Abstract
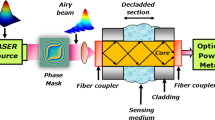
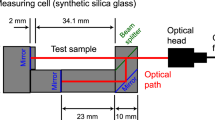
This paper demonstrates the Refractive Index (RI) sensing characteristics of the proposed evanescent wave absorbance (EWA) sensor in reflective mode. The end reflective-EWA (ER-EWA) sensor is fabricated using Tollens’ reagent for depositing silver (Ag) layer throughout the length of sensing region and to fabricate in-line reflective mirror at the end of sensing probe. The fabricated ER-EWA sensor measures changes in RI of seawater sample with a sensitivity of 48.036 arbitrary unit per RI unit (a.u./RIU) in the range of 1.332 RIU to 1.344 RIU. The proposed sensor is further analyzed for its sensitivity towards changes in salinity at constant turbidity and variation in turbidity at constant salinity values. By validating the functionality of the proposed ER-EWA sensor against commercial sensors, accuracies for salinity and turbidity measurements are obtained as 98.1791% and 93.5737%, respectively. This proves the potential of the proposed ER-EWA sensor in real time monitoring of ocean parameters such as salinity and turbidity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- a.u.:
-
Arbitrary unit
- BBLS:
-
Broad-band light source
- CTD:
-
Conductivity-temperature-depth
- ER-EWA:
-
End reflective-evanescent wave absorbance
- EWA:
-
Evanescent wave absorbance
- FBG:
-
Fiber Bragg grating
- FNU:
-
Formazin Nephelometric unit
- HF:
-
HydroFluoric acid
- PSU:
-
Practical salinity unit
- RI:
-
Refractive Index
- RIU:
-
Refractive Index unit
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- SLM:
-
Skip length model
- SMF:
-
Single mode fiber
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
- TR:
-
Tollens’ reagent
- αm :
-
Bulk absorption coefficient of medium
- Ag:
-
Silver
- AgNO3 :
-
Silver nitrate
- C6H12O6 :
-
Glucose
- C:
-
Concentration of aquatic medium
- dc :
-
Core diameter
- dBm:
-
Decibel per milliwatt
- Δ:
-
Displacement
- Γ:
-
Evanescent wave absorption coefficient
- KOH:
-
Potassium Hydroxide
- λi :
-
Wavelength of incident light
- La :
-
Absorption length
- LA :
-
Overall absorption length
- Li :
-
Interaction length
- Ls :
-
Skip length
- M:
-
Molarity
- mS:
-
MilliSiemens
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- nc :
-
Refractive index of fiber core
- nm :
-
Refractive index of aquatic medium
- Nm:
-
Nanometer
- P(0):
-
Power transmitted through optical fiber in the absence of medium under analysis
- rc :
-
Fraction of total guided power confined within sensing region
- SnCl2 :
-
Stannous chloride
- Μm:
-
Micrometer
- θi :
-
Angle of incidence at the interface of fiber core and medium under analysis
- θl :
-
Launching angle of optical signal inside fiber core
- θr :
-
Angle of reflection from the interface of fiber core and medium under analysis
References
Hou, B. (2012). An optical solution for simultaneous in-situ sea water salinity and turbidity measurements (Doctoral dissertation).
Duarte, D. P., Nogueira, R. N., & Bilro, L. (2020). Turbidity and RI dependency of a polymer optical fiber-based chromatic sensor. Sensors, 20(1), 19.
Chen, J., Guo, W., Xia, M., Li, W., & Yang, K. (2018). In situ measurement of seawater salinity with an optical refractometer based on total internal reflection method. Optics express, 26(20), 25510–25523.
Kumari, C. U., Samiappan, D., Kumar, R., & Sudhakar, T. (2019). Fiber optic sensors in ocean observation: A comprehensive review. Optik, 179, 351–360.
Bin Omar, A. F., MatJafri, B., & Zubir, M. (2009). Turbidimeter design and analysis: A review on optical fiber sensors for the measurement of water turbidity. Sensors, 9(10), 8311–8335.
Sharma, A. K., Gupta, J., & Sharma, I. (2019). Fiber optic evanescent wave absorption-based sensors: A detailed review of advancements in the last decade (2007–18). Optik, 183, 1008–1025.
Hou, B., Grosso, P., & Le Menn, M. (2013). Principle and implementations of a refracto-nephelo-turbidimeter for seawater measurements. Optical Engineering, 52(4), 044402.
Kumari, C. U., Samiappan, D., Kumar, R., & Sudhakar, T. (2019). Development of a highly accurate and fast responsive salinity sensor based on Nuttall apodized Fiber Bragg Grating coated with hygroscopic polymer for ocean observation. Optical Fiber Technology, 53, 102036.
Lamb, D. W., Bunganaen, Y., Louis, J., Woolsey, G. A., Oliver, R., & White, G. (2004). Fibre evanescent field absorption (FEFA): An optical fibre technique for measuring light absorption in turbid water samples. Marine and Freshwater Research, 55(5), 533–543.
