Abstract
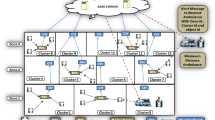
The internet of things (IoT) is one of the emerging network paradigms that are reducing the distance between the physical and cyber world. In wireless sensor Network (WSN)-assisted IoT, hundreds to thousands of sensor nodes are deployed at a large scale, which in turn increases the complexity. Therefore, the issues and challenges of such network differ from WSN. The sensor nodes are an important component of WSN-Assisted IoT network running on limited and non-rechargeable energy resource. So, developing robust and energy-efficient routing protocol is a challenging task to prolong the network lifetime. In contrast to the state-of-the-art techniques this paper introduces: (1) a hierarchical cluster framework for network deployment; (2) an effective Relay Node (RN) selection scheme by considering the following parameters: node density in the cluster, shortest distance node selection as a RN, RN communication range as threshold distance for next RN selection; (3) an efficient routing algorithm to meet the requirement of proposed model. The proposed protocol has been compared with standard WSN routing protocols, viz., LEACH, MOD-LEACH, ME-CBCCP, EESAA, TDEEC, DEEC, and SEP. By extensive simulation for various network parameters, the proposed effective relay node selection for energy efficient consumption protocol found to be more effective in terms of network lifetime, energy consumption and supports scalability.



























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balaji, S., Nathani, K., & Santhakumar, R. (2019). IoT technology, applications and challenges: a contemporary survey. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06407-w.
Jelicic, V., Magno, M., Brunelli, D., Paci, G., & Benini, L. (2013). Context-adaptive multimodal wireless sensor network for energy-efficient gas monitoring. IEEE Sensors Journal,13(1), 328–338.
Dener, M. (2018). A new energy efficient hierarchical routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications,101(1), 269–286.
Huang, J., Meng, Y., Gong, X., Liu, Y., & Duan, Q. (2014). A novel deployment scheme for green internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal,1(2), 196–205.
Shen, W., & Wu, Q. (2011). Exploring redundancy in sensor deployment to maximize network lifetime and coverage. In Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc communications and networks (SECON), 2011 8th annual IEEE communications society conference on (pp. 557–565). IEEE.
Li, F., Luo, J., Wang, W., & He, Y. (2015). Autonomous deployment for load balancing k-surface coverage in sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,14(1), 279–293.
Li, F., Luo, J., Xin, S. Q., Wang, W. P., & He, Y. (2012). LAACAD: Load balancing k-area coverage through autonomous deployment in wireless sensor networks. In Distributed computing systems (ICDCS), 2012 IEEE 32nd international conference on (pp. 566–575). IEEE.
Rani, S., Malhotra, J., & Talwar, R. (2013). EEICCP—energy efficient protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless sensor network,5(07), 127.
Rani, S., Malhotra, J., & Talwar, R. (2014). Energy efficient protocol for densely deployed homogeneous network. In Issues and challenges in intelligent computing techniques (ICICT), 2014 international conference on (pp. 292–298). IEEE.
Xu, M., & Leung, H. (2011). A joint fusion, power allocation and delay optimization approach for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal,11(3), 737–744.
Lee, J. S., & Cheng, W. L. (2012). Fuzzy-logic-based clustering approach for wireless sensor networks using energy predication. IEEE Sensors Journal,12(9), 2891–2897.
Majumder, R., Bag, G., & Kim, K. H. (2012). Power sharing and control in distributed generation with wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid,3(2), 618–634.
Ye, W., Heidemann, J., & Estrin, D. (2002). An energy-efficient MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. In INFOCOM 2002, Twenty-First annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies. Proceedings. IEEE (Vol. 3, pp. 1567–1576). IEEE.
Cardei, M., Thai, M. T., Li, Y., & Wu, W. (2005). Energy-efficient target coverage in wireless sensor networks. In INFOCOM 2005, 24th annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies. Proceedings IEEE (Vol. 3, pp. 1976–1984). IEEE.
Liu, C., & Cao, G. (2012). Distributed critical location coverage in wireless sensor networks with lifetime constraint. In INFOCOM, 2012 proceedings IEEE (pp. 1314–1322). IEEE.
Rani, S., Talwar, R., Malhotra, J., Ahmed, S. H., Sarkar, M., & Song, H. (2015). A novel scheme for an energy efficient internet of things based on wireless sensor networks. Sensors,15(11), 28603–28626.
Mohamed, R. E., Saleh, A. I., Abdelrazzak, M., & Samra, A. S. (2018). Survey on wireless sensor network applications and energy efficient routing protocols. Wireless Personal Communications,101(2), 1019–1055.
Kapnadak, V., & Coyle, E. J. (2011). Optimal non-uniform deployment of sensors for detection in single-hop wireless sensor networks. In Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc communications and networks (SECON), 2011 8th annual IEEE communications society conference on (pp. 89–97). IEEE.
Xu, X., Ansari, R., & Khokhar, A. (2013). Power-efficient hierarchical data aggregation using compressive sensing in WSNs. In 2013 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 1769–1773). IEEE.
Yang, D., Misra, S., Fang, X., Xue, G., & Zhang, J. (2012). Two-tiered constrained relay node placement in wireless sensor networks: computational complexity and efficient approximations. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing,11(8), 1399–1411.
Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In System sciences, 2000. Proceedings of the 33rd annual Hawaii international conference on (p. 10). IEEE.
