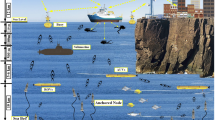
Abstract
In modern times, applications such as port security, navigation, tsunami alert, etc., need real-time data transfer in shallow waters. These applications require large data rates for multimedia communication between underwater nodes and base-station. Although wired networks provide large data rates, the wires would be an obstacle to moving objects in the water. Alternatively, wireless acoustic communication is used in deep water applications. Notably, in shallow water, radio frequency (RF) communication serves a higher data rate than acoustic but, suffers from less transmission range due to large attenuation. The objective of this research is to study the feasibility of RF propagation in shallow waters and analyze the requirements and challenges for RF-based shallow water wireless networks. A range enhancement technique for RF communication, multi-hop communication, is also surveyed and its challenges for shallow waters are discussed. In the oceans around the Indian subcontinent, the shallow water can be considered as a lossy-dielectric medium and the physical parameters affect the electrical properties. The conductivity of the water increases linearly with an increase in salinity and temperature though this rate is higher with the increase in salinity. The variation in conductivity, in turn, affects the attenuation and path loss. The path loss in Bay-of-Bengal is approximately 2% less than in the Arabian Sea which affects the performance of RF propagation. It is also observed that the RF communication range using a multi-hop technique can be increased up to 240 m in shallow water with a bit error rate of 10−2 at 1 Mbps data rate.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., Pompili, D., & Melodia, T. (2005). Underwater acoustic sensor networks: research challenges. Ad Hoc Networks, 3(3), 257–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2005.01.004.
Felemban, E., Shaikh, F. K., Qureshi, U. M., Sheikh, A. A., & Qaisar, S. B. (2015). Underwater Sensor Network Applications: A Comprehensive Survey. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks., 11(11), 896832. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/896832
Zhu, Q., Xiong, W., Liu, H., Zhu, Y., & Xie, G. (2016). A brief review of underwater electric current communication. In: IEEE 20th international conference on computer supported cooperative work in design (CSCWD). https://doi.org/10.1109/cscwd.2016.7566034
Sozer, E. M., Stojanovic, M., & Proakis, J. G. (2000). Underwater acoustic networks. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 25(1), 72–83. https://doi.org/10.1109/48.820738.
Awan, K. M., Shah, P. A., Iqbal, K., Gillani, S., Ahmad, W., & Nam, Y. (2019). Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks: A Review of Recent Issues and Challenges. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6470359
Demirors, E., Sklivanitis, G., Santagati, G. E., Melodia, T., & Batalama, S. N. (2018). A high-rate software-defined underwater acoustic modem with real-time adaptation capabilities. IEEE Access, 6, 18602–18615. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2815026.
Zeng, Z., Fu, S., Zhang, H., Dong, Y., & Cheng, J. (2017). A survey of underwater optical wireless communications. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 19(1), 204–238. https://doi.org/10.1109/comst.2016.2618841.
Hanson, F., & Radic, S. (2008). High bandwidth underwater optical communication. Applied Optics, 47(2), 277. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.47.000277.
Akyildiz, I. F., Wang, P., & Sun, Z. (2015). Realizing underwater communication through magnetic induction. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(11), 42–48. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcom.2015.7321970.
Tyler, R. H., Sanford, T. B., & Unsworth, M. J. (1998). Propagation of electromagnetic fields in the coastal ocean with applications to underwater navigation and communication. Radio Science, 33(4), 967–987. https://doi.org/10.1029/98rs00748.
