Abstract
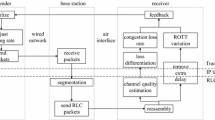
High speed network covers several means of communication and the innovation accomplished in networks had a significant impact on communication concerning terminals and computers. Obviously asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) has appeared as the most significant technology in supporting imminent broadband multimedia communication services, considered to decrease the complexity of the network and advancement in the flexibility of traffic performance and a conventional technique incorporate network management for ATM network is stochastic estimator learning algorithm. Although introduced numerous methods, high speed is the fundamental issue in networking and as it is the asynchronous mode, the sending process continuous to send the data cells that prompts the temporary memory overflow at the receiver side. In this paper propose a new protocol integrated speed bit protocol (ISBP) for integrated network management to preserve the objects. Initially the ISB protocol preserves speed bit manager which encloses the prioritized objects and the objects having the data about the systems, the objects priority vanquished through specific priority factors. As a result the transaction process done faster and the synchronization have the capacity to finish in asynchronous mode, so the temporary memory losses get avoided and consumed more time. Thus the proposed integrated network management for ATM and Broadband networks using ISB protocol system has embraced with the assistance of the speed bit protocol and the experimental results demonstrated that the performance of the system enhanced significantly.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khalil, E. A. (2012). Comparative performance of high speed networks carrying multimedia. International Journal of Engineering Sciences and Emerging Technologies, 3(1), 9–21.
Agarwal, S., & Gautam, A. K. (2012). Alternate multi path routing architecture for ATM networks. International Journal of Computer Science and Communication Engineering, 1(2), 37–42.
Mishra, B., Baudha, S., & Pandey, S. (2012). Changing data rate during handoff in GSM–ATM networks. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Engineering and Technology, 1(3), 170–176.
Ojesanmi, O. A. (2011). Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM). Georgian Electronic Scientific Journal: Computer Science and Telecommunications, 6, 70–82.
Bali, V., & Rathore, R. S. (2010). Performance analysis of priority scheme in ATM network. International Journal of Computer Applications, 1(13), 26–31.
Shanmuganathan, C., & Raviraj, P. (2012). Performance measures of wireless protocols for ATM networks. International Journal of Mobile Network Communications and Telematics, 2(2), 31–44.
Sasirekha, V., & Chandrasekar, C. (2011). Enhancing security in ATM networks through congestion control technique. Journal of Computer Applications, 4(2), 63–67.
Kanji, S. S. (2014). ATM congestion control & call admission control using admission factor and DIFA (database info fuzzy logic). International Journal for Science and Emerging Technologies with Latest Trends, 14, 17–21.
Bhatia, K., Pal, A. K., & Chaudhary, A. (2009). Performance analysis of high speed data networks using priority discipline. BVICAM’s International Journal of Information Technology, 1(2), 141–146.
El-Madbouly, H. (2007). Bandwidth allocation in ATM network for different QOS requirements. International Journal of Electrical, Electronic Science and Engineering, 1(8), 68–71.
Yoon, J., Ju, H., & Hong, J. W. (2003). Development of SNMP-XML translator and gateway for XML-based integrated network management. International Journal of Network Management, 13, 1–18.
Jing, Y., Zeng, H., Jing, Q., & Yuan, P. (2008). ATM rate based traffic control with bode principle. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 6(2), 214–222.
Alagu, S., & Meyyappan, T. (2012). An efficient call admission control scheme for handling handoffs in wireless mobile networks. International Journal on AdHoc Networking Systems, 2(3), 29–46.
Goel, Sagar R. (2014). Wireless ATM based network for multimedia personal communication service. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 4(3), 424–429.
Rani, M. U., & Sailaja, K. (2013). Implementation of fast restoration mechanisms in ATM networks. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 3(7), 1299–1306.
Sreenivasulu, M., Prasad, E. V., & Raju, G. S. S. (2011). Enhanced ERICA congestion control scheme for ATM networks. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, 11(5), 133–140.
Loukas, N. H., Merakos, L., & Veniens, I. S. (2001). Mobility management and control in intelligent. Computer Communications, 24, 1780–1807.
Ahamed, S. S. R. (2008). The role of ATM technology in future data communication systems. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 4, 624–628.
Sreenivasulu, M., Prasad, E. V., & Raju, G. S. S. (2011). Performance evaluation of rate based congestion control schemes for ATM networks. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, 11(6), 190–196.
Caytiles, R. D., & Park, B. (2013). Future directions of information and telecommunication systems through the technological advancement convergence. International Journal of Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering, 8(1), 101–106.
Huang, S., & Lin, C. (2014). Application of ATM-based network for an integrated distribution SCADA-GIS system. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 17(1), 80–86.
Agarwal, S., & Gautam, A. K. (2012). Alternate multi path routing architecture for ATM networks. International Journal of Computer Science and Communication Engineering, 1(2), 37–42.
Akki, C. B., & Chadchan, S. M. (2009). The survey of handoff issues in wireless ATM networks. International Journal of Nonlinear Science, 7(2), 189–200.
Atlasis, A. F., Loukas, N. H., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2000). The use of learning algorithms in ATM networks call admission control problem: A methodology. Computer Networks, 34, 341–353.
Athanasios Vasilakos, M. P., Saltouros, A. F., & Atlassis, Witold Pedrycz. (2003). Optimizing QoS routing in hierarchical ATM networks using computational intelligence techniques. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 33(3), 297–312.
Routray, S. (2010). An enhanced genetic algorithm for dynamic routing in ATM networks. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 16(2), 153–159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaddam, S.V.K., Lobial, D.K. & Lal, M. Integrated Network Management for ATM and Broadband Networks using Integrated Speed Bit Protocol. Wireless Pers Commun 98, 2925–2941 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-5008-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-5008-3