Manap, Z., Ali, B. M., Ng, C. K., Noordin, N. K., & Sali, A. (2013). A review on hierarchical routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications,72(2), 1077–1104.
Aslam, M., Javaid, N., Rahim, A., Nazir, U., Bibi, A., & Khan, Z. A. (2012). Survey of extended LEACH-based clustering routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. In High performance computing and communication and 2012 IEEE 9th international conference on embedded software and systems (HPCC-ICESS), 2012 IEEE 14th international conference on (pp. 1232–1238). IEEE.
Buttyán, L., & Schaffer, P. (2010). Position-based aggregator node election in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,6(1), 679205.
Jung, S. M., Han, Y. J., & Chung, T. M. (2007). The concentric clustering scheme for efficient energy consumption in the PEGASIS. In Advanced communication technology, The 9th international conference on (Vol. 1, pp. 260–265). IEEE.
Saini, P., & Sharma, A. K. (2010). Energy efficient scheme for clustering protocol prolonging the lifetime of heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Computer Applications,6(2), 30–36.
Shah, T., Javaid, N., & Qureshi, T. N. (2012). Energy efficient sleep awake aware (EESAA) intelligent sensor network routing protocol. In Multitopic conference (INMIC), 2012 15th international (pp. 317–322). IEEE.
Smaragdakis, G., Matta, I., & Bestavros, A. (2004). SEP: A stable election protocol for clustered heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Boston University Computer Science Department.
Loscri, V., Morabito, G., & Marano, S. (2005). A two-levels hierarchy for low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy (TL-LEACH). In Vehicular technology conference, 2005. VTC-2005-Fall. 2005 IEEE 62nd (Vol. 3, pp. 1809–1813). IEEE.
Kumar, D., & Patel, R. B. (2011). Multi-hop data communication algorithm for clustered wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,7(1), 984795.
Younis, O., & Fahmy, S. (2004). HEED: a hybrid, energy-efficient, distributed clustering approach for ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing,3(4), 366–379.
Yueyang, L., Hong, J., & Guangxin, Y. (2006). An energy-efficient PEGASIS-based enhanced algorithm in wireless sensor networks. China Communications, 91–97.
Lee, S., Yoo, J., & Chung, T. (2004). Distance-based energy efficient clustering for wireless sensor networks. In Local computer networks, 2004. 29th annual IEEE international conference on (pp. 567–568). IEEE.
Dehghani, S., Barekatain, B., & Pourzaferani, M. (2018). An enhanced energy-aware cluster-based routing algorithm in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications,98(1), 1605–1635.
Mahmood, D., Javaid, N., Mahmood, S., Qureshi, S., Memon, A. M., & Zaman, T. (2013). MODLEACH: a variant of LEACH for WSNs. In Broadband and wireless computing, communication and applications (BWCCA), 2013 Eighth international conference on (pp. 158–163). IEEE.
Muruganathan, S. D., Ma, D. C., Bhasin, R. I., & Fapojuwo, A. O. (2005). A centralized energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Magazine,43(3), S8–13.
Ye, M., Li, C., Chen, G., & Wu, J. (2005). EECS: an energy efficient clustering scheme in wireless sensor networks. In Performance, computing, and communications conference, 2005. IPCCC 2005. 24th IEEE international (pp. 535–540). IEEE.
Dehni, L., Krief, F., & Bennani, Y. (2006). Power control and clustering in wireless sensor networks. In Challenges in Ad Hoc networking (pp. 31–40). Springer, Boston, MA.
Rani, S., Malhotra, J., & Talwar, R. (2014). On the development of realistic cross layer communication protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Sensor Network,6(05), 57.
Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,1(4), 660–670.
Hussain, S., Matin, A. W., & Islam, O. (2007). Genetic algorithm for hierarchical wireless sensor networks. JNW,2(5), 87–97.
Bara’a, A. A., & Khalil, E. A. (2012). A new evolutionary based routing protocol for clustered heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Applied Soft Computing,12(7), 1950–1957.
Mittal, V., Gupta, S., & Choudhury, T. (2018). Comparative analysis of authentication and access control protocols against malicious attacks in wireless sensor networks. In Smart computing and informatics (pp. 255–262). Springer, Singapore.
Han, Z., Wu, J., Zhang, J., Liu, L., & Tian, K. (2014). A general self-organized tree-based energy-balance routing protocol for wireless sensor network. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science,61(2), 732–740.
Chang, J. H., & Tassiulas, L. (2000). Energy conserving routing in wireless ad-hoc networks. In INFOCOM 2000, Nineteenth annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies. Proceedings. IEEE (Vol. 1, pp. 22–31). IEEE.
Solaiman, B. (2016). Energy optimization in wireless sensor networks using a hybrid k-means pso clustering algorithm. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences,24(4), 2679–2695.
Deniz, F., Bagci, H., & Korpeoglu, I. (2016). An adaptive, energy-aware and distributed fault-tolerant topology-control algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks,44, 104–117.
Islam, K., Shen, W., & Wang, X. (2012). Wireless sensor network reliability and security in factory automation: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews),42(6), 1243–1256.
Yildiz, H. U., Temiz, M., & Tavli, B. (2015). Impact of limiting hop count on the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Letters,19(4), 569–572.
Amjad, M., Afzal, M. K., Umer, T., & Kim, B. S. (2017). QoS-aware and heterogeneously clustered routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access,5, 10250–10262.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, A., Tripathi, S. An Effective Relay Node Selection Technique for Energy Efficient WSN-Assisted IoT. Wireless Pers Commun 112, 2611–2641 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07167-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07167-8