Abstract
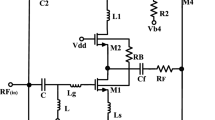
In this work, we present a self cascode based ultra-wide band (UWB) low noise amplifier (LNA) with improved bandwidth and gain for 3.1–10.6 GHz wireless applications. The self cascode (SC) or split-length compensation technique is employed to improve the bandwidth and gain of the proposed LNA. The improvement in the bandwidth of SC based structure is around 1.22 GHz as compared to simple one. The significant enhancement in the characteristics of the introduced circuit is found without extra passive components. The SC based CS–CG structure in the proposed LNA uses the same DC current for operating first stage transistors. In the designed UWB LNA, a common source (CS) stage is used in the second stage to enhance the overall gain in the high frequency regime. With a standard 90 nm CMOS technology, the presented UWB LNA results in a gain \(\hbox {S}_{21}\) of \(20.10 \pm 1.65\,\hbox {dB}\) across the 3.1–10.6 GHz frequency range, and dissipating 11.52 mW power from a 1 V supply voltage. However, input reflection, \(\hbox {S}_{11}\), lies below \(-\,10\) dB from 4.9–9.1 GHz frequency. Moreover, the output reflection (\(\hbox {S}_{22}\)) and reverse isolation (\(\hbox {S}_{12}\)), is below \(-\,10\) and \(-\,48\) dB, respectively for the ultra-wide band region. Apart from this, the minimum noise figure (\(\hbox {NF}_{min}\)) value of the proposed UWB LNA exists in the range of 2.1–3 dB for 3.1–10.6 GHz frequency range with a a small variation of \(\pm \,0.45\,\hbox {dB}\) in its \(\hbox {NF}_{min}\) characteristics. Linearity of the designed LNA is analysed in terms of third order input intercept point (IIP3) whose value is \(-\,4.22\) dBm, when a two tone signal is applied at 6 GHz with a spacing of 10 MHz. The other important benefits of the proposed circuit are its group-delay variation and gain variation of \(\pm \,115\,\hbox {ps}\) and \(\pm \,1.65\,\hbox {dB}\), respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slimane, A., Trabelsi, M., & Belaroussi, M. T. (2011). A 0.9-V, 7-mW UWB LNA for 3.1–10.6 GHz wireless applications in \(0.18\,\upmu \text{ m }\) CMOS technology. Microelectronics Journal, 42(11), 1263–1268.
Toofan, S., Rahmati, A. R., Abrishamifar, A., & Roientan Lahiji, G. (2008). Low power and high gain current reuse LNA with modified input matching and inter-stage inductors. Microelectronics Journal, 39(12), 1534–1537.
Rastegar, H., Saryazdi, S., & Hakimi, A. (2012). Wideband and multiband CMOS LNAs: State-of-the-art and future prospects. Microelectronics Journal, 44(9), 774–786.
Nakhlestani, A., et al. (2012). A novel configuration for UWB LNA suitable for low-power and low-voltage applications. Microelectronics Journal, 43(7), 444–451.
Shim, J., Yang, T., & Jeong, J. (2013). Design of low power CMOS ultra wide band low noise amplifier using noise canceling technique. Microelectronics Journal, 44(9), 821–826.
Sapone, G., & Palmisano, G. (2011). A 3–10 GHz low-power CMOS low-noise amplifier for ultra-wideband communication. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory Techniques, 59(3), 678–686.
Lu, Y., Yeo, K. S., Cabuk, A., Ma, J., Do, M. A., & Lu, Z. (2006). A novel CMOS low noise amplifier design for 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra-wide-band wireless receiver. IEEE Transactions on Circuits System I: Regular Papers, 53(8), 1683–1692.
Yang, H. Y., Lin, Y. S., & Chen, C. C. (2008). 2.5 dB NF 3.1–10.6 GHz CMOS UWB LNA with small group-delay variation. Electronics Letters, 44(8), 528–529.
Chen, C. C., & Wang, Y. C. (2013). 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra-wideband LNA design using dual-resonant broadband matching technique. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 67(6), 500–503.
Lee, J. H., Chen, C. C., & Lin, Y. S. (2007). \(0.18\,\upmu \text{ m }\) 3.1–10.6 GHz CMOS UWB LNA with \(11.4 \pm 0.4\,\text{ dB }\) gain and \(100.7 \pm 17.4\,\text{ ps }\) group-delay. Electronics Letters, 43(24), 1359–1360.
Rastegar, H., Saryazdi, S., & Hakimi, A. (2013). A low power and high linearity UWB low noise amplifier (LNA) for 3.1–10.6 GHz wireless applications in \(0.13\,\upmu \text{ m }\) CMOS process. Microelectronics Journal, 44(3), 201–209.
Wan, Q., Wang, Q., & Zheng, Z. (2015). Design and analysis of a 3.1–10.6 GHz UWB low noise amplifier with forward body bias technique. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 69, 119–125.
Reiha, M.-T., & Long, J.-R. (2007). A 1.2 V reactive feedback 3.1–10.6 GHz low-noise amplifier in \(0.13\,\upmu \text{ m }\) CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 42(5), 1023–1033.
Chang, J.-F., & Lin, Y.-S. (2009). 3–10 GHz low-power, low-noise CMOS distributed amplifier using splitting-load inductive peaking and noise-suppression techniques. Electronics Letters, 45(20), 78–81.
Yan, S., & Sanchez-Sinencio, E. (2000). Low voltage analog circuit design techniques: A tutorial. IEICE Transactions on Analog Inegrated Circuits and Systems, 2, 1–17.
Galup-Montoro, C., Schneider, M. C., & Loss, I. J. B. (1994). Series-parallel association of fet’s for high gain and high frequency applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 29(9), 1094–1101.
Rajput, S. S., & Jamuar, S. S. (2002). Low voltage analog circuit design techniques. Circuits and Systems Magazine, 2(1), 24–42.
Saxena, V., Balagopal, S., & Baker, R. J. (2011). Systematic design of three-stage op-amps using split-length compensation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 54th midwest symposium on circuits and systems (MWSCAS) (pp. 1–4).
Saxena, V., & Baker, R. J. (2008). Compensation of CMOS Op-amps using split-length transistors. In Proceedings of the IEEE 51st midwest symposium on circuits and systems (MWSCAS) (pp. 109–112).
Pepe, D., & Zito, D. (2009). 22.7-dB gain- 19.7-dBm \(\text{ ICP }_{1{\rm dB}}\) UWB CMOS LNA. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, Express Briefs, 56(9), 689–693.
Brederlow, R., Weber, W., Sauerer, J., Donnay, S., Wambacq, P., & Vertregt, M. (2001). A mixed-signal design roadmap. IEEE Design and Test of Computers, 18(6), 34–36.
Hsu, M.-T., Chang, Y.-C., & Huang, Y.-Z. (2013). Design of low power UWB LNA based on common source topology with current-reused technique. Microelectronics Journal, 44(12), 1223–1230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, S., Gawande, T. & Kondekar, P.N. A 3.1–10.6 GHz UWB LNA Based on Self Cascode Technique for Improved Bandwidth and High Gain. Wireless Pers Commun 101, 1867–1882 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5795-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5795-1