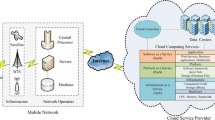
Abstract
In the existing environment, 30% of the base station has to handle the 70% of the network load. For a fact, the installation of additional base radio stations increases the deployment costs. The Computing Improved Aggregator Node B (CIANB) has been introduced for the 5G vehicular environment to fix this issue. The CIANB is the base radio station which consists of virtual cloud, storage space, and Aggregator Node B (ANB) pool. This paper discusses the forthcoming infrastructure, such as CIANB, which is progressing towards its innovation in the 5G vehicular environment. The CIANB and virtual ANB instance have been introduced in this paper to reduce congestion and to maximize the utilization of services without interruption. The evaluation metrics justify that the forthcoming infrastructure, CIANB, and virtual ANB greatly enhances the efficiency of the 5G vehicular environment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Yu, R., & Xie, S. (2015). Integrated energy and spectrum harvesting for 5G wireless communications. IEEE Network, 29(3), 75–81.
Hossain, E., & Hasan, M. (2015). 5G cellular: Key enabling technologies and research challenges. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 18(3), 11–21.
Akyildiz, I. F., Lina, S.-C., & Wang, P. (2015). Wireless software-defined networks (W-SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) for 5G cellular systems: An overview and qualitative evaluation. Computer Networks, 93, 66–79.
Nguyen, V.-G., Do, T.-X., & Kim, Y. H. (2016). SDN and virtualization-based LTE mobile network architectures: A comprehensive survey. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(3), 1401–1438.
Dharanyadevi, P., & Venkatalakshmi, K. (2016). Proficient routing by adroit algorithm in 5G-Cloud-VMesh network. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2016, 89.
Sunitha, C., & Anithadevi, M. (2016). Cloud-assisted safety message dissemination in hybrid vehicular network. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 4(3), 4513–4519.
Nithyavathi, K., Vigneshwaran, K., & Sumithra, S. (2016). A gateway selection algorithm in a hybrid clustered VANET-LTE advanced network. International Journal of Advanced Research in Biology Engineering Science and Technology (IJARBEST), 2(6), 37–44.
Mohsen, M., Nasr, M., Mohamed, A., Abdelgader, S., Wang, Z.-G., & Shen, L.-F. (2016). VANET clustering based routing protocol suitable for deserts. Sensors (Basel), 6(4), 1–12.
Mer, S. B. (2015). Smart vehicle-to-vehicle communication with 5G technology. International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication, 3(5), 3241–3244.
Prasan, D., & Murugappan, S. (2016). An analysis on vehicular ad-hoc networks: Research issues, challenges and applications. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 11(6), 4569–4575.
Kulkarni, A., Gupta, P., & Avhad, K. (2016). Distance and priority based routing protocol in VANET. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 5(7), 13931–13935.
Wubben, D., Rost, P., Bartelt, J. S., Lalam, M., Savin, V., Gorgoglione, M., Dekorsy, A., & Fettweis, G. (2014). Benefits and impact of cloud computing on 5G signal processing: Flexible centralization through cloud-RAN. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 31(6), 35–44.
Checko, A., Christiansen, H. L., Yan, Y., Scolari, L., Kardaras, G., Berger, M. S., & Dittmann, L. (2015). Cloud RAN for mobile networks—A technology overview. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(1), 405–426.
NTT DOCOMO. (2016, August). R3-161687, Draft TR 38.801 (v030) Study on new radio access technology: Radio access architecture and interfaces. NTT DOCOMO, INC (Rapporteur), 3GPP TSG RAN3.
Small Cell Forum. (2016, January). Document 159.07.02, Small cell virtualization functional splits and use cases. Small Cell Forum.
He, Z., Cao, J., & Liu, X. (2016). SDVN: Enabling rapid network innovation for heterogeneous vehicular communication. IEEE Network, 30(4), 10–15.
Salahuddin, M. A., Al-Fuqaha, A., & Guizani, M. (2015). Software-defined networking for RSU clouds in support of the internet of vehicles. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2(2), 133–144.
Dharanyadevi, P., & Venkatalakshmi, K. (2015). Potent gateway selection algorithm for integrated 3G-VMesh milieu. World Applied Sciences Journal, ISSN: 1818-4952, 33(7), 1228–1233.
Dharanyadevi, P., & Venkatalakshmi, K. (2017). Persuasive gateway and eNB selection algorithm for 4G-VMesh network. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, ISSN: 1991-8178, 11(11), 118–121.
Kim, C., & Kim, K.-I. (2019). IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), USA
Papcun, P., Kajati, E., Cupkova, D., Mocnej, J., Miskuf, M., & Zolotova, I. (2019). Edge-enabled IoT gateway criteria selection and evaluation. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 32(13), 219.
Abboud, S., El Rachkidy, N., Guitton, A., & Safa, H. (2019, April) Gateway selection for downlink communication in LoRaWAN. IEEE WCNC 2019, IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference 2019, Apr Marrakech, Morocco.
Agyapong, P. K., Iwamura, M., Staehle, D., Kiess, W., & Benjebbour, A. (2014). Design considerations for a 5G network architecture. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52, 65–75.
Gupta, A., & Jha, R. K. (2015). Survey of 5G network: Architecture and emerging technologies. IEEE Access, 3, 1206–1232.
Guerzoni, R., Trivisonno, R., & Soldani, D. (2014). SDN-based architecture and procedures for 5G networks. In 1st International Conference on 5G for Ubiquitous Connectivity (5GU) (pp. 204–209). New York: IEEE.
Nam, H. (2015). Intelligent content delivery over wireless via SDN. In IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC): Track 4 - Services, Applications, and Business (pp. 2185–2190). New York: IEEE.
Ameigeiras, P., Ramos-Munoz, J. J., Schumacher, L., Prados-Garzon, J., Navarro-Ortiz, J., & Lopez-Soler, J. M. (2015). Link-level access cloud architecture design based on SDN for 5G networks. IEEE Network, 29(2), 24–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dharanyadevi, P., Krishnan, V. Effectual Computing Enhanced Aggregator Node B for 5G Vehicular Milieu. Wireless Pers Commun 117, 623–636 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07890-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07890-2