Abstract
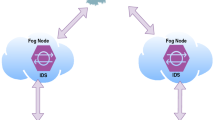
With the deployment of billions of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, more and more cyber attacks involving or even targeting such devices are rife. Cyberattack vectors are in constant evolvement in terms of diversity and complexity. Thus, to detect novel cyberattacks, we use anomaly-based techniques which model the expected behavior of the IoT device to identify occurrences of attacks. In this paper, we propose a new distributed and lightweight intrusion detection system (IDS). To provide efficient and accurate intrusion detection, the proposed IDS combines variational AutoEncoder and multilayer perceptron. The IDS operates within a two-layered fog architecture, an anomaly detector within fog node, and attack identification module within the cloud. The proposed approach is evaluated on two recent cyber attack datasets. The experimental results showed that the proposed system is able to characterize accurately the normal behavior within fog nodes, and detect different attack types such as DDoS attacks with high detection rate (\(99.98\%\)) and low false alarms rate (less than \(0.01\%\)). The proposed system outperforms other existing techniques in terms of detection and false positive rates.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaba, F. A., Othman, M., Hashem, I. A. T., & Alotaibi, F. (2017). Internet of things security: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 88, 10–28.
Yang, Y., Wu, L., Yin, G., Li, L., & Zhao, H. (2017). A survey on security and privacy issues in internet-of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(5), 1250–1258.
Sadeeq, M. A., Zeebaree, S. R., Qashi, R., Ahmed, S. H., & Jacksi, K. (2018, October). Internet of things security: A survey. In 2018 international conference on advanced science and engineering (ICOASE) (pp. 162-166). IEEE.
Atlam, H. F., Walters, R. J., & Wills, G. B. (2018). Fog computing and the internet of things: A review. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 2(2), 10.
Atlam, H. F., Alenezi, A., Alharthi, A., Walters, R., & Wills, G. Integration of cloud computing with internet of things: Challenges and open issues. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE international conference on internet of things (iThings) and IEEE green computing and communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, physical and social computing (CPSCom) and IEEE smart data (SmartData), Exeter, UK, 21-23 June 2017 (pp. 670-675).
Ai, Y., Peng, M., & Zhang, K. (2017). Edge cloud computing technologies for internet of things: A primer. Digital Communication Network in press.
Sudqi Khater, B., Abdul Wahab, A. W. B., Idris, M. Y. I. B., Abdulla Hussain, M., & Ahmed Ibrahim, A. (2019). A lightweight perceptron-based intrusion detection system for fog computing. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 178.
An, X., Lü, X., Yang, L., Zhou, X., & Lin, F. (2019). Node state monitoring scheme in fog radio access networks for intrusion detection. IEEE Access, 7, 21879–21888.
Hu, P., Dhelim, S., Ning, H., & Qiu, T. (2017). Survey on fog computing: Architecture, key technologies, applications and open issues. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 98, 27–42.
Ali, M. H., Al Mohammed, B. A. D., Ismail, A., & Zolkipli, M. F. (2018). A new intrusion detection system based on fast learning network and particle swarm optimization. IEEE Access, 6, 2025-5-20261
Abeshu, A., & Chilamkurti, N. (2018). Deep learning: The frontier for distributed attack detection in fog-to-things computing. IEEE Communications Magazine, 56(2), 169–175.
da Costa, K. A., Papa, J. P., Lisboa, C. O., Munoz, R., & de Albuquerque, V. H. C. (2019). Internet of things: A survey on machine learning-based intrusion detection approaches. Computer Networks, 151, 147–157.
Kim, J., Kim, J., Thu, H. L. T., & Kim, H. (2016, February). Long short term memory recurrent neural network classifier for intrusion detection. In 2016 International conference on platform technology and service (PlatCon) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Koroniotis, N., & Moustafa, N. (2020). Enhancing network forensics with particle swarm and deep learning: The particle deep framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.00722.
Hosseinpour, F., Vahdani Amoli, P., Plosila, J., Hämäläinen, T., & Tenhunen, H. (2016). An intrusion detection system for fog computing and IoT based logistic systems using a smart data approach. International Journal of Digital Content Technology and its Applications, 10.
An, X., Zhou, X., Lü, X., Lin, F., & Yang, L. (2018). Sample selected extreme learning machine based intrusion detection in fog computing and MEC. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018.
