Abstract
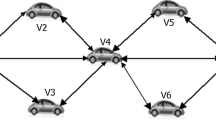
Vehicular ad-hoc network (VANET) is a technology used to create a wireless ad-hoc network on demand basis using mobile vehicles. In VANET, mobile vehicles behave like a transmitter and they participate during data transmission on the network. In VANET, the nodes are highly movable in any direction. Due to this, links may be broken and the data delivery may fail. It may be recovered when other alternative links can be reestablished immediately. Thus, the network performance and reliability of the VANET depend upon the selection of next forwarder (N F ) node in forward area (F A ) of request zone. In this paper, we propose an Improved Directional LAR routing protocol that finds the best next-hop forwarder node in forward area and thus reduces unnecessary transmissions. Two algorithms have been proposed as one to select best next-hop forwarder node and other to forward data packets in the network. We have mathematically analyzed the nodes distribution in forward area direction. Furthermore, we have also evaluated the selection of next forwarder node, its expected distance, average numbers of hops and expected distance between source and destination nodes. The performance analysis has been done with existing D-LAR and LAR routing protocols.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tee, C. A. T. H., & Lee, A. C. R. (2008) Survey of position based routing for Inter Vehicle Communication system. In First international conference on distributed framework and applications (pp. 174–182).
Harsch, C., Festag, A., & Papadimitratos, P. (2007). Secure position-based routing for VANETs. In Vehicular technology conference (pp. 26–30).
Stojmenovic, I., Ruhil, A. P., Lobiyal, D. K., et al. (2006). Voronoi diagram and convex hull based geocaching and routing in wireless networks. In J. Aguiar (Ed.), Wireless communications and mobile computing special issue on ad-hoc wireless networks (pp. 247–258). New York: Wiley.
Takano, A., Okada, H., & Mase, K. (2007). Performance comparison of a position-based routing protocol for VANET. In IEEE international conference on mobile ad-hoc and sensor systems (pp. 1–6).
Wu, H., Fujimoto, R., Guensler, R., & Hunter, M. (2004). MDDV: a mobility-centric data dissemination algorithm for a vehicular network. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM international workshop on vehicular ad-hoc networks (pp. 47–56).
Karp, B., & Kung, H. T. (2000). GPSR: Greedy perimeter stateless routing for wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 6th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking (pp. 243–254). MobiCom 00, ACM, New York, NY.
Lochert, C., Hartenstein, H., Tian, J., Herrmann, D., Füßler, H., & Mauve, M. (2003). A routing strategy for vehicular Ad hoc networks in city environments. In Proceedings of IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium (IV2003) (pp. 156–161).
Tian, J., Stepanov, I., & Rothermel, K. (2012). Spatial aware geographic forwarding for mobile ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings of MobiHoc, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Raw, R. S., Das, S., Singh, N., Kumar, S., et al. (2012). Feasibility evaluation of VANET using directional-location aided routing (D-LAR) protocol. International Journal of Computer Science Issues, 9(5), 404–410.
Lee, K. C., Lee, U., & Gerla, M. (2010). Survey of routing protocols in vehicular Ad hoc networks. In M. Watfa (Ed.), Advances in vehicular ad-hoc networks: Developments and challenges (pp. 149–170). Hershey: IGI Global.
Yamaguchi, H., Sun, W., & Higashino, T. (2010). Geographic routing in vehicular Ad hoc networks. In M. Watfa (Ed.), Advances in vehicular Ad hoc networks: Developments and challenges. Hershey: IGI Global.
Boukerche, A., Oliveira, H. A. B. F., Nakamura, E. F., &Loureiro, A. A. F. (2008). Vehicular Ad hoc networks: A new challenge for localization-based systems. In Computer communication. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Haenggi, M. (2005). On distances in uniformly random networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(10), 3584–3586.
Kumar, V., & Kumar, S. (2016). Position based beaconless routing in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communication, 86(2), 1061–1085.
Kranakis, E., Krizanc, D., & Markou, E. (2010). The mobile agent rendezvous problem in the ring Morgan and Claypool publishers. Synthesis lectures on distributed computing theory. ISBN: 9781608451364 Paperback.
Ko, Y.-B., Vaidya, N. H., et al. (1998). Location-aided routing (LAR) in mobile ad-hoc networks. In ACM/IEEE, MOBICOM’98 (pp. 66–75).
Dommety, G., & Jain, R. (1996). Potential networking applications of global positioning systems (GPS). In M. Conti (Ed.), Technical Report TR-24. Columbus: Ohio State University.
Camp, T., Boleng, J., Williams, B., Wilcox, L., & Navidi, W. (2002). Performance comparison of two location based routing protocols for ad-hoc networks. In Proceeding of the 21st annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies (Infocom 2002) (pp. 1678–1687).
Ko, Y.-B., & Vaidya, N. H. (2000). Location-aided routing (LAR) in mobile ad-hoc networks. Wireless Networks, 6, 307–321.
Raw, R. S., & Das, S. (2013). Performance analysis of P-GEDIR protocol for vehicular ad-hoc network in urban traffic environments. Wireless Personal Communication, 68(1), 65–78.
Raw, R. S., Toor, V., & Singh, N. (2012). Estimation and analysis of path duration in vehicular ad-hoc networks using position-based routing protocol. Special issue of international journal of computer applications (0975–8887) on issues and challenges in networking, intelligence, and computing technologies—ICNICT 2012.
Wang, N., Chen, J., Huang, Y., & Wang, S., et al. (2002). A greedy Location-aided routing protocol for mobile ad-hoc networks. In The WSEAS international conference on applied computer and applied computational science (pp. 175–180).
Yi, C., Chuang, Y., Yeh, H., Tseng, Y., & Liu, P. (2010). Street cast: An urban broadcast protocol for vehicular ad-hoc networks. In 71st IEEE vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–5).
Lochert, C., Mauve, M., Füßler, H., & Hartenstein, H. (2005). Geographic Routing in city scenarios. In SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review (Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 69–72).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, K.K., Tripathi, S. & Raw, R.S. Analytical Analysis of Improved Directional Location Added Routing Protocol for VANETS. Wireless Pers Commun 98, 2403–2426 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4980-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4980-y