Abstract
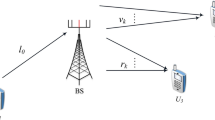
This paper considers device-to-device (D2D) together with single input single output and multiple input single output models in transmitting of nearby devices under help of wireless power transfer. To support more harvested energy, two modes are studied in which multiple-antenna/single antenna power beacons are proposed to robust D2D transmission network. Especially, enhanced successful communication is explored with short distance transmission. Accordingly, the alternative energy source can be used to maintain small devices which can operate at close position efficiently. In this paper, a model of radio frequency-assisted wireless energy transfer for D2D system with two realistic transmission schemes will be investigated, namely pure D2D and D2D with interference impact of conventional user equipment. As an important result, we derive analytical expressions for outage probability to achieve performance evaluation. This paper will analyze outage probability by matching Monte-Carlo and analytical simulations to corroborate the exactness of derived expressions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Do, D.-T., Nguyen, H.-S., Voznak, M., & Nguyen, T.-S. (2017). Wireless powered relaying networks under imperfect channel state information: System performance and optimal policy for instantaneous rate. Radioengineering, 26(3), 869–877.
Do, D.-T., & Nguyen, H.-S., (2016). A tractable approach to analyzing the energy-aware two-way relaying networks in the presence of co-channel interference. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 271(2016), 1–10.
Nguyen, H.-S., Bui, A.-H., Do, D.-T., & Voznak, M. (2016). Imperfect channel state information of AF and DF energy harvesting cooperative networks. China Communications, 13(10), 11–19.
Le, N. P. (2018). Throughput analysis of power-beacon-assisted energy harvesting wireless systems over non-identical Nakagamim Fading channels. IEEE Communications Letters, 22(4), 840–843.
CES 2017 Innovation Awards. Retrieved September 7, 2018 from http://www.ces.tech/Events-Experiences/Innovation-Awards-Program/Honorees.aspx
Lu, X., Wang, P., Niyato, D., Kim, D. I., & Han, Z. (2015). Wireless networks with RF energy harvesting: A contemporary survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 17(2), 757–789.
Nguyen, X.-X., & Do, D.-T. (2017) Optimal power allocation and throughput performance of full-duplex DF relaying networks with wireless power transfer-aware channel. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking.
Chu, Z., et al. (2016). Simultaneous wireless information power transfer for MISO secrecy channel. IEEE Transaction on Vehicular Technology, 65(9), 6913–6925.
Zhou, X., Zhang, R., & Ho, C.K. (2012). Wireless information and power transfer: Architecture design and rate-energy tradeoff. In Proceedings of the IEEE global communication conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 3982–3987).
Zhang, R., & Ho, C. K. (2013). MIMO broadcasting for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(5), 1989–2001.
Huang, Y., Zhang, P., Wang, J., & Wu, Q. (2017). Secure transmission in power beacon assisted wireless communication networks. In Proceedings of 2017 IEEE 28th annual international symposium on personal, indoor, and mobile radio communications (PIMRC) (pp. 1–6).
Liang, H., Zhong, C., Lin, H., Suraweera, H. A., Qu, F., & Zhang, Z. (2017). Optimization of power beacon assisted wireless powered two-way relaying systems under user fairness. In IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM 2017) (pp. 1–6).
Park, J.-H., et al. (2017). Energy beamforming for wireless power transfer in MISO heterogeneous network with power beacon. IEEE Communications Letters, 21(5), 1163–1166.
Nguyen, T. D., Khan, J. Y., & Ngo, D. T. (2018). A distributed energy-harvesting-aware routing algorithm for heterogeneous IoT networks. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2(4), 1115–1127.
Nguyen, K. T., Do, D.-T., Nguyen, X. X., Nguyen, N. T., & Ha, D. H. (2015). Wireless information and power transfer for full duplex relaying networks: Performance analysis. In Proceedings of recent advances in electrical engineering and related sciences (AETA 2015) (pp. 53-62). Vietnam: HCMC.
Ying, L., Peilin, H., & Runzhou, L. (2018). Energy efficiency-delay tradeoff in energy harvesting-based D2D communication: An experimental learning approach. IEEE Communications Letters, 22, 1704–1707.
Calvo-Fullana, M., Anton-Haro, C., Matamoros, J., & Ribeiro, A. R. (2018). Stochastic routing and scheduling policies for energy harvesting communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 66, 3363–3376.
Nguyen, X.-X., & Do, D.-T. (2017). Maximum harvested energy policy in full-duplex relaying networks with SWIPT. International Journal of Communication Systems (Wiley), 30(17), e3359.
