Abstract
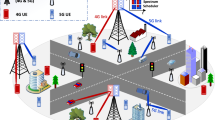
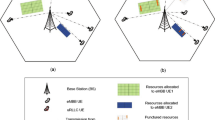
Heterogeneous networks are used to meet both capacity and coverage demands in a cellular network. As the frequencies are reused due to the limited spectrum availability, there exists co-channel interference (CCI) between the high power and low power nodes in such networks apart from the CCI between high power nodes. Inter cell interference coordination (ICIC) is a big challenge towards heterogeneous network deployments since users located at the cell range expansion (CRE) area are more vulnerable to stronger interference caused by the signals from the high power nodes. To enhance capacity, achieve good user experience and improve spectral efficiency interference management techniques like fractional frequency reuse (FFR) with enhanced scheduling strategies and ICIC using expectation maximization algorithm are proposed to mitigate the effects of the CCI. The resource allocation in FFR is done for the users in the cell center (full reuse) and CRE (partial reuse) regions based on the optimum post processing signal to interference plus noise ratio threshold with different schedulers in the two regions. It is shown that a particular combination shows the best throughput performance for the proposed enhanced FFR scheme.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engel, J. (1969). The effects of cochannel interference on the parameters of a small-cell mobile telephone system. IEEE Transactions on vehicular technology, 18(3), 110–116.
Schoenen, R., Teijeiro, C., & Bultmann, D. (2010). System level performance evaluation of LTE with MIMO and relays in reuse-1 IMT-advanced scenarios. In 2010 6th International conference on wireless communications networking and mobile computing (WiCOM), IEEE, pp. 1–5.
Mahadevappa, R. H., & Proakis, J. G. (2002). Mitigating multiple access interference and intersymbol interference in uncoded CDMA systems with chip-level interleaving. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 781–792.
Soret, B., Wang, H., Pedersen, K. I., & Rosa, C. (2013). Multicell cooperation for LTE-advanced heterogeneous network scenarios. IEEE Wireless Communications, 20(1), 27–34.
Trabelsi, N., Roullet, L., & Feki, A. (2014). A generic framework for dynamic EICIC optimization in LTE heterogeneous networks. In 2014 IEEE 80th vehicular technology conference (VTC2014-Fall), IEEE, pp. 1–6.
Saquib, N., Hossain, E., & Kim, D. I. (2013). Fractional frequency reuse for interference management in LTE-advanced HETNETS. IEEE Wireless Communications, 20(2), 113–122.
Bilios, D., Bouras, C., Kokkinos, V., Papazois, A., & Tseliou, G. (2012). A performance study of fractional frequency reuse in OFDMA networks. In 2012 5th Joint IFIP wireless and mobile networking conference (WMNC), IEEE, pp. 38–43
Qamar, F., Dimyati, K. B., Hindia, M. N., Noordin, K. A. B., & Al-Samman, A. M. (2017). A comprehensive review on coordinated multi-point operation for LTE-A. Computer Networks, 123, 19–37.
Ali, E., Ismail, M., Nordin, R., & Abdulah, N. F. (2017). Beamforming techniques for massive MIMO systems in 5g: Overview, classification, and trends for future research. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 18(6), 753–772.
Sawahashi, M., Kishiyama, Y., Morimoto, A., Nishikawa, D., & Tanno, M. (2010). Coordinated multipoint transmission/reception techniques for LTE-advanced [coordinated and distributed MIMO. IEEE Wireless Communications, 17(3), 26–34.
Lopez-Perez, D., Guvenc, I., De la Roche, G., Kountouris, M., Quek, T. Q., & Zhang, J. (2011). Enhanced intercell interference coordination challenges in heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wireless communications, 18(3), 22–30.
Zhang, H., Chen, S., Li, X., Ji, H., & Du, X. (2015). Interference management for heterogeneous networks with spectral efficiency improvement. IEEE Wireless Communications, 22(2), 101–107.
Abdullahi, S. U., Liu, J., & Mohadeskasaei, S. A. (2019). Efficient resource allocation with improved interference mitigation in FFR-aided OFDMA heterogeneous networks. Journal of Electronic Science and Technology, 17(1), 73–89.
Noliya, A., & Kumar, S. (2020). Performance analysis of resource scheduling techniques in homogeneous and heterogeneous small cell LTE—A networks. In Wireless personal communications, pp. 1–30.
Kawser, M. T., Farid, H., Hasin, A. R., Sadik, A. M., & Razu, I. K. (2012). Performance comparison between round robin and proportional fair scheduling methods for LTE. International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, 2(5), 678–681.
Yadav, A., & Dobre, O. A. (2018). All technologies work together for good: A glance at future mobile networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 25(4), 10–16.
Boaz, J. V., & Palanichamy, Y. (2016). Interference mitigation techniques using receiver processing and resource allocation. Circuits and Systems, 7(10), 2893–2903.
Mehlführer, C., Ikuno, J. C., Šimko, M., Schwarz, S., Wrulich, M., & Rupp, M. (2011). The Vienna LTE simulators-enabling reproducibility in wireless communications research. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2011(1), 29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veancy, B.J., Yogesh, P. Fractional Frequency Reuse with Enhanced Scheduling Strategies. Wireless Pers Commun 117, 2541–2553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07993-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07993-w