Abstract
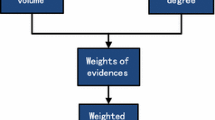
When a new event occurs, the nodes in the neighborhood of the event sense and then send many packets to the sink node. Such circumstances need their networks to be simultaneously reliable and event-driven. Moreover, it should be remove redundant packets in order to lower the average energy consumption. A data fusion algorithm based on event-driven and Dempster–Shafer evidence theory is proposed in this paper to reduce data packet quantities and reserve energy for wireless sensor networks upon detecting abnormal data. Sampling data is compared against the set threshold, and the nodes enter the relevant state only when there are abnormal datum; at this point, cluster formation begins. All cluster members incorporate a local forwarding history to decide whether to forward or to drop recent sampling data. Dempster–Shafer evidence theory is exploited to process the data. The basic belief assignment function, with which the output of each cluster member is characterized as a weighted-evidence, is constructed. Then, the synthetic rule is subsequently applied to each cluster head to fuse the evidences gathered from cluster member nodes to obtain the final fusion result. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can effectively ensure fusion result accuracy while saving energy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia, X., Chen, Z., Li, D., & Li, W. (2014). Proposal for efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor network in coal mine goaf. Wireless Personal Communications, 77(3), 1699–1711.
Owojaiye, G., & Sun, Y. (2013). Focal design issues affecting the deployment of wireless sensor networks for pipeline monitoring. Ad Hoc Networks, 11(3), 1237–1253.
Tsai, C. W., Hong, T. P., & Shiu, G. N. (2016). Metaheuristics for the lifetime of WSN: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(9), 2812–2831.
Dauwe, S., Renterghem, T. V., Botteldooren, D., & Dhoedt, B. (2012). Multiagent-based data fusion in environmental monitoring networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2012, (2012-6-5), 2012(1–2), 15.
Huy, D. V., & Viet, N. D. (2015). DF-AMS: Proposed solutions for multi-sensor data fusion in wireless sensor networks. In International conference on knowledge and systems engineering (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Bouabdallah, N., Rivero-Angeles, M. E., & Sericola, B. (2009). Continuous monitoring using event-driven reporting for cluster-based wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(7), 3460–3479.
Kamarei, M., Hajimohammadi, M., Patooghy, A., & Fazeli, M. (2015). An efficient data aggregation method for event-driven WSNs: A modeling and evaluation approach. Wireless Personal Communications, 84(1), 1–20.
Bahrami, S., Yousefi, H., & Movaghar, A. (2012). DACA: Data-aware clustering and aggregation in query-driven wireless sensor networks. In International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (Vol. 7204, pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Izadi, D., Abawajy, J. H., Ghanavati, S., & Herawan, T. (2015). A data fusion method in wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 15(2), 2964.
Yager, R. R., Kacprzyk, J., & Fedrizzi, M. (1994). Advances in the Dempster–Shafer theory of evidence. New York: Wiley.
Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (Vol. 18, p. 8020). IEEE Computer Society.
Manjeshwar, A., & Agrawal, D. P. (2002). APTEEN: A hybrid protocol for efficient routing and comprehensive information retrieval in wireless. In Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium. Proceedings International, IPDPS 2002, Abstracts and CD-ROM (p. 8). IEEE.
Ozger, M., & Akan, O. B. (2013). Event-driven spectrum-aware clustering in cognitive radio sensor networks. In IEEE INFOCOM (Vol. 12, pp. 1483–1491). IEEE.
Adulyasas, A., Sun, Z., & Wang, N. (2013). An event-driven clustering-based technique for data monitoring in wireless sensor networks. In Consumer Communications and NETWORKING Conference (Vol. 14, pp. 653–656). IEEE.
Hou, X., Zhang, D., & Zhong, M. (2014). Data aggregation of wireless sensor network based on event-driven and neural network. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 27(1), 142–148.
Shafer, G. (1978). A mathematical theory of evidence. Technometrics, 20(1), 242.
Shen, B., Liu, Y., & Fu, J. S. (2014). An integrated model for robust multisensor data fusion. Sensors, 14(10), 19669–19686.
Wang, W. Q., Yang, Y. L., & Yang, C. J. (2013). A data fusion algorithm based on evidence theory. Kongzhi Yu Juece/Control and Decision, 28(9), 1427–1430.
Liu, K., Yang, T., Ma, J., & Cheng, Z. (2015). Fault-tolerant event detection in wireless sensor networks using evidence theory. KSII Transactions on Internet & Information Systems, 9(10), 3965–3982.
Jousselme, A. L., Grenier, D., & Bossé, É. (2001). A new distance between two bodies of evidence. Information Fusion, 2(2), 91–101.
Hong, C., Xiong, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2016). A hybrid beaconless geographic routing for different packets in WSN. New York: Springer.
Mcgrattan, K. B., Hostikka, S., & Floyd, J. E. (2007). Fire dynamics simulator (version 5): User’s guide. NIST Special Publication, 4(4), 206–207.
Acknowledgements
This work was in part supported by the State Key Laboratory of Safety and Health for Metal Mines (2016-JSKSSYS-04); the Key Scientific Projects of Hunan Education Committee (15A161).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Zhang, F., Zhou, L. et al. Novel Data Fusion Algorithm Based on Event-Driven and Dempster–Shafer Evidence Theory. Wireless Pers Commun 100, 1377–1391 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5644-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5644-2