Fan, R., Atapattu, S., Chen, W., Zhang, Y., & Evans, J. (2018). Throughput maximization for multi-hop decode-and-forward relay network with wireless energy harvesting. IEEE Access, 6, 24582–24595.
Singh, K., Meng-Lin, K., Jia-Chin, L., & Ratnarajah, T. (2018). Toward optimal power control and transfer for energy harvesting amplify-and-forward relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 17, 4971–4986.
Ma, Y., Chen, H., Lin, Z., Li, Y., & Vucetic, B. (2015). Distributed and optimal resource allocation for power beacon-assisted wireless powered communications. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 63(10), 3569–3583.
Bi, S., & Zhang, R. (2016). Placement optimization of energy and information access points in wireless powered communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(3), 2351–2364.
Asadi, A., Wang, Q., & Mancuso, V. (2014). A survey on device-to-device communication in cellular networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 16(4), 1801–1819.
Krikidis, I., Timotheou, S., Nikolaou, S., Zheng, G., Ng, D. W. K., & Schober, R. (2014). Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer in modern communication systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(11), 104–110.
Lin, Y. D., & Hsu, Y. C. (2000). Multihop cellular: A new architecture for wireless communications. Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, 3, 1273–1282.
Atat, R., Liu, L., Mastronarde, N., & Yi, Y. (2017). Energy harvesting-based D2D-assisted machine-type communications. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 65(3), 1289–1302.
Atapattu, S., & Evans, J. (2016). Optimal energy harvesting protocols for wireless relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(8), 5789–5803.
Jiang, L., et al. (2016). Social-aware energy harvesting device-to-device communications in 5G networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 23(4), 20–27.
Wijesiri, G. P., Chowdhury, S. S., & Li, F. Y. (2016). Energy harvesting-aware backoff algorithms for distributed device-to-device communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE VTC (pp. 1–5).
Zhou, Z., Ma, G., Xu, C., & Chang, Z. (2016). A game-theoretical approach for green power allocation in energy-harvesting device-to-device communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE VTC (pp. 1–5).
Darak, S. J., Zhang, H., Palicot, J., & Moy, C. (2015). An efficient policy for D2D communications and energy harvesting in cognitive radios: Go Bayesian! In 2015 23rd European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 1231–1235). Nice: EUSIPCO.
Sun, H. Z. P., Shin, K. G., & He, L. (2017). Transmit power control for D2D-underlaid cellular networks based on statistical features. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(5), 4110–4119.
Zhong, C., Chen, X., Zhang, Z., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2015). Wireless-powered communications: Performance analysis and optimization. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 63(12), 5178–5190.
Shi, L., et al. (2018). Wireless energy transfer enabled D2D in underlaying cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(2), 1845–1849.
Le, S.-P. et. al. (2018). Device-to-device network with MISO scheme for wireless power transfer: Outage performance analysis. In Proceedings of the 41st international conference on telecommunications and signal processing (TSP) (pp. 464–467).
Gradshteyn, I. S., & Ryzhik, I. M. (2007). Table of integrals, series and products (7th ed.). New York, NY: Academic Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Proof of Proposition 2
We denote two new variables \(A = {{{{\left| g \right| }^2}} \over {{{\left| {g_c} \right| }^2} + {\varPsi _1}}}\) and \(B = {\left| {\left| {\mathbf{h}} \right| } \right| ^2}{P \over {{N_0}}}\). It can be shown the SINR as below
We first examine the outage probability as following expression
It can be shown the outage probability as [36]
Such expression can be re-calculated as
And then we obtain new expression as
We only examine the special case of the PB where is equipped with large number of antenna which result in simple following result
As a result, to clear evaluate outage performance, we can be obtain the closed-form expression as
This is end of proof.\(\square\)
Proof of Proposition 3
Having a look on the outage probability in CDD SISO mode, it can be given by
We first define new variables as \(x = {\left| h \right| ^2}{\left| g \right| ^2},y = {\left| {g_c} \right| ^2}\), conditioned on y, the outage probability can be computed as
Utilizing the popular result in [1, 3], the CDF of x can be shown as
To this end, averaging over y, the desired result can be obtained as in Proposition 3.
This completes the proof.\(\square\)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, HP., Le, CB., Do, DT. et al. Power Beacon-Based Wireless Power Transfer in MISO/SISO: An Application in Device-to-Device Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 110, 381–402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06733-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06733-z