Massaccesi, A., & Pirinoli, P. (2016). Analysis of underwater EM propagation for scuba diving communication systems. In: 10th European conference on antennas and propagation (EuCAP)https://doi.org/10.1109/eucap.2016.7481224
Al-Shamma’a, A. I., Shaw, A., & Saman, S. (2004). Propagation of electromagnetic waves at MHz frequencies through seawater. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 52(11), 2843–2849. https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2004.834449
Shaw, A., Al-Shamma’a, A., & i., Wylie, S. R., & Toal, D. (2006). Experimental investigations of electromagnetic wave propagation in seawater. European Microwave Conference. https://doi.org/10.1109/eumc.2006.281456
Abdou, A. A., Shaw, A., Mason, A., Al-Shamma’a, A., Cullen, J., & Wylie, S. (2011). Electromagnetic (EM) wave propagation for the development of an underwater Wireless Sensor Network (WSN). 2011 IEEE SENSORS Proceedings https://doi.org/10.1109/icsens.2011.6127319
Akka, M. A., & Sokullu, R. (2015). Channel modeling and analysis for wireless underground sensor networks in water medium using electromagnetic waves in the 300–700 MHz range. Wireless Personal Communications, 84(2), 1449–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2697-3.
Park, D., Kwak, K., Kim, J., & Chung, W. K. (2016). 3D underwater localization scheme using EM wave attenuation with a depth sensor. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA)https://doi.org/10.1109/icra.2016.7487422
Bush, B. F., Tripp, V. K., & Naishadham, K. (2012). Practical modeling of radio wave propagation in shallow seawater. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE international symposium on antennas and propagation. https://doi.org/10.1109/aps.2012.6348625
Sendra, S., Lloret, J., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C., & Aguiar, J. M. (2013). Underwater wireless communications in freshwater at 2.4 GHz. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(9), 1794–1797. https://doi.org/10.1109/lcomm.2013.072313.131214.
Zoksimovski, A., Sexton, D., Stojanovic, M., & Rappaport, C. (2015). Underwater electromagnetic communications using conduction–channel characterization. Ad Hoc Networks, 34, 42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2015.01.017.
Qureshi, U., Shaikh, F., Aziz, Z., Shah, S., Sheikh, A., Felemban, E., & Qaisar, S. (2016). RF path and absorption loss estimation for underwater wireless sensor networks in different water environments. Sensors, 16(6), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16060890.
Jimenez, E., Quintana, G., Mena, P., Dorta, P., Perez-Alvarez, I., Zazo, S., & Quevedo, E. (2016). Investigation on radio wave propagation in shallow seawater: Simulations and measurements. IEEE Third Underwater Communications and NetworkingConference (UComms) https://doi.org/10.1109/ucomms.2016.7583453
Ganesh, P. S. S. P., & Venkataraman, H. (2019). RF-based multihop wireless communication for shallow underwater environment. In: 2019 International conference on wireless communications signal processing and networking (WiSPNET). https://doi.org/10.1109/wispnet45539.2019.9032810
Pavan Ganesh, P. S. S., & Venkataraman, H. (2020). E-CRUSE: energy-based throughput analysis for cluster-based RF shallow underwater communication. IET Communications,14(15), 2544–2553. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-com.2019.1294.
Che, X., Wells, I., Dickers, G., Kear, P., & Gong, X. (2010). Re-evaluation of RF electromagnetic communication in underwater sensor networks. IEEE Communications Magazine., 48(12), 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcom.2010.5673085
Mathew.N.O. Sadiku. . (2012). Principles of electromagnetics (p. 2012). India: Oxford University Press.
Ellison, W., Balana, A., Delbos, G., Lamkaouchi, K., Eymard, L., Guillou, C., & Prigent, C. (1998). New permittivity measurements of seawater. Radio Science., 33(3), 639–648. https://doi.org/10.1029/97rs02223
Stogryn, A. (1971). Equations for calculating the dielectric constant of saline water (Correspondence). IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques., 19(8), 733–736. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmtt.1971.1127617
Lang, R., Zhou, Y., Utku, C., & Le Vine, D. (2016). Accurate measurements of the dielectric constant of seawater at L band. Radio Science 51(1), 2–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015rs005776
Underwater RF modem video (2019). Accessed 2019-04-01. https://www.wfs-tech.com/product/seatooth-video/
Underwater RF modem- pipelogger (2019). https://www.wfs-tech.com/product/seatooth-pipelogger-temperature-1608005l/. Accessed 2019-04-01.
