Abstract
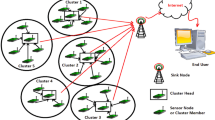
Researchers concentrate on big data. Wireless sensor network is one of the sources of big data. Wireless sensor network has hundreds of sensor nodes with limited energy and computational capability. Clustering is a technique used to reduce the energy expended and extend the network lifetime. Generally, nodes are deployed in a square network field. The nodes at the edges of the network have to transmit longer distance to the sink than the nodes at the sides. This depletes the node energy and reduces the network lifetime. Our proposed work Efficient Energy Heterogeneous Circular field Clustering Protocol (EEHCCP), deploys two tier energy heterogeneity nodes: normal and advance nodes in different zones of concentric circular network field. A hybrid direct and clustered communication in a circular network field has increased the network lifetime and throughput of the sensor network. The network lifetime and throughput of EEHCCP is better than SEP, DEEC and EDEEC. Also, performance metric of heterogeneous clustered EEHCCP is compared with Efficient Energy Homogeneous Circular field Protocol with no clustering.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guiloufi, A. B. F., Nasri, N., & Kachouri, A. (2015). An energy-efficient unequal clustering algorithm using ‘Sierpinski triangle’ for WSNs. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-3137-0.
Saeidmanesh, M., Haji Mohammadi, M., & Movaghar, A. (2009). Energy and distance based clustering: An energy efficient clustering method for WSNs. World Acadamy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 55, 555.
Saravanakumar, R., Susila, S. G., & Raja, J. (2011). Energy efficient homogeneous and heterogeneous system for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Computer Applications, 17, 4.
Kumar, N., Tyagi, S., & Deng, D.-J. (2014). LA-EEHSC: Learning automata-based energy efficient heterogeneous selective clustering for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications., 46, 264–279.
Mishra, N. K., Jain, V., & Sahu, S. (2013). Survey on recent clustering algorithms in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 3(4), 1.
Katiyar, V., Chand, N., & Soni, S. (2010). Clustering algorithms for heterogeneous wireless sensor network: A survey. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 1(2), 273.
Singh, S. K., Singh, M. P., & Singh, D. K. (2010). Applications, classifications, and selections of energy-efficient routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Sciences and Technologies, 1(2), 085–095.
Sheikhpour, R., Jabbehdari, S., & Khadem-Zadeh, A. (2011). Comparison of energy efficient clustering protocols in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 36, 27.
Yarvis, M., Kushalnagar, N., Singh, H., Rangarajan, A., Liu, Y., & Singh, S. (2005). Exploiting heterogeneity in sensor networks. In IEEE INFOCOM.
Smaragdakis, G., & Matta, I. (2010). SEP: A stable election protocol for clustered heterogeneous wireless sensor networks (pp. 1–11). Boston: Boston University.
Heinzelman, W. B., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2002). An application specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–670.
Bala, M., & Awasthi, L. (2012). Proficient D-SEP protocol with heterogeneity for maximizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications, 7, 1–15.
Faisal, S., Javaid, N., Javaid, A., Khan, M. A., Bouk, S. H., & Khan, Z. A. (2013). Z-SEP: Zonal-stable election protocol for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research., 3(5), 132–139.
Qing, L., Zhu, M., & Wang, M. (2006). Design of a distributed energy-efficient clustering algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 29(12), 2230–2237.
Saini, P., & Ajay, S. K. (2010). E-DEEC-enhanced distributed energy efficient clustering scheme for heterogeneous WSN. In 1st international conference on parallel, distributed and grid computing (PDGC) (pp. 205–210).
Chithra, A., & Shantha Selva Kumari, R. (2017). A novel 3-level energy heterogeneity clustering protocol with hybrid routing for a concentric circular wireless sensor network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chithra, A., Shantha Selva Kumari, R. A New Energy Efficient Clustering Protocol for a Novel Concentric Circular Wireless Sensor Network. Wireless Pers Commun 103, 2455–2473 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5937-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5937-5