Abstract
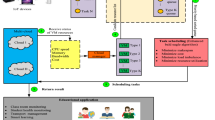
The Cloud-IoT framework offers on-demand service for numerous applications with the aid of data gathered by IoT and the computing resources of cloud computing. The quality of service (QoS) degrades due to task-VM mismatch due to the heterogeneous service request from IoT devices. The tasks processed by an inappropriate VM may cause delay and affect the Quality of Service (QoS). The proposed task allocation and scheduling algorithm aim is to improve the QoS of education service offered by Cloud-IoT in an educational organisation. In the task allocation stage, task VM pairs are prioritized initially and task-VM pairs are selected based on the minimum of the expected completion time (ECT) with the approach named Priority Based Task Allocation and Buffering (PBTAB) Algorithm. In this stage, at each of the clouds, the selected task-VM pairs are placed on queues based on the proximal value of the MCT. In the scheduling stage, task-VM pair matching (T-VMBS) Algorithm schedules the task with the selection of the best of the VM from the total clouds to speed up the task execution. The PBTAB and T-VMBS algorithm achieved throughput performance of more than 90% with larger dataset and huge number of VM. The proposed approach achieved a decreased makespan of less than 50%. Similarly deadline violation rate and average reliability exhibited a better performance.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Díaz, M., Martín, C., & Rubio, B. (2016). State-of-the-art, challenges, and open issues in the integration of Internet of things and cloud computing. Journal of Network and Computer applications, 67, 99–117.
Zaslavsky AB, Perera C, Georgakopoulos D. (2012) Sensing as a service and big data. In: International conference on advances in cloud computing (ACC-2012). Bangalore, India, pp. 21–9.
Botta A, de Donato W, Persico V, Pescapé A. (2014) On the integration of cloud computing and internet of things. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on future internet of things and cloud (FiCloud-2014), Barcelona, Spain p. 27–9
Arunarani, A. R., Manjula, D., & Sugumaran, V. (2019). Task scheduling techniques in cloud computing: A literature survey. Future Generation Computer Systems, 91, 407–415.
Khambre, P. D., Deshpande, A., Mehta, A., & Saini, A. (2014). Modified pheromone update rule to implement ant colony optimization algorithm for workflow scheduling algorithm problem in grids. International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Technology, 2(2), 424–429.
Fahmy, M. M. (2010). A fuzzy algorithm for scheduling non-periodic jobs on soft realtime single processor system. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 1, 31–38.
Adhikary, T., Das, A. K., Razzaque, M. A., Almogren, A., Alrubaian, M., & Hassan, M. M. (2016). Quality of service aware reliable task scheduling in vehicular cloud computing. Mobile Networks and Applications, 21(3), 482–493.
Boveiri, H. R., Khayami, R., Elhoseny, M., & Gunasekaran, M. (2019). An efficient Swarm-Intelligence approach for task scheduling in cloud-based internet of things applications. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 10(9), 3469–3479.
Xavier, V. A., & Annadurai, S. (2019). Chaotic social spider algorithm for load balance aware task scheduling in cloud computing. Cluster Computing, 22(1), 287–297.
Hussain, A., Aleem, M., Khan, A., Iqbal, M. A., & Islam, M. A. (2018). RALBA: A computation-aware load balancing scheduler for cloud computing. Cluster Computing, 21(3), 1667–1680.
Panda, S. K., & Jana, P. K. (2018). Normalization-based task scheduling algorithms for heterogeneous multi-cloud environment. Information Systems Frontiers, 20(2), 373–399.
Rani, S., & Suri, P. K. (2018). An efficient and scalable hybrid task scheduling approach for cloud environment. International Journal of Information Technology, 12, 1451–1457.
Thirumalaiselvan, C., & Venkatachalam, V. (2019). A strategic performance of virtual task scheduling in multi cloud environment. Cluster Computing, 22(4), 9589–9597.
Lavanya, M., Shanthi, B., & Saravanan, S. (2020). Multi objective task scheduling algorithm based on SLA and processing time suitable for cloud environment. Computer Communications, 151, 183–195.
Guo, M., Guan, Q., Chen, Weiqi, Ji, F., & Peng, Z. (2019). Delay-optimal scheduling of VMs in a queueing cloud computing system with heterogeneous workloads. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2019.2920954
Rafieyan, E., Khorsand, R., & Ramezanpour, M. (2020). An adaptive scheduling approach based on integrated best-worst and VIKOR for cloud computing. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 140, 106272.
Bugingo, E., Zhang, D., Chen, Z., & Zheng, W. (2021). Towards decomposition based multi-objective workflow scheduling for big data processing in clouds. Cluster Computing, 24(1), 115–139.
Ghobaei-Arani, M., Souri, A., Safara, F., & Norouzi, M. (2020). An efficient task scheduling approach using moth-flame optimization algorithm for cyber-physical system applications in fog computing. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 31(2), e3770.
Jiao, J., Wang, L., Li, Y., Han, D., Yao, M., Li, K. C., & Jiang, H. (2021). CASH: Correlation-aware scheduling to mitigate soft error impact on heterogeneous multicores. Connection Science, 33(2), 113–135.
Keshanchi, B., Souri, A., & Navimipour, N. J. (2017). An improved genetic algorithm for task scheduling in the cloud environments using the priority queues: Formal verification, simulation, and statistical testing. Journal of Systems and Software, 124, 1–21.
Abualigah, L., & Diabat, A. (2020). A novel hybrid antlion optimization algorithm for multi-objective task scheduling problems in cloud computing environments. Cluster Computing, 24, 1–19.
Tripathi, G., & Ahad, M. A. (2019). IoT in education: An integration of educator community to promote holistic teaching and learning. In J. Nayak, A. Abraham, B. M. Krishna, G. T. C. Sekhar, & A. K. Das (Eds.), Soft computing in data analytics (pp. 675–683). Singapore: Springer.
Abdel-Basset, M., Manogaran, G., Mohamed, M., & Rushdy, E. (2019). Internet of things in smart education environment: Supportive framework in the decision-making process. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 31(10), e4515.
Uskov, V., Pandey, A., Bakken, J.P. and Margapuri, V.S., Smart engineering education: The ontology of Internet-of-Things applications. In: 2016 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) (2016) pp. 476–481.
Panda, S.K., & Jana, P.K. An efficient task scheduling algorithm for heterogeneous multi-cloud environment. In: Third International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications & Informatics, IEEE, pp. 1204–1209.
Panda, S. K., & Jana, P. K. (2015). Efficient task scheduling algorithms for heterogeneous multi-cloud environment. The Journal of Supercomputing, 71(4), 1505–1533.
Panda, S. K., Gupta, I., & Jana, P. K. (2019). Task scheduling algorithms for multi-cloud systems: Allocation-aware approach. Information Systems Frontiers, 21(2), 241–259.
Funding
There is no funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have participated in writing the manuscript and have revised the final version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhary, S.K., Rao, A.L.N. QoS Enhancement in Cloud-IoT Framework for Educational Institution with Task Allocation and Scheduling with Task-VM Matching Approach. Wireless Pers Commun 121, 267–286 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08634-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08634-6