Underwater RF modem pipeloggerT1. (2019). Accessed 2019-04-01. https://www.wfs-tech.com/product/seatooth-pipelogger-t1-10-thermal-insulation-200m-1603009j/
Underwater RF modem S100 (2019). https://www.wfs-tech.com/product/seatooth-s100-1000m-controller-system-1-1546003/. Accessed 2019-04-01.
Underwater RF modem S400 (2019). https://www.wfs-tech.com/product/seatooth-s400-subsea-datalogger/. Accessed 2019-04-01.
Underwater RF modem SMSS (2019). https://www.wfs-tech.com/product/seatooth-subsea-motion-sensing-system/. Accessed: 2019-04-01.
Underwater RF modem Wips (2019). https://www.wfs-tech.com/product/seatooth-wireless-integrated-pressure-sensor-4000m-1603001j/. Accessed: 2019-04-01.
Heidemann, J., Stojanovic, M., & Zorzi, M. (2012). Underwater sensor networks: Applications, advances and challenges. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences., 370(1958), 158–175. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2011.0214
Aboderin, O., Inacio, S. ., Santos, H. M., Pereira, M. R., Pessoa, L. M., & Salgado, H. M. (2016). Analysis of J-Pole antenna configurations for underwater communications. OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey. https://doi.org/10.1109/oceans.2016.7761402
Sporer, M., Weigel, R., & Koelpin, A. (2014). Open-ended dielectric-filled waveguide antenna for underwater usage. In 2014 11th European radar conference https://doi.org/10.1109/eurad.2014.6991287
Alvertos, K. N., Karagianni, E. A., Vardakis, K. D., Mpountas, T. K., & Kaklamani, D. I. (2017). Bow-tie antenna for underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. In 2017 International workshop on antenna technology: Small antennas, innovative structures, and applications (iWAT) https://doi.org/10.1109/iwat.2017.7915391
Llamas, R. A., Niemeier, J. J., & Kruger, A. (2015). Curved spiral antennas for freshwater applications. In 2015 IEEE radio andwireless symposium (RWS). https://doi.org/10.1109/rws.2015.7129723
Inacio, S. I., Pereira, M. R., Santos, H. M., Pessoa, L. M., Teixeira, F. B., Lopes, M. J., & Salgado, H. M. (2016). Dipole antenna for underwater radio communications. In 2016 IEEE third underwater communications and networking conference (UComms) https://doi.org/10.1109/ucomms.2016.7583457
Deschamps de Paillette, T., Gaugue, A., Parlier, E., & Dardenne, S. (2017). Antenna design for underwater wireless telemetry systems. In 2017 11th European conference on antennas and propagation (EUCAP). https://doi.org/10.23919/eucap.2017.7928513
Yingying, Z., Xia, L., & Shiliang, F. (2011). Deployment analysis in two-dimensional underwater acoustic wireless sensor networks. In 2011 IEEE International conference on signal processing, communications and computing (ICSPCC). https://doi.org/10.1109/icspcc.2011.6061819
Ducrocq, T., Hauspie, M., Mitton, N., & Pizzi, S. (2014). On the impact of network topology on wireless sensor networks performances: Illustration with geographic routing. In 2014 28th International conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops. https://doi.org/10.1109/waina.2014.118
Shams, R., Khan, F. H., Amir, M., Otero, P., & Poncela, J. (2020). Critical analysis of localization and time synchronization algorithms in underwater wireless sensor networks: Issues and challenges. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07233-1
Ullah, I., Chen, J., Su, X., Esposito, C., & Choi, C. (2019). Localization and detection of targets in underwater wireless sensor using distance and angle based algorithms. IEEE Access., 7, 45693–45704. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2909133
Kim, B. S., Park, H., Kim, K. H., Godfrey, D., & Kim, K. I. (2017). A survey on real-time communications in wireless sensor networks. Hindawi: Wireless communications and mobile computing.
