Abstract
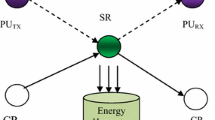
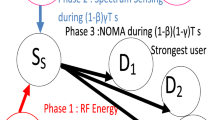
Applying energy harvesting technology in cognitive radio networks (CRNs) leads to a tradeoff between the time allocated for spectrum sensing followed by spectrum accessing and that for energy harvesting. This tradeoff can be formulated as a mode selection problem for the secondary users. In this paper, we consider a CRN working in the time-slotted manner. The secondary users powered by radio frequency energy harvesting can perform overlay transmission or cooperate with the primary users. To maximize the long-term throughput of the secondary network, we propose two optimal mode selection policies by formulating this problem under a partially observable Markov decision process framework. Numerical simulations show that both of our proposed policies achieve more throughput than the overlay-only policy. Finally, we also evaluate the effect of the cooperative threshold and the energy harvesting process on the optimal policies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shusen, Y., Yad, T., Po-yu, C., Alan, M., & Julie, M. (2016). Distributed optimization in energy harvesting sensor networks with dynamic in-network data processing. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM). https://doi.org/10.1109/INFOCOM.2016.7524475.
Cong, W., Ji, L., Yuanyuan, Y., & Ye, F. (2016). A hybrid framerwork combining solar energy harvesting and wireless charging for wireless sensor networks. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM). https://doi.org/10.1109/INFOCOM.2016.7524337.
Xiao, L., Ian, F., Dusit, N., & Nicolas, P. (2016). Self-sustainable communications with RF energy harvesting: Ginibre point process modeling and analysis. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas Communications, 34(5), 1518–1535.
Mohjazi, L., Dianati, M., Karagiannidis, G. K., & Muhaidat, S. (2015). RF-powered cognitive radio networks: Technical challenges and limitations. IEEE communications Magazine, 53(4), 94–100.
Xiao, L., Ping, W., Dusit, N., Dong, I. K., & Zhu, H. (2014). Wireless networks with RF energy harvesting: A contemporary survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(2), 757–789.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) (2003). Et docket No. 03-222 notice of proposed rule making and order.
Akyildiz, I. F., Lee, W. Y., Vuran, M. C., & Mohanty, S. (2006). NeXt generation/dynamic spectrum access/cognitive radio wireless networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 50(13), 2127–2159.
Ahmed, S. (2012). Sensing and transmit energy optimization for an energy harvesting cognitive radio. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 1(5), 500–503.
Hoang, A. T., Yingchang, L., Wong, D. T. C., Yonghong, Z., & Rui, Z. (2009). Opportunistic spectrum access for energy-constrained cognitive radios. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(3), 1206–1211.
Mao, S., Cheung, M. H., & Wong, V. W. S. (2012). An optimal energy allocation algorithm for energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. IEEE International Conference on Communications, 11(18), 265–270.
Muhammad, U., & Insoo, K. (2014). Throughput maximization of the cognitive radio using hybrid (overlay–underlay) approach with energy harvesting. In International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (pp. 22–27).
Muhammad, U., & Insoo, K. (2014). Access strategy for hybrid underlay–overlay cognitive radios with energy harvesting. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(9), 3164–3173.
Wenjun, X., Yan, W., Kai, N., Zhiqiang, H., & Jiaru, L. (2015). Joint overlay and underlay resource allocation with weighted fairness in OFDM-based cognitive radio systems. International Journal of Communication Systems, 28(10), 1692–1708.
Juhi, G., Vikram, K., & Vivek, K. D. (2015). Joint overlay–underlay optimal power allocation in cognitive radio. Wireless Personal Communications, 83(3), 1–12.
Jin, Z., & Qian, Z. (2009). Stackelberg game for utility-based cooperative cognitive radio networks. In ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking & Computing (pp. 23–32).
Sungsoo, P., & Daesik, H. (2014). Achievable throughput of energy harvesting cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(2), 1010–1022.
Sungsoo, P., Jihaeng, H., Beomju, K., Wonsuk, C., Hano, W., Daesik, H. (2012). Optimal mode selection for cognitive radio sensor networks with RF energy harvesting. In IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC) (Vol. 11(4), pp. 2155–2159).
Wild, B., & Ramchandran, K. (2005). Detecting primary receivers for coginitive radio applications. First IEEE International Symposium on New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (pp. 124–130).
Jeya, P. J., Sanket, S. K., & Adrish, B. (2014). Energy harvesting cognitive radio with channel-aware sensing strategy. IEEE Communications Letters, 18(7), 1171–1174.
Sungsoo, P., Seokwon, L., Beomju, K., Daesik, H., Jemin, L. (2011). Energy-efficient opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks with energy harvesting. In International Conference on Cognitive Radio and Advanced Spectrum Management. https://doi.org/10.1145/2093256.2093318.
Shixin, L., Rui, Z., & Tengjoon, L. (2012). Optimal save-then-transmit protocol for energy harvesting wireless transmitters. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(3), 1196–1207.
Kaelbling, L. P., Littman, M. L., & Cassandra, A. R. (1998). Planning and acting in partially observable stochastic domains. Artificial Intelligence, 101(1–2), 99–134.
Kaelbling, L. P., Littman, M. L., & Cassandra, A. R. (1998). Planning and acting in partially observable stochastic domains. Artificial Intelligence, 101(1), 99–134.
Bertsekas, D. P. (2001). Dynamic programming and optimal control (2nd ed., Vols. 1–2). Belmont, MA: Athena Scientific.
Cassandra, A., Littman, M. L., Zhang, N. L. (2013). Increnebtal prunting: A simple, fast, exact method for partially observable markov decision processes. In Thirteenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (pp. 54–61).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, T., Ding, J., Zhang, F. et al. Optimal Mode Selection Policies in Cognitive Radio Networks with RF Energy Harvesting. Wireless Pers Commun 98, 3319–3334 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-5016-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-5016-3