Abstract
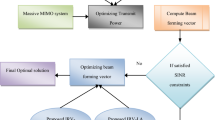
Massive multiple-input multiple output (mMIMO) is considered as one of the most in demand and innovative technologies for the fifth-generation wireless communication systems. This paper attempts to frame a mMIMO system model, intends to improve the spectral efficiency, energy efficiency and performance gain. Here, the system performance achievements are premeditated in a multi-cell downlink mMIMO system under the core considerations such as “imperfect channel estimation, perfect channel estimation and the effect of interference among cells due to pilot sequences contamination”. The performance gains such as “spatial multiplexing gain, array gain and spatial diversity gain” are considered to maximize in this paper. For attaining this multi-objective function, an improved meta-heuristic algorithm called rider optimization algorithm (ROA) known as trial-based ROA adopted, and analyse the performance of the proposed model by comparing over existing models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paulraj, A. J., Gore, D. A., Nabar, R. U., & Bolcskei, H. (2004). An overview of MIMO communications - a key to gigabit wireless. Proceedings of the IEEE, 92(2), 198–218.
Xing, C., Ma, S., & Zhou, Y. (2015). Matrix-monotonic optimization for MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 63(2), 334–348.
Marzetta, T. L. (2010). Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(11), 3590–3600.
Zhang, J., Wen, C., Jin, S., Gao, X., & Wong, K. (2013). On capacity of large-scale MIMO multiple access channels with distributed sets of correlated antennas. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(2), 133–148.
Yin, H., Gesbert, D., Filippou, M., & Liu, Y. (2013). A coordinated approach to channel estimation in large-scale multiple-antenna systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 31(2), 264–273.
Ma, Z., Zhang, Z. Q., Ding, Z. G., Fan, P. Z., & Li, H. C. (2015). Key techniques for 5G wireless communications: network architecture, physical layer, and MAC layer perspectives. Science China Information Sciences, 58(4), 1–20.
Padarti, V. K., & Rao, N. V. (2020). (2020) Adaptive SOICAF algorithm for PAPR mitigation in OFDM systems. Wireless Personal Communication, 113, 927–943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07260-y
Yang, A., He, Z., Xing, C., Fei, Z., & Kuang, J. (2016). The role of large-scale fading in uplink massive MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(1), 477–483.
Alouini, M., & Goldsmith, A. (1997). Area spectral efficiency of cellular mobile radio systems. In 1997 IEEE 47th Vehicular Technology Conference (vol. 2). Technology in Motion, Phoenix, AZ, USA (pp. 652–656).
Zhang, L., Yang, H., & Hasna, M. O. (2014). Generalized area spectral efficiency: An effective performance metric for green wireless communications. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 62(2), 747–757.
Fei, Z. S., Ding, H. C., Xing, C. W., Ni, J. Q., & Kuang, J. M. (2014). Performance analysis for range expansion in heterogeneous networks. Science China Information Sciences, 57(8), 1–10.
Yang, J., Fan, P., Duong, T. Q., & Lei, X. (2011). Exact performance of two-way AF relaying in Nakagami-m fading environment. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(3), 980–987.
Zhang, H., Xing, H., Cheng, J., Nallanathan, A., & Leung, V. C. M. (2016). Secure resource allocation for OFDMA two-way relay wireless sensor networks without and with cooperative jamming. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 12(5), 1714–1725.
Cui, H., Song, L., & Jiao, B. (2014). Multi-pair two-way amplify-and-forward relaying with very large number of relay antennas. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(5), 2636–2645.
Dai, Y., & Dong, X. (2016). Power allocation for multi-pair massive MIMO two-way AF relaying with linear processing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(9), 5932–5946.
Ngo, H. Q., Suraweera, H. A., Matthaiou, M., & Larsson, E. G. (2014). Multipair full-duplex relaying with massive arrays and linear processing. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(9), 1721–1737.
Zhao, L., Zheng, K., Long, H., Zhao, H., & Wang, W. (2014). Performance analysis for downlink massive multiple-input multiple-output system with channel state information delay under maximum ratio transmission precoding. IET Communications, 8(3), 390–398.
Zheng, L., & Tse, D. N. C. (2003). Diversity and multiplexing: a fundamental tradeoff in multiple-antenna channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 49(5), 1073–1096.
Shi, C., Qiu, W., Wang, F., Salous, S. & Zhou, J. (2019). Power control scheme for spectral coexisting multistatic radar and massive MIMO communication systems under uncertainties: A robust Stackelberg game model. Digital Signal Processing. Available online, 15 May 2019.
Saba, J., & Yu, L. (2016). Analysis and evaluation of performance gains and tradeoffs for massive MIMO systems. Applied Sciences, 6, 268.
Hao, W., Zeng, M., Chu, Z., & Yang, S. (2017). Energy-efficient power allocation in millimeter wave massive MIMO with non-orthogonal multiple access. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 6(6), 782–785.
Yang, J., Wang, H., Ding, J., Gao, X., & Ding, Z. (2017). Spectral and energy efficiency analysis for massive MIMO multi-pair two-way relaying networks under generalized power scaling. Science China Information Sciences.
Xin, Y., Wang, D., Li, J., Zhu, H., Wang, J., & You, X. (2016). Area spectral efficiency and area energy efficiency of massive MIMO cellular systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(5), 3243–3254.
Panda, S. (2018). Performance optimization of cell-free massive MIMO system with power control approach. AEU—International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 97, 210–219.
Roshandeh, K. P., Kuhestani, A., Ardakani, M., & Tellambura, C. (2017). Ergodic sum rate analysis and efficient power allocation for a massive MIMO two-way relay network. IET Communications, 11(2), 211–217.
Cui, Q., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Xie, W., & Zhao, Y. (2018). Multi-pair massive MIMO amplify-and-forward relaying system with low-resolution ADCs: Performance analysis and power control. Science China Information Sciences
Padarti, V. K., & Rao, N. V. (2020). Adaptive SOICAF algorithm for PAPR mitigation in OFDM systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 113, 927–943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07260-y.
Gao, X., Dai, L., Han, S., I, C.-L., & Heath, R. W. (2016). Energy-efficient hybrid analog and digital precoding for mmWave MIMO systems with large antenna arrays. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34(4), 998–1009.
Binu, D. & Kariyappa, B. S. (2018) RideNN: A new rider optimization algorithm-based neural network for fault diagnosis in analog circuits. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement.
Pedersen, M. E. H., & Chipperfield, A. J. (2010). Simplifying particle swarm optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 10(2), 618–628.
Mirjalili, S., Mirjalili, S. M., & Lewis, A. (2014). Grey wolf optimizer. Advances in Engineering Software, 69, 46–61.
Boothalingam, R. (2018). Optimization using lion algorithm: A biological inspiration from lion’s social behavior. Evolutionary Intelligence, 11(1–2), 31–52.
Nimmagadda, S. M. (2020). Optimal spectral and energy efficiency trade-off for massive MIMO technology: analysis on modified lion and grey wolf optimization. Soft Comput, 24, 12523–12539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04690-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nimmagadda, S.M. Enhancement of Efficiency and Performance Gain of Massive MIMO System Using Trial-Based Rider Optimization Algorithm. Wireless Pers Commun 117, 1259–1277 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07921-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07921-y