Abstract
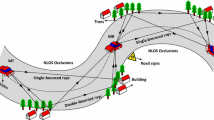
In this paper, we develop a three-dimensional (3D) eccentricity-based cylindrical geometrical channel model for nonisotropic multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) communication systems under umbrella macrocellular environment. We use elliptic cylindrical geometry to model the scattering phenomenon in streets, canyons and highways. The scattering objects like, high-rise building, trees and vegetation that lie along the roadside premises are modeled by the height of an elliptical cylinder. The proposed channel model targets fast moving vehicles on the highways in an umbrella-cell of cellular communication networks. We assume that both ends of the communication link are equipped with multiple antenna arrays, where, mobile-station antenna height is lower than base-station antenna. Utilizing the proposed MIMO communication channel model, we obtain closed-form expressions for the space–time correlation function among the MIMO antenna elements. The obtained theoretical expressions are plotted and analyzed for different values of channel parameters. Finally, we compare the proposed model with the existing models in the literature and prove that our model can be deduced to the existing two-dimensional and 3D channel models.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi, A., Barger, J. A., & Kaveh, M. (2002). A parametric model for the distribution of the angle of arrival and the associated correlation function and power spectrum at the mobile station. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 51(3), 425–434.
Abdi, A., & Kaveh, M. (2002). A space–time correlation model for multielement antenna systems in mobile fading channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 20(3), 550–560.
Ahmed, A., Nawaz, S. J., Khan, N. M., Patwary, M. N., & Abdel-Maguid, M. (2015). Angular characteristics of a unified 3-D scattering model for emerging cellular networks. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), IEEE (pp. 2450–2456).
Awasthi, B. (2014). Hand off problem analysis in personal communication system using splitted-rating channel technique. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 3, 13–14.
Baltzis, K. (2008). On the geometric modeling of the uplink channel in a cellular system. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 1(1), 1.
Boban, M., Vinhoza, T. T., Ferreira, M., Barros, J., & Tonguz, O. K. (2011). Impact of vehicles as obstacles in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 29(1), 15–28.
Borhani, A., Patzöld, M. (2011). Time-of-arrival, angle-of-arrival, and angle-of-departure statistics of a novel simplistic disk channel model. In Proceedings of international conference on signal processing and communication systems (ICSPCS), IEEE, (pp. 1–7).
Cheng, X., He, Y., & Guizani, M. (2017). 3-D geometrical model for multi-polarized MIMO systems. IEEE Access, X(X), 1–20.
Cheng, X., Wang, C. X., & Laurenson, D. I. (2007). A generic space-time-frequency correlation model and its corresponding simulation model for narrowband MIMO channels. In: Proceedings of European conference on antennas propagation, IET (pp. 1–6).
Chung, Y. U., & Cho, D. (2001). Velocity estimation using adaptive array antennas. In: Proceedings of IEEE vehicular technology conference (Vol. 4, pp. 2565–2569).
Chung, Y. U., Lee, D. J., Cho, D. H., & Shin, B. C. (2002). Macrocell/microcell selection schemes based on a new velocity estimation in multitier cellular system. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 51(5), 893–903.
Clarke, R. H., & Khoo, W. L. (1997). 3-D mobile radio channel statistics. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 46(3), 798–799.
Crichton, P., Oberoi, R. S., & Thomas, H. (1998). Handover based on measured time of signals received from neighboring cells. US Patent 5,722,072.
Ekiz, N., Salih, T., Kucukoner, S., & Fidanboylu, K. (2005). An overview of handoff techniques in cellular networks. International Journal of Information Technology, 2(3), 132–136.
Ertel, R. B., & Reed, J. H. (1999). Angle and time of arrival statistics for circular and elliptical scattering models. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 17(11), 1829–1840.
Feng, L., Fan, P., Wang, C., & Ghazal, A. (2015) A 3D GBSM for high-speed train communication systems under deep cutting scenarios. In Proceedings of international workshop on high mobility wireless communications (HMWC), IEEE, (pp. 86–90).
Gesbert, D., Bolcskei, H., Gore, D. A., & Paulraj, A. J. (2002). Outdoor MIMO wireless channels: Models and performance prediction. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 50(12), 1926–1934.
Ghazal, A., Wang, C. X., Ai, B., Yuan, D., & Haas, H. (2015). A nonstationary wideband MIMO channel model for high-mobility intelligent transportation systems. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 16(2), 885–897.
Goldsmith, A., Jafar, S. A., Jindal, N., & Vishwanath, S. (2002). Fundamental capacity of MIMO channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 21, 684–702.
Goldsmith, A., Jafar, S. A., Jindal, N., & Vishwanath, S. (2003). Capacity limits of MIMO channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 21(5), 684–702.
Gradshtejn, I. S., & Ryzhik, I. M. (1965). Table of integrals, series and products. London: Academic.
Hampton, J. R., Hammons, R. A, Jr., Cruz, M. A., Merheb, N. M., Paunil, D. E., & Ouyang, F. (2011). Multiple-input multiple-output(mimo) channel measurements for urban military applications. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest, 30(2), 135–143.
Hong, D., & Rappaport Stephen, S. (1986). Traffic model and performance analysis for cellular mobile radio telephone systems with prioritized and nonprioritized handoff procedures. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 35(3), 77–92.
