Abstract
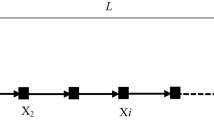
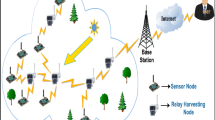
One of the applications of Sparse Linear Wireless Sensor Networks is environmental monitoring. In these networks, sensors are deployed in sensitive and strategic areas, such as highways and streets, to collect environmental data. Due to the long-term monitoring of the environment by the sensors and the lack of replacement of the energy source of the sensors, network lifetime is significantly reduced. Therefore, this paper presents the New Environment Monitoring Approach using Sparse Linear Wireless Sensor Networks (NEMA) for monitoring the environment using Dual Sinks. In the proposed NEMA method, static sensor nodes are scattered and equidistant from each other and monitor the environment. Due to being less, the number of sensor nodes relative to the area covered, data communication, and correlation are reduced. Therefore, the sensor nodes send the received packets to the destination without performing any data aggregation process. The proposed method was simulated in Simulator version 2 (NS-2). According to the criteria of average energy consumption, maximum waiting time, probability of sending data packets to the mobile sink node, average data packet delivery delay and network lifetime, the proposed method was compared with Classical approach 1 and Classical approach 2. The results obtained from the simulation data show the superiority of the proposed method over previous methods.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data availability can be accessed through the external portal.
References
Gupta, M., & Sinha, A. (2021). Distributed temporal data prediction model for wireless sensor network. Wireless Personal Communications, 65, 1–19.
Ifzarne, S., Hafidi, I., & Idrissi, N. (2021). Secure data collection for wireless sensor network in emerging trends in ICT for sustainable development. Cham: Springer.
Gallicchio, R., Scapicchio, D., Nardelli, A., Pellegrino, T., Prisco, M., Mainenti, P., & Storto, G. (2020). Assessment of residual radioactivity by a comprehensive wireless, wearable device in thyroid cancer patients undergoing radionuclide therapy and comparison with the results of a home device: a feasibility study. IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine, 9, 1–6.
Noori, M., & Ardakani, M. (2008). Characterizing the traffic distribution in linear wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 12, 554–556.
Karveli, T., Voulgaris, K., Ghavami, M., & Aghvami, A. H. (2009) "DiS-MAC: A MAC protocol for sensor networks used for roadside and highway monitoring," International Conference on Ultra Modern Telecommunications & Workshops, pp. 1–6, 2009.
Shokri, R., Yazdani, N., & Khonsari, A. (2007) "Chain-based anonymous routing for wireless ad hoc networks," IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, pp. 297–302, 2007.
Dutta, D. (2005). Data acquisition in multiple-sink sensor networks. Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 9, 82–85.
Wan, B.-T., & Zhang, W.-F. (2014). The lifetime optimization strategy of linear random wireless sensor networks based on mobile sink. International Conference on Wireless Communication and Sensor Network, 45, 258–261.
Borgia, E., Anastasi, G., & Conti, M. (2013). Energy efficient and reliable data delivery in urban sensing applications: A performance analysis. Computer Networks, 57, 3389–3409.
Alnuaimi, M., Shuaib, K., Alnuaimi, K., & Abed-Hafez, M. (2014) "Clustering in Wireless Sensor networks Based on Node Ranking," IEEE International Conference on Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, pp. 488–493.
Al Nuaimi, M., Shuaib, K., & Al Nuaimi, K. (2014) "Clustering in WSN Using Node Ranking with Hybrid Nodes Duty-Cycle and Energy Threshold," IEEE International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications, pp. 245–252.
Jawhar, M. Ammar, S. Zhang, J. Wu, and N. Mohamed, "Ferry-based linear wireless sensor networks," IEEE Global Communications Conference, pp. 304–309, 2013.
Tan, H. O., Korpeoglu, I., & Stojmenovi, I. (2011). Computing localized power-efficient data aggregation trees for sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22, 489–500. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2010.68
Vieira, M. A., Vieira, L. F., Ruiz, L. B., Loureiro, A. A. F., Fernandes, A. O., and Nogueira, J. M. S. (2003). Scheduling Nodes in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Voronoi Approach. Proceedings 28th Annual IEEE International Conference on Local Computer Networks - LCN 2003, Bonn/Konigswinter, Germany, 20–24 October 2003, 423–429. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LCN.2003.1243168
Xu, Y., Ding, O., Qu, R., & Li, K. (2018). Hybrid multi-objective evolutionary algorithms based on decomposition for wireless sensor network coverage optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 68, 268–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.03.053
Teng, R., Li, H. B., & Miura, R. (2017). Mobile base station with conformational selections for the network maintenance in wireless multihop infrastructure. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 28, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.3130
Kaswan, A., Nitesh, K., & Jana, P. K. (2017). Energy efficient path selection for mobile sink and data gathering in wireless sensor networks. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 73, 110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2016.12.005
Bettstetter, C., Hartenstein, H., & Pérez-Costa, X. (2004). Stochastic properties of the random waypoint mobility model. Wireless Networks, 10, 555–567. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WINE.0000036458.88990.e5
Anastasi, G., Conti, M., Di Francesco, M., & Passarella, A. (2009). Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Ad hoc networks, 7, 537–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2008.06.003
Anastasi, G., Conti, M., & Di Francesco, M. (2009). Reliable and energy-efficient data collection in sparse sensor networks with mobile elements. Performance Evaluation, 66, 791–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peva.2009.08.005z
Chao, C. M., & Hsiao, T. Y. (2014). Design of structure-free and energy-balanced data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 37, 229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2013.02.013
Anastasi, G., Conti, M., Di Francesco, M. & Passarella, A. (2006) "An adaptive and low-latency power management protocol for wireless sensor networks," ACM International Workshop on Mobility management and wireless access, pp. 67–74.
Younis, M., Youssef, M., & Arisha, K. (2003). Energy-aware management for cluster-based sensor networks. Computer Networks, 43, 649–668.
M. Younis, M. Youssef, and K. Arisha, "Energy-aware routing in cluster-based sensor networks," IEEE International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunications Systems, pp. 129–136, 2002.
Adams, W. F. (1936). Road traffic considered as a random series. Institution Civil Engineers J/UK/, 4, 121–130. https://doi.org/10.1680/ijoti.1936.14802
Cowan, R. J. (1975). Useful headway models. Transportation Research, 9, 371–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-1647(75)90008-8
Forbes, C., Evans, M., Hastings, N., & Peacock, B. (2011). Statistical distributions (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Zaki, G. F., Elsayed, H. M., Amer, H. H., and El-Soudani, M. S. (2009). Energy Balanced Model for Data Gathering in Wireless Sensor Networks with Fixed and Mobile Sinks. 2009 Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11 September 2009, 1–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCN.2009.5235358.
Heinzelman, W. B. (2000). Application-specific protocol architectures for wireless networks (Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology).
Hussein, A., El-Nakib, A., & Kishk, S. (2017). Energy-efficient linear wireless sensor networks applications in pipelines monitoring and control. Energy, 1, 6.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other supports was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pakdel, H., Jahanshahi, M. & Fotohi, R. An Approach to Environmental Monitoring in Sparse Linear Wireless Sensor Networks for Energy Conservation Using Dual Sinks. Wireless Pers Commun 126, 635–663 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09763-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09763-2