Zhang, Y., Xie, L., Chen, H., & Cui, J.-H. (2014). On the use of sliding LT code in underwater acoustic real-time data transfer with high propagation latency. 2014 Oceans - St. John’s.https://doi.org/10.1109/oceans.2014.7002982
Jiang, S. (2018). On reliable data transfer in underwater acoustic networks: A survey from networking perspective. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials., 20(2), 1036–1055. https://doi.org/10.1109/comst.2018.2793964
Aimtongkham, P., Nguyen, T. G., & So-In, C. (2018). Congestion control and prediction schemes using fuzzy logic system with adaptive membership function in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing., 2018, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6421717
Cui, Jun-Hong., Kong, Jiejun, Gerla, M., & Zhou, Shengli. (2006). The challenges of building scalable mobile underwater wireless sensor networks for aquatic applications. IEEE Network., 20(3), 12–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/mnet.2006.1637927
Guan, Q., Ji, F., Liu, Y., Yu, H., & Chen, W. (2019). Distance-vector-based opportunistic routing for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal., 6(2), 3831–3839. https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2019.2891910
Roy, A., & Sarma, N. (2018). Effects of various factors on performance of MAC protocols for underwater wireless sensor networks. Materials Today: Proceedings., 5(1), 2263–2274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.09.228
Fang, D., Li, Y., Huang, H., & Yin, L. (2010). A CSMA/CA-based MAC protocol for underwater acoustic networks. In 2010 International Conference on computational intelligence and software engineering https://doi.org/10.1109/wicom.2010.5601361
Cheng, Xilin, Fengzhong, Qu., & Yang, Liuqing. (2011). Single carrier FDMA over underwater acoustic channels. In 2011 6th International ICST conference on communications and networking in China (CHINACOM). https://doi.org/10.1109/chinacom.2011.6158311
Chen, K., Ma, M., Cheng, E., Yuan, F., & Su, W. (2014). A survey on MAC protocols for underwater wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials., 16(3), 1433–1447. https://doi.org/10.1109/surv.2014.013014.00032
Pompili, D., Melodia, T., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2009). A CDMA-based medium access control for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications., 8(4), 1899–1909. https://doi.org/10.1109/twc.2009.080195
Fan, G., Chen, H., Xie, L., & Wang, K. (2011). An improved CDMA-based MAC protocol for underwater acoustic wireless sensor networks. In 2011 7th international conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/wicom.2011.6040323
Alam, M. I. I., & Hossain, M. F. (2017). A TDMA based EM controlled multi-channel MAC protocol for underwater sensor networks. In 2017 International conference on electrical, computer and communication engineering (ECCE). https://doi.org/10.1109/ecace.2017.7912918
Venkataraman, H., Kalyampudi, P., & Muntean, G.-M. (2010). CASHeW: Cluster-based adaptive scheme for multimedia delivery in heterogeneous wireless networks. Wireless Personal Communications., 62(3), 517–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-010-0067-8
Abdel Hamid, S., Hassanein, H. S., & Takahara, G. (2013). Introduction to wireless multi-hop networks. Routing for wireless multi-hop networks. SpringerBriefs in Computer Science (pp. 1–9). New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6357-3_1
Venkataraman, H., Gandhi, D., & Tomar, V. (2013). Multi-hop multi-band intelligent relay-based architecture for LTE-advanced multi-hop wireless cellular networks. Wireless Personal Communications., 75(1), 131–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1352-0
Che, X., Wells, I., Kear, P., Dickers, G., Gong, X., & Rhodes, M. (2009). A static multi-hop underwater wireless sensor network using RF electromagnetic communications. In 2009 29th IEEE international conference on distributed computing systems workshops. https://doi.org/10.1109/icdcsw.2009.36
Che, X., Wells, I., Dickers, G., Kear, P., Gong, X., & Rhodes, M. (2009). Failure tolerance analysis of a small scale underwater sensor network with RF electromagnetic communications. In 2009 Third international conference on sensor technologies and applications. https://doi.org/10.1109/sensorcomm.2009.108
Sagar, . (2006). A pocket notebook on the ocean with reference to the waters around India. National Institute of Oceanography. Report
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganesh, P.S.S.P., Venkataraman, H. RF-based Wireless Communication for Shallow Water Networks: Survey and Analysis. Wireless Pers Commun 120, 3415–3441 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09068-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09068-w