Ivanov, K., & Spring, G. (1995). Mobile speed sensitive handover in a mixed cell environment. Proceedings of IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, 2, 892–896.
Jaafar, I., Boujemâa, H., & Siala, M. (2008). Angle and time of arrival statistics for hollow-disc and elliptical scattering models. In Proceedings of 2nd international conference signals, circuits systems (pp. 1–4).
Janaswamy, R. (2002). Angle of arrival statistics for a 3D spheroid model. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 51(5), 1242–1247.
Janaswamy, R. (2002). Effect of element mutual coupling on the capacity of fixed length linear arrays. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 1(1), 157–160.
Khan, N. M., Simsim, M. T., & Ramer, R. (2006). Modeling spatial aspects of mobile channel for macrocells using Gaussian scattering distribution. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on wireless communication systems (ISWCS’06), IEEE (pp. 616–620).
Khan, N. M., Simsim, M. T., & Rapajic, P. B. (2008). A generalized model for the spatial characteristics of the cellular mobile channel. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(1), 22–37.
Kuchar, A., Aparicio, E. A., Rossi, J. P., & Bonek, E. (2002). Azimuth, elevation, and delay of signals at mobile station site. In Wireless personal communications (pp. 99–110). Boston: Springer.
Kuchar, A., Rossi, J. P., & Bonek, E. (2000). Directional macro-cell channel characterization from urban measurements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 48(2), 137–146.
Mac Donald, V. H. (1979). Advanced mobile phone service: The cellular concept. Bell System Technical Journal, 58(1), 15–41.
Madhusudhanan, P., Restrepo, J. G., Liu, Y., Brown, T. X., & Baker, K. R. (2011). Multi-tier network performance analysis using a shotgun cellular system. In Proceedings of IEEE global telecommunications conference (GLOBECOM), IEEE (pp. 1–6).
Marichamy, P., Chakrabarti, S., & Maskara, S. (1999). Overview of handoff schemes in cellular mobile networks and their comparative performance evaluation. Proceedings of IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, 3, 1486–1490.
Michailidis, E. T., & Kanatas, A. G. (2010). Three-dimensional HAP-MIMO channels: Modeling and analysis of space–time correlation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(5), 2232–2242.
Misra, S., Krishna, P. V., & Saritha, V. (2012). LACAV: An energy-efficient channel assignment mechanism for vehicular ad hoc networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, 62(3), 1241–1262.
Nawaz, S. J., Qureshi, B. H., & Khan, N. M. (2010). A generalized 3D scattering model for a macrocell environment with a directional antenna at the BS. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(7), 3193–3204. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2010.2050015.
Olenko, A. Y., Wong, K. T., & Hui-On Ng, E. (2006). Analytically derived uplink/downlink To A and 2 D- Do A distributions with scatterers in a 3 D hemispheroid surrounding the mobile. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 54(9), 2446–2454.
Parsons, J., & Turkmani, A. (1991). Characterisation of mobile radio signals: Model description. In: Proceedings of IEE communications, speech and vision, IET (Vol. 138, pp. 549–556).
Petrus, P., Reed, J. H., & Rappaport, T. S. (1997). Effects of directional antennas at the base station on the doppler spectrum. IEEE Communications Letters, 1(2), 40–42.
Petrus, P., Reed, J. H., & Rappaport, T. S. (2002). Geometrical-based statistical macrocell channel model for mobile environments. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 50(3), 495–502. https://doi.org/10.1109/26.990911.
Rade, L., & Westergren, B. (2013). Mathematics handbook for science and engineering. Berlin: Springer.
Rappaport, T. S. (1996). Wireless communications: Principles and practice (Vol. 2). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall PTR.
Salz, J., & Winters, J. H. (1994). Effect of fading correlation on adaptive arrays in digital mobile radio. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 43(4), 1049–1057.
Stüber, G. L. (2011). Principles of mobile communication. Berlin: Springer.
Talha, B., & Patzold, M. (2011). Channel models for mobile-to-mobile cooperative communication systems: A state of the art review. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 6(2), 33–43.
Tripathi, N. D., Reed, J. H., & VanLandinoham, H. F. (1998). Handoff in cellular systems. IEEE Personal Communications, 5(6), 26–37.
Wang, L., Min, G., & Kouvatsos, D. (2008). Performance analysis of a dynamic handoff scheme in wireless networks with heterogeneous call arrival processes. Telecommunication Systems, 39(2), 157–167.
Wani, M. Y., Riaz, M., & Khan, N. M. (2016). Modeling and characterization of MIMO mobile-to-mobile communication channels using elliptical scattering geometry. Wireless Personal Communications, 91(2), 509–524.
Yamada, Y., Ebine, Y., & Nakajima, N. (1987). Base station/vehicular antenna design techniques employed in high-capacity land mobile communications system. Review of the Electrical Communication Laboratories, 35(2), 115–121.
Zajić, A. G., & Stüber, G. L. (2008). Three-dimensional modeling, simulation, and capacity analysis of space–time correlated mobile-to-mobile channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(4), 2042–2054. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2007.912150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wani, M.Y., Riaz, M. & Khan, N.M. Geometrical Modeling of Scattering Environment for Highways in Umbrella Cell Based MIMO Communication Systems. Wireless Pers Commun 101, 59–74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5666-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5666-9