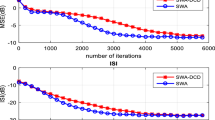
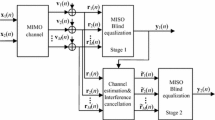
Abstract
The performance of blind equalization algorithm is closely related to the characteristics of the channel. Eigenvalue spread of the channel can reflect the influence of the channel on the input signal. The paper presents a method to distinguish eigenvalue spread of the wireless channel by the correlation coefficient of the input vector. For channels with different eigenvalue spread, based on the consideration of the complexity and the performance, different blind equalization algorithms are chosen. At the same time a decorrelation blind equalization algorithm is proposed. Simulations verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benveniste, A., & Goursat, M. (1980). Robust identification of non-minimum phase system: Blind adjustment of a linear equalizer in data communication. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 25, 385–399.
Shalvi, O., & Weinstein, E. (1990). New criteria for blind deconvolution of nonminimum phase systems (channels). IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 42, 1145–1156.
Haykin, S. (1994). Blind deconvolution. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Ding, Z., & Li, Y. (2001). Blind equalization and identification. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.
Miranda, M. D., Silva, M., & Nascimento, V. H. (2008). Avoiding divergence in the Shalvi–Weinstein algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(11), 5403–5413.
Haykin, S. (2013). Adaptive filter theory (5th ed.). London: Pearson Publisher.
Bellini, S. (1986). Bussgang techniques for blind equalization. In Proceedings of IEEEGLOBECOM (pp. 1634–1640).
Godard, D. (1980). Self-recovering equalization and carrier tracking in two-dimensional data communication systems. IEEE Transactions in Communications, 28(11), 1867–1875.
Li, X.-L., & Zhang, X.-D. (2006). A family of generalized constant modulus algorithms for blind equalization. IEEE Transactions in Communications, 54(11), 1913–1917.
Abrar, S., & Nandi, A. K. (2010). Blind equalization of square-QAM signals: A multimodulus approach. IEEE Transactions in Communications, 58(6), 1674–1685.
Yang, J., Werner, J.-J., & Dumont, G. A. (2002). The multimodulus blind equalization and its generalized algorithms. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 20(5), 997–1015.
Mendes Filho, J., Miranda, M. D., & Silva, M. T. M. (2012). A regional multimodulus algorithm for blind equalization of QAM signals: Introduction and steady-state analysis. Signal Processing, 92, 2643–2656.
Azim, A. W., Abrar, S., Zerguine, A., & Nandi, A. K. (2015). Steady-state performance of multimodulus blind equalizers. Signal Processing, 108, 509–520.
Fki, S., Messai, M., Aïssa-El-Bey, A., & Chonavel, T. (2014). Blind equalization based on pdf fitting and convergence analysis. Signal Processing, 101, 266–277.
Shalvi, O., & Weinstein, E. (1993). Super-exponential methods for blind deconvolution. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 39(2), 504–519.
Silva, M. T. M., & Miranda, M. D. (2004). Tracking issues of some blind equalization algorithms. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 11(9), 760–763.
Godard, D. (1980). Self-recovering equalization and carrier tracking in two-dimensional data communication systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 28(11), 1867–1875.
Treichler, J., & Agee, B. (1983). A new approach to multipath correction of constant modulus signals. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 31(2), 459–472.
Johnson, R., Jr., Schniter, P., Endres, T., Behm, J., Brown, D., & Casas, R. (1998). Blind equalization using the constant modulus criterion: A review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(10), 1927–1950.
Yuan, J.-T., & Lin, T.-C. (2010). Equalization and carrier phase recovery of CMA and MMA in blind adaptive receivers. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58(6), 3206–3217.
Doherty, J. F., & Porayath, R. (1997). A robust echo canceler for acoustic environments. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems—II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 44(5), 389–396.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61571340 and the program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities under Granted B0803.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Wang, F., Jia, C. et al. Blind Equalization Algorithm for Different Eigenvalue Spread Channels. Wireless Pers Commun 101, 1003–1018 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5743-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5743-0