Abstract
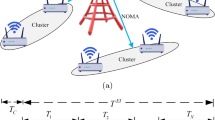
In this paper, we derive and optimize the total throughput of non orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) with energy harvesting. The source S harvests energy from radio frequency signal received from node A. The source uses the harvested energy to transmit data to N NOMA users classified using instantaneous or average power of channel gains. We optimize the powers allocated to NOMA users and harvesting duration to maximize the total throughput. We also derive packet waiting time and total delays for all NOMA users. We optimize powers allocated to NOMA users and harvesting duration to minimize a combination of total delays of all users. Our results are valid for Nakagami channels with arbitrary positions of users.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material (data transparency):
Data and material are not available.
References
Li, Q. C., Niu, H., Papathanassiou, A. T., & Wu, G. (2014). 5G network capacity: Key elements and technologies. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 9(1), 71–78.
Saito, Y., Benjebbour, A., Kishiyama, Y., & Nakamura, T. (2013). System- level performance evaluation of downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA). In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium Personal, Indoor Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), pp. 611–615.
Ding, Z., Peng, M., & Poor, H. V. (2015). Cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access in 5G systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(8), 1462–1465.
Ding, Z., Dai, H., & Poor, H. V. (2016). Relay selection for cooperative NOMA. IEEE Communications Letters, 5(4), 416–419.
Men, J., & Ge, J. (2015). Non-orthogonal multiple access for multiple-antenna relaying networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(10), 1686–1689.
Niu, Y., Gao, C., Li, Y., Su, L., & Jin, D. (2016). Exploiting multi-hop relaying to overcome blockage in directional mmwave small cells. Journal of Communications and Networks, 18(3), 364–374.
Kim, J. B., & Lee, I. H. (2015). Non-orthogonal multiple access in coordinated direct and relay transmission. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(11), 2037–2040.
Zhong, C., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Non-orthogonal multiple access with co- operative full-duplex relaying. IEEE Communications Letters, 20(12), 2478–2481.
Liu, Y., Ding, Z., Elkashlan, M., & Poor, H. V. (2016). Cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34(4), 938–953.
Varshney, L. (2008). Transporting information and energy simultaneously. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Toronto, Canada, pp. 1612–1616.
Sun, H., Zhou, F., Hu, R. Q., & Hanzo, L. (2019). Robust beamforming design in a NOMA cognitive radio network relying on SWIPT. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 37(1), 142–155.
Liu, Y., Ding, Z., Elkashlan, M., & Yuan, J. (2016). Non-orthogonal multiple access in large-scale underlay cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(12), 10152–10157.
Bhattacharjee, S., Acharya, T., & Bhattacharya, U. (2018). NOMA inspired multicasting in cognitive radio networks. IET Communications, 12(15), 1845–1853.
Zhou F., Chu Z., Sun, H., & Leung, V. C. M. (2018). Resource allocation for secure MISO-NOMA cognitive radios relying on SWIPT. In IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 1–6.
Liu, M., Song, T., & Gui, G. (2018). Deep cognitive perspective: Resource allocation for NOMA based heterogeneous IoT with imperfect SIC. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(2), 2885–2894.
Xu, L., Zhou, Y., Wang, P., & Liu, W. (2018). Max–Min resource allocation for video transmission in NOMA-based cognitive wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 66(11), 5804–5813.
Manglayev, T., Kizilirmak, R., Caglar, K., & Yau, H. (2018). GPU accelerated successive interference cancellation for NOMA uplink with user clustering. Wireless Personal Communications, 103, 2391–2400.
Panda, S. (2020). Joint user patterning and power control optimization of MIMO-NOMA systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 112, 2557–2573.
Le, T. A., & Kong, H. Y. (2020). Effects of hardware impairment on the cooperative NOMA EH relaying network over Nakagami-m fading channels. Wireless Personal Communications, Online Published November.
Reddy, B. S. K. (2020). Experimental validation of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) technique using software defined radio. Wireless Personal Communications, Online Published November.
Withers, C. S., & Nadarajah, S. (2013). On the product of gamma random variables. Quality & Quantity, 47, 545–552.
Xi, Y., Burr, A., Wei, J. B., & Grace, D. (2011). A general upper bound to evaluate packet error rate over quasi-static fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(5), 1373–1377.
Proakis, J. (2007). Digital communications (5th ed.). New York: Mac Graw-Hill.
Vaughan, R. J., & Venables, W. N. (1972). Permanent expressions for order statistics densities. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 34, 308–310.
Chan, W. C., Lu, T. C., & Chen, R. J. (1997). Pollaczek–Khinchin formula for the M/G/1 queue in discrete time with vacations. IEE Proceedings-Computers and Digital Techniques, 144(4), 222–226.
Funding
This publication received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors’ contributions: The paper is the contribution of Prof. Nadhir Ben Halima and Prof. Hatem Boujemaa.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest for this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Halima, N., Boujemaa, H. Optimal Power Allocation and Harvesting Duration for NOMA Systems in the Presence of Nakagami Channels. Wireless Pers Commun 118, 1793–1819 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08116-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08116-9