Diro, A. A., & Chilamkurti, N. (2018). Distributed attack detection scheme using deep learning approach for internet of things. Future Generation Computer Systems, 82, 761–768.
Peng, K., Leung, V., Zheng, L., Wang, S., Huang, C., & Lin, T. (2018). Intrusion detection system based on decision tree over big data in fog environment. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018.
An, X., Su, J., Lü, X., & Lin, F. (2018). Hypergraph clustering model-based association analysis of DDOS attacks in fog computing intrusion detection system. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2018(1), 1–9.
Illy, P., Kaddoum, G., Moreira, C. M., Kaur, K., & Garg, S. (2019, April). Securing fog-to-things environment using intrusion detection system based on ensemble learning. In 2019 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
Pacheco, J., Benitez, V. H., Félix-Herrán, L. C., & Satam, P. (2020). Artificial neural networks-based intrusion detection system for internet of things fog nodes. IEEE Access, 8, 73907–73918.
Almiani, M., AbuGhazleh, A., Al-Rahayfeh, A., Atiewi, S., & Razaque, A. (2020). Deep recurrent neural network for IoT intrusion detection system. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 101, 102031.
Krzysztoń, M., & Marks, M. (2020). Simulation of watchdog placement for cooperative anomaly detection in bluetooth mesh intrusion detection system. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 101, 102041.
Rahman, M. A., Asyharia, A. T., Leong, L. S., Satrya, G. B., Tao, M. H., & Zolkipli, M. F. (2020). Scalable machine learning-based intrusion detection system for IoT-enabled smart cities. Sustainable Cities and Society, 102324.
de Souza, C. A., Westphall, C. B., Machado, R. B., Sobral, J. B. M., & dos Santos Vieira, G. (2020). Hybrid approach to intrusion detection in fog-based IoT environments. Computer Networks, 107417.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980.
https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-backpropagation-algorithm-7bb3aa2f95fd
https://towardsdatascience.com/an-overview-of-monte-carlo-methods-675384eb1694
https://ieee-dataport.org/open-access/iot-network-intrusion-dataset
Stoian, N. A. (2020). Machine learning for anomaly detection in IoT networks: Malware analysis on the IoT-23 data set (Bachelor’s thesis, University of Twente).
Ullah, I., & Mahmoud, Q. H. (2021). Design and development of a deep learning-based model for anomaly detection in IoT networks. IEEE Access, 9, 103906–103926.
Dutta, V., Choras, M., Pawlicki, M., & Kozik, R. (2020). Detection of cyberattacks traces in IoT data. Journal of Universal Computer Science, 26(11), 1422–1434.
Hegde, M., Kepnang, G., Al Mazroei, M., Chavis, J. S., & Watkins, L. (2020, October). Identification of botnet activity in IoT network traffic using machine learning. In 2020 International conference on intelligent data science technologies and applications (IDSTA) (pp. 21-27). IEEE.
Booij, T. M., Chiscop, I., Meeuwissen, E., Moustafa, N., & den Hartog, F. T. (2021). ToN.IoT: The role of heterogeneity and the need for standardization of features and attack types in IoT network intrusion datasets. IEEE Internet of Things Journal.
Kozik, R., Pawlicki, M., & Choraś, M. (2021). A new method of hybrid time window embedding with transformer-based traffic data classification in IoT-networked environment. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 1-9.
Chunduri, H., Kumar, T. G., & Charan, P. S. (2021, February). A multi class classification for detection of IoT botnet malware. In International conference on computing science, communication and security (pp. 17-29). Cham: Springer.
Liu, Z., Thapa, N., Shaver, A., Roy, K., Yuan, X., & Khorsandroo, S. (2020, August). Anomaly detection on iot network intrusion using machine learning. In 2020 International conference on artificial intelligence, big data, computing and data communication systems (icABCD) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Acknowledgements
This research is a result from PRFU project C00L07UN23 0120180009 funded in Algeria by La Direction Générale de la Recherche Scientifique et du Développement Technologique (DGRSDT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labiod, Y., Amara Korba, A. & Ghoualmi, N. Fog Computing-Based Intrusion Detection Architecture to Protect IoT Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 125, 231–259 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09548-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09548-7