Yeoh, S., Matjafri, M. Z., Mutter, K. N., & Oglat, A. A. (2019). Plastic fiber evanescent sensor in measurement of turbidity. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 285, 1–7.
Pahurkar, V. G., Tamgadge, Y. S., Gambhire, A. B., & Muley, G. G. (2015). Evanescent wave absorption based polyaniline cladding modified fiber optic intrinsic biosensor for glucose sensing application. Measurement, 61, 9–15.
Tian, Y., Wang, W., Wu, N., Zou, X., & Wang, X. (2011). Tapered optical fiber sensor for label-free detection of biomolecules. Sensors, 11(4), 3780–3790.
Lou, J., Xu, H. Z., Xu, B., Huang, J., Li, B. C., & Shen, W. M. (2014). Fiber-optic evanescent wave sensor with a segmented structure. Applied Optics, 53(19), 4200–4205.
Gao, S. S., Qiu, H. W., Zhang, C., Jiang, S. Z., Li, Z., Liu, X. Y., Yue, W. W., Yang, C., Huo, Y. Y., Feng, D. J., & Li, H. S. (2016). Absorbance response of a graphene oxide coated U-bent optical fiber sensor for aqueous ethanol detection. RSC Advances, 6(19), 15808–15815.
Wang, J. N., & Luo, C. Y. (2012). Long-period fiber grating sensors for the measurement of liquid level and fluid-flow velocity. Sensors, 12(4), 4578–4593.
Kim, D. W., Zhang, Y., Cooper, K. L., & Wang, A. (2005). In-fiber reflection mode interferometer based on a long-period grating for external refractive-index measurement. Applied Optics, 44(26), 5368–5373.
Bremer, K., & Roth, B. (2015). Fibre optic surface plasmon resonance sensor system designed for smartphones. Optics Express, 23(13), 17179–17184.
Samavati, Z., Samavati, A., Ismail, A. F., Rahman, M. A., & Othman, M. H. D. (2018). Intensity modulated silver coated glass optical fiber refractive index sensor. Chinese Optics Letters, 16(9), 090602.
Messica, A., Greenstein, A., & Katzir, A. (1996). Theory of fiber-optic, evanescent-wave spectroscopy and sensors. Applied Optics, 35(13), 2274–2284.
Xiong, F. B., Zhu, W. Z., Lin, H. F., & Meng, X. G. (2014). Fiber-optic sensor based on evanescent wave absorbance around 2.7 μm for determining water content in polar organic solvents. Applied Physics B, 115(1), 129–135.
Bal, H. K., Brodzeli, Z., Dragomir, N. M., Collins, S. F., & Sidiroglou, F. (2012). Uniformly thinned optical fibers produced via HF etching with spectral and microscopic verification. Applied Optics, 51(13), 2282–2287.
Franz, G., Schamberger, F., Zare, H. H., Bröskamp, S. F., & Jocham, D. (2017). Bi-layer sandwich film for antibacterial catheters. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 8(1), 1982–2001.
Apriyanto, H., Ravet, G., Bernal, O. D., Cattoen, M., Seat, H. C., Chavagnac, V., & Sharp, J. H. (2018). Comprehensive modeling of multimode fiber sensors for refractive index measurement and experimental validation. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–13.
Austin, R. W., & Halikas, G. (1976). The index of refraction of seawater. Technical Report, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California.
Reef Edition, Refractometers And Salinity Measurement. http://www.reefedition.com/refractometers-salinity-measurement/. Accessed 3 April 2020
Sequeira, F., Duarte, D., Bilro, L., Rudnitskaya, A., Pesavento, M., Zeni, L., & Cennamo, N. (2016). Refractive index sensing with D- shaped plastic optical fibers for chemical and biochemical applications. Sensors, 16(12), 2119.
Kundu, T., Sai, V. V. R., Dutta, R., Titas, S., Kumar, P., & Mukherjee, S. (2010). Development of evanescent wave absorbance-based fibre-optic biosensor. Pramana, 75(6), 1099–1113.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Nano Research Center of SRM Institute of Science and Technology for helping in fabricating the proposed sensor. The authors also thank the authorities of the National Institute of Ocean Technology, Pallikaranai, Chennai for permitting to utilize commercial salinity and turbidity sensors to validate the proposed fiber optic sensor.
Funding
This work was supported by the Naval research Board, Defense Research and Development Organization, India [Grant number: NRB/4003/PG/405 and NRB-405/OEP/17–18]; and Selective Excellence Initiative, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, India [Grant number: SRMU/R/AR(A)/2015/126/1866].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uma Kumari, C.R., Kumar, R., Samiappan, D. et al. Development of a High Sensitive Refractive Index Sensor Based on Evanescent Wave Absorbance effect in Reflective Mode for Ocean Observation. Wireless Pers Commun 121, 411–427 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08643-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08643-5