Abstract
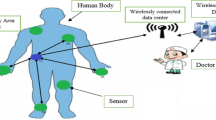
The medical enhancements have been improved to increase the life span of mankind. High penetration of Wireless Sensor Network in medical field helped the doctors to diagnose the patience in accurate manner and prescribe the medicines accordingly. In this modern Era, many people have permanent implant like face maker and it is life threatening to keep changing this body enhancement and it is need to have a system in place to increase the functionality of the Wireless Body Sensors. The important parameter which drags the battery energy and reduces its life span is path loss, and transmission loss. This paper proposes enhanced life time improvement for wireless body sensor networks using optimal clustering and advanced path selection protocol in short Energy Proficient Reliable Multi-hop Routing protocol. The EPMR designed in two stages, the first stage start with the collection of data from all body sensors is done through optimal clustering technique based Modified Conditional Spider Optimization (M-CSO) which avoids continuous individual transmission of data by the sensing nodes to base station in multi- hop distance (this stage the transmission loss is eliminated or reduced) hence the protocol concentrate to reduce transmission losses and the second stage implements the discovery of distance is done through by deploying Modified Flower Bee Algorithm (M-FBA), this stage the protocol finds best suitable and shortest next node to transmit the data. The finding of this paper is simulated using Math lab Simulink and verified through Network Simulator – 2 (NS-2) tools for validation and real time implementation of the results. The result obtained by this proposed method suggests that it has enhanced the sensor life term in many folds in comparisons with existing methodologies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashok, R., & Agrawal, D. (2003). Computing practices - Next-generation wearable networks. Computer, 36(11), 31–39.
Patel, M., & Wang, J. (2010). Applications, challenges, and prospective in emerging body area networking technologies. IEEE Wireless Communication, 17(1), 80–88.
Su, H., & Zhang, X. (2009). Battery-dynamics driven tdma mac protocols for wireless body-area monitoring networks in healthcare applications. IEEE Journal Select Areas Communication, 27(4), 424–434.
Manfredi, S. (2014). Congestion control for differentiated healthcare service delivery in emerging heterogeneous wireless body area networks. IEEE Wireless Communication, 21(2), 81–90.
He, Y., Zhu, W., & Guan, L. (2011). Optimal resource allocation for pervasive health monitoring systems with body sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 10(11), 1558–1575.
Ghasemzadeh, H., Loseu, V., Ostadabbas, S., & Jafari, R. (2010). Burst communication by means of buffer allocation in body sensor networks: Exploiting signal processing to reduce the number of transmissions. IEEE Journal Select Areas Communication, 28(7), 1073–1082.
Zhang, X., Jiang, H., Zhang, L., Zhang, C., Wang, Z., & Chen, X. (2010). An Energy-efficient ASIC for wireless body sensor networks in medical applications. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 4(1), 11–18.
Rebeiz, E., Caire, G., & Molisch, A. (2012). Energy-delay tradeoff and dynamic sleep switching for bluetooth-like body-area sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 60(9), 2733–2746.
Robles, T., Kadelka, A., Velayos, H., Lappetelainen, A., Kassler, A., Hui Li, D., Mandato, J. Ojala., & Wegmann, B. (2001). QoS support for an all IP system beyond 3G. IEEE Communication Magazine, 39(8), 64–72.
Thotahewa, K., Khan, J., & Yuce, M. (2014). Power efficient ultra wide band based wireless body area networks with narrowband feedback path. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 13(8), 1829–1842.
Ghosh, A., Halder, A., & Dhar, A. (2012). A Variable RF carrier modulation scheme for ultralow power wireless body-Area Network. IEEE Systems Journal, 6(2), 305–316.
Abouei, J., Brown, J., Plataniotis, K., & Pasupathy, S. (2011). Energy efficiency and reliability in wireless biomedical implant Systems. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 15(3), 456–466.
Chang, J., & Ju, P. (2014). An energy-saving routing architecture with a uniform clustering algorithm for wireless body sensor networks. Future Generation Computer Systems, 35, 128–140.
Bader, A., Abed-Meraim, K., & Alouini, M. (2012). An efficient multi-carrier position-based packet forwarding protocol for wireless Sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(1), 305–315.
Sharma, S., & Jena, S. (2015). Cluster based multipath routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 45(2), 14–20.
S. Babaie, Ahmad Khadem Zadeh, Mehdi Golsorkhtabar Amiri, (2010). "The New Clustering Algorithm with Cluster Members bounds for energy dissipation avoidance in wireless sensor network", 2010 International Conference On Computer Design and Applications.
Elhabyan, R., & Yagoub, M. (2015). Two-tier particle swarm optimization protocol for clustering and routing in wireless sensor network. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 52, 116–128.
