple constellations. In IEEE international black sea conference on communications and networking (BlackSeaCom).
Cheng, C. C., Sari, H., Sezginer, S., & Su, Y. T. (2015). Enhanced spatial modulation with multiple signal constellations. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 63(6), 2237–2248.
Mesleh, R., Ikki, S. S., & Aggoune, H. M. (2014). Quadrature Spatial Modulation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64, 1. doi:10.1109/TVT.2014.2344036.
Mesleh, R., Di Renzo, M., Haas, H., & Grant, P. M. (2010). Trellis coded spatial modulation. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communication, 9(7), 2349–2361.
Jeganathan, J., Ghrayeb, A., & Szczecinski, L. (2008). Spatial modulation: Optimal detection and performance analysis. IEEE Communications Letters, 12(8), 545–547.
Mesleh, R. et.al. (2009) On the performance of trellis coded spatial modulation. ITG workshop on smart antennas, Berlin Germany.
Afana, A., Atawi, I., Ikki, S. & Mesleh, R. (2015) Energy efficient quadrature spatial modulation MIMO cognitive radio systems with imperfect channel estimation. In IEEE international conference on ubiquitous wireless broadband (ICUWB) (pp. 1–5).
Mesleh, R., Ikki, S. S., & Aggoune, H. M. (2015). Quadrature spatial modulation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(6), 2738–2742.
Proakis, J. G. (2000). Digital communications (4th ed.). New York: McGraw–Hill.
Mobile Broadband Evolution Towards 5G: 3GPP Rel-12 & Rel-13 and Beyond 2015.
Hedayat, A., Shah, H., & Nosratinia, A. (2005). Analysis of space-time coding incorrelated fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(6), 2882–2891.
Forenza, A. Love, D., Heath, R. Jr. (2004). A low complexity algorithm to simulate the spatial covariance matrix for clustered MIMO channel models. In IEEE vehicular technology conference—VTC 2004-Fall, Los Angeles, CA, USA, May, 2004 (pp. 889–893).
MacLeod, H., Loadman, C., Chen, Z. (2005). Experimental studies of the 2.4-GHz ISM wireless indoor channel. In Proceedings of the 3rd annual communication networks and services research conference (CNSR’05).
Duman, T. M., & Ghrayeb, A. (2007). Coding for MIMO communication systems. Hoboken: Wiley.
Zelst and, A. V. & Hammerschmidt, J. S. (2002) A single coefficient spatial correlation model for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radio channels. In 27th general assembly of the international union of radio science (URSI), Maastricht, The Netherlands, Aug. 17–24 2002 (pp. 1–4).
Mesleh, R. Y. (2007) Spatial Modulation: A spatial multiplexing technique for efficient wireless data transmission. (Ph.D Thesis, School of Engineering and Science Jacobs University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Proof of Eq. (24)
In this equation, \(n_{t}\) is the active transmit antenna, \(s_{t}\) is the transmit symbol, η is the spectral efficiency. \(N\left( {x_{{n_{t} ,s_{t} ,}} x_{n,s} } \right)\) is the total number of bits in error between \(x_{{n_{t} s_{t} ,}} x_{n,s}\). \(E_{H} \left\{ \cdot \right\}\) is the expectation across the channel matrix \(\varvec{H}\).
PEP is given by

where 
Following from [3] an alternative integral expression of the Q-function and taking the expectation of Eq. (37) we arrive at
where \(\varphi \left( \cdot \right)\) is the moment generating function (MGF) of the random variable  . From [3] it is clear that any i.i.d. Gaussian random variable with mean \(\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\smile}$}}{v}\) and any Hermitian matrix
. From [3] it is clear that any i.i.d. Gaussian random variable with mean \(\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\smile}$}}{v}\) and any Hermitian matrix  . The MGF then can be written as
. The MGF then can be written as

\(L_{v}\) is the covariance matrix of v. From (38) invoking MGF of  we can write
we can write

\(I_{n}\) is an \(n \times n\) identity matrix, \({\mathbf{vec}}\left( \varvec{H} \right)\) is the column of matrix \(\varvec{H}\) into a column vector.  \({\mathcal{L}}_{H}\) is the covariance matrix, \(\varvec{\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\smile}$}}{H} }\) is the mean matrix, \(\otimes\) is the Kronecker product and \(\left( \cdot \right)^{H}\) is the Hermitian.
\({\mathcal{L}}_{H}\) is the covariance matrix, \(\varvec{\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\smile}$}}{H} }\) is the mean matrix, \(\otimes\) is the Kronecker product and \(\left( \cdot \right)^{H}\) is the Hermitian.
Making use of the Chernoff bound, PEP then can be written as,

Finally the upper bound is given by

1.1 Appendix 2
See Table 6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simha, G.D.G., Koila, S., Neha, N. et al. Redesigned Spatial Modulation for Spatially Correlated Fading Channels. Wireless Pers Commun 97, 5003–5030 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4762-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4762-6