Abstract
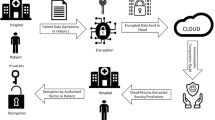
More computations have to be done through less powerful mobile devices which includes ultra modern wearables. The huge overhead lies in the processing of the humongous key space each and computation of the intelligible message. The uniqueness of the elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) lies in the processing of data using shorter keys which are capable to achieve the performance of long key requirement of RSA. In order to reduce the overhead involved in the computation of less powerful mobile devices the fuzzy genetic elliptic curve Diffie Hellman is proposed in this paper. The intelligent rules are used for ranking during key selection process, multi attribute decision making model with fuzzy reasoning for obtaining keys and genetic algorithms for effective optimization of computation in ECC contributes to obtain the proposed FGECDH algorithm.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdanov, A., Knudsen, L. R., Leander, G., Standaert, F. X., Steinberger, J., & Tischhauser, E. (2012). Key-alternating ciphers in a provable setting: Encryption using a small number of public permutations. In D. Pointcheval & T. Johansson (Eds.), Annual international conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques (Vol. 7237, pp. 45–62). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Libert, B., Peters, T., Joye, M., & Yung, M. (2015). Linearly homomorphic structure-preserving signatures and their applications. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 77(2–3), 441–477.
Zadeh, L. A. (2012). Computing with words: Principal concepts and ideas (Vol. 277). Berlin: Springer.
Lin, F.-T., & Kao, C.-Y. (1995). A genetic algorithm for ciphertext-only attack in cryptanalysis. In Systems, man and cybernetics, 1995. Intelligent systems for the 21st century, IEEE international conference on (Vol. 1, pp. 650–654). IEEE.
Faugère, J.-C., Perret, L., Petit, C., & Renault, G. (2012). Improving the complexity of index calculus algorithms in elliptic curves over binary fields. In D. Pointcheval & T. Johansson (Eds.), Annual international conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques (Vol. 7237, pp. 27–44). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Rivest, R. L., Shamir, A., & Adleman, L. (1978). A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Communications of the ACM, 21(2), 120–126.
Needham, R. M., & Schroeder, M. D. (1978). Using encryption for authentication in large networks of computers. Communications of the ACM, 21(12), 993–999.
Seredynski, F., Bouvry, P., & Zomaya, A. Y. (2004). Cellular automata computations and secret key cryptography. Parallel Computing, 30(5), 753–766.
Bhasin, H. (2012). Corpuscular random number generator. International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, 2(2), 197.
Burke, L. (1999). A review of optimization in operations research Ronald L. Rardin Prentice-Hall, 1998, 919pp, ISBN 0-02-398415-5. Iie Transactions, 31(3), 279–280.
Goldberg, D. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search. Optimization, and Machine Learning.
Ruttor, A., Kinzel, W., Naeh, R., & Kanter, I. (2006). Genetic attack on neural cryptography. Physical Review E, 73(3), 036121.
Khan, F. U., & Bhatia, S. (2012). A novel approach to genetic algorithm based cryptography. International Journal of Research in Computer Science, 2(3), 7.
Holland, J. H., & Goldberg, D. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Stein, G., Chen, B., Wu, A. S., & Hua, K. A. (2005). Decision tree classifier for network intrusion detection with GA-based feature selection. In Proceedings of the 43rd annual Southeast regional conference (Vol. 2, pp. 136–141). ACM.
Kaya, Y., Uyar, M., et al. (2011). A novel crossover operator for genetic algorithms: Ring crossover. arXiv preprint arXiv:1105.0355.
Picek, S., & Golub, M. (2010). Comparison of a crossover operator in binary-coded genetic algorithms. WSEAS Transactions on Computers, 9, 1064–1073.
Jhingran, R., Thada, V., & Dhaka, S. (2015). A study on cryptography using genetic algorithm. International Journal of Computer Applications, 118(20), 10–14.
Ma, Z., & Zeng, S. (2014). Confidence intuitionistic fuzzy hybrid weighted operator and its application in multi-criteria decision making. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography, 17(5–6), 529–538.
Zimmermann, H.-J. (2011). Fuzzy set theory and its applications. Berlin: Springer.
Ganapathy, Sethukkarasi, Sethukkarasi, R., Yogesh, P., Vijayakumar, P., & Kannan, A. (2014). An intelligent temporal pattern classification system using fuzzy temporal rules and particle swarm optimization. Sadhana, 39(2), 283–302.
Selvi, M., Logambigai, R., Ganapathy, S., Ramesh, L. S., Nehemiah, H. K., & Arputharaj, K. (2016). Fuzzy temporal approach for energy efficient routing in WSN. In Proceedings of the international conference on informatics and analytics (p. 117). ACM.
Selvi, M., Logambigai, R., Ganapathy, S., Nehemiah, H. K., & Arputharaj, K. (2017). An intelligent agent and FSO based efficient routing algorithm for wireless sensor network. In Recent trends and challenges in computational models (ICRTCCM), 2017 second international conference on (pp. 100–105). IEEE.
Ganapathy, S., Kulothungan, K., Yogesh, P., & Kannan, A. (2012). A novel weighted fuzzy C-means clustering based on immune genetic algorithm for intrusion detection. Procedia Engineering, 38, 1750–1757.
Baas, S. M., & Kwakernaak, H. (1977). Rating and ranking of multiple-aspect alternatives using fuzzy sets. Automatica, 13(1), 47–58.
Zadeh, L. A. (1998). Roles of soft computing and fuzzy logic in the conception, design and deployment of information/intelligent systems. In O. Kaynak, L. A. Zadeh, B. Türkşen & I. J. Rudas (Eds.), Computational intelligence: Soft computing and fuzzy-neuro integration with applications (pp. 1–9). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer
Logambigai, R., Ganapathy, S., & Kannan, A. (2018). Energy-efficient grid-based routing algorithm using intelligent fuzzy rules for wireless sensor networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 68, 62–75.
Mihret, Z., & Ahmad, M. W. (2016). The reverse engineering of reverse encryption algorithm and a systematic comparison to DES. Procedia Computer Science, 85, 558–570.
Riyaldhi, R., Kurniawan, A., et al. (2017). Improvement of advanced encryption standard algorithm with shift row and S. box modification mapping in mix column. Procedia Computer Science, 116, 401–407.
Tang, H., Sun, Q. T., Yang, X., & Long, K. (2018). A network coding and DES based dynamic encryption scheme for moving target defense. IEEE Access, 6, 26059–26068.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethuraman, P., Tamizharasan, P.S. & Arputharaj, K. Fuzzy Genetic Elliptic Curve Diffie Hellman Algorithm for Secured Communication in Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 105, 993–1007 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06132-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06132-4