Du, T., Qu, S., Liu, F., & Wang, Q. (2015). An energy efficiency semi-static routing algorithm for WSNs based on HAC clustering method. Information Fusion, 21, 18–29.
Mahajan, S., Malhotra, J., & Sharma, S. (2014). An energy balanced QoS based cluster head selection strategy for WSN. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 15(3), 189–199.
M. Handy, M. Haase, D. Timmermann, "Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy with deterministic cluster-head selection", 4th International Workshop on Mobile and Wireless Communications Network.
Ren, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, K., & Shen, X. (2016). Adaptive and Channel-Aware detection of selective forwarding attacks in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(5), 3718–3731. https://doi.org/10.1109/twc.2016.2526601
Hacioglu, G., Kand, V. F. A., & Sesli, E. (2016). Multi objective clustering for wireless sensor networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 59, 86–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.016
Anwar, A., & Sridharan, D. (2018). A predictive routing algorithm for wbsn based on kalman filter iterations. IEEE Sensors Journal. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2018.2847049
Afsana, F., Asif-Ur-Rahman, M., Ahmed, M. R., Mahmud, M., & Kaiser, M. S. (2018). An energy conserving routing scheme for wireless body sensor nanonetwork communication. IEEE Access, 6, 9186–9200. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2789437C
DelBello, C., Raihan, K., & Zhang, T. (2015). Reducing energy consumption of mobile phones during data transmission and encryption for wireless body area network applications. Security and Communication Networks, 8(17), 2973–2980. https://doi.org/10.1002/sec.1223
Chen, D.-R., Hsu, C.-C., Chen, M.-Y., & Guo, C.-F. (2018). A power-aware 2-covered path routing for wireless body area networks with variable transmission ranges. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 118, 379–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2017.08.006
Kaur, N., & Singh, S. (2017). Optimized cost effective and energy efficient routing protocol for wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 61, 65–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2017.03.008
Khan, R., Mohammadani, K., Soomro, A., Hussain, J., Khan, S., Arain, T., & Zafar, H. (2018). An energy efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 99(4), 1443–1454.
Sangeetha Priya, N., Sasikala, R., Alavandar, S., & Bharathi, L. (2018). Security aware trusted cluster based routing protocol for wireless body sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 102(4), 3393–3411.
Bhangwar, A., Kumar, P., Ahmed, A., & Channa, M. (2017). Trust and thermal aware routing protocol (ttrp) for wireless body area networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 97(1), 349–364.
Rangi, S., Vashist, S., & Chakarvarti, Prof(Dr)SK. . (2016). A review on wireless body area network (wban) for health monitoring system: Implementation protocols. Communications on Applied Electronics., 4, 16–20. https://doi.org/10.5120/cae2016652130
Raja Basha, A., & Yaashuwanth, C. (2019). Optimal partial aggregation based energy delay compromise technique for wireless sensor network. IETE Journal of Research, 65(6), 855–871. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2018.1464966
Basha, A. R., & Yaashuwanth, C. (2020). Double secure optimal partial aggregation using trust inference and hybrid syncryption algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 15(2), 423–436. https://doi.org/10.1166/jctn.2018.7106
Zuhra, F. T., Bakar, K. A., Ahmed, A., & Tunio, M. A. (2017). Routing protocols in wireless body sensor networks: A comprehensive survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 99, 73–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2017.10.002
Ullah, F., Abdullah, A., Kaiwartya, O., & Arshad, M. (2017). Traffic priority-aware adaptive slot allocation for medium access control protocol in wireless body area network. Computers, 6(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers6010009
Razzaque, M. A., Hira, M. T., & Dira, M. (2017). QoS in body area networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 13(3), 1–46. https://doi.org/10.1145/3085580
Culpepper, B. J., Dung, L., & Moh, M. (2004). Design and analysis of Hybrid Indirect transmissions (HIT) for data gathering in wireless micro sensor networks. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review., 8, 61–83.
Sharma, S., Agarwal, P., & Jena, S. K. (2013). Energy Aware Multipath Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Nabendu Chaki, Natarajan Meghanathan, & Dhinaharan Nagamalai (Eds.), Computer Networks & Communications (NetCom) (pp. 753–60). New York: Springer.
Coello, C. A. (2000). An updated survey of GA-based multiobjective optimization techniques. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 32, 109–143.
Esmaeili, H., & Minaei Bidgoli, B. (2018). EMRP: Evolutionary-based multi-hop routing protocol for wireless body area networks. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 93, 63–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basha, A.R., Manoharan, H. Enhanced Life Time Improvement for Wireless Body Sensor Networks using Optimal Clustering and Advanced Path Selection Protocol. Wireless Pers Commun 119, 2123–2146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08322-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08322-5