Abstract
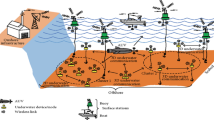
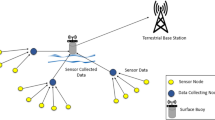
Autonomous underwater vehicle networks is a significant resource for aquatic life maintenance and monitoring underwater pollution. It is necessary to study the underwater localization algorithms which self-localize themselves. The proposed work concentrates only on the range-free localization model with a goal is to use only very few sensing nodes in the network with low cost and high battery power to self-localize themselves. Few beacon nodes have been used to localize the sensor nodes in the definite position of the network. Compressive sensing theory based on hop count information for localizing the sensor nodes has also been used for localization. This research aims to collect the connectivity information of all the nodes in the network with compressive sensing theory and improve the localization accuracy. The analysis presents that the proposed method works well with location accuracy. Compressive Sensing Node Localization reduces cost and enhances sensors' energy efficiency compared to other underwater localization algorithms.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Umamaheswari, S. (2021). Hybrid optimization model for energy efficient cloud assisted wireless sensor network. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-08048-w
Choudhary, M., & Goyal, N. (2022). Dynamic topology control algorithm for node deployment in mobile underwater wireless sensor networks. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6942
Nain, M., Goyal, N., Awasthi, L. K., & Malik, A. (2022). A range based node localization scheme with hybrid optimization for underwater wireless sensor network. International Journal of Communication Systems. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.5147
Rady, A., Shokair, M., El-Rabaie, E. S. M., & Sabor, N. (2021). Joint nodes and sink mobility based immune routing-clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-08066-8
Arunkumar, J. R., Anusuya, R., Rajan, M. S., & Prabhu, M. R. (2020). Underwater wireless information transfer with compressive sensing for energy efficiency. Wireless Personal Communications, 113(2), 715–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07249-7
Pacharaney, U. S., & Gupta, R. K. (2019). Clustering and compressive data gathering in wireless sensor network. Wireless Personal Communications, 109(2), 1311–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06614-5
Alwan, N. A., & Hussain, Z. M. (2019). Compressive sensing with chaotic sequences: An application to localization in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 105(3), 941–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06129-z
Randhawa, S., & Jain, S. (2017). Data aggregation in wireless sensor networks: Previous research, current status and future directions. Wireless Personal Communications, 97(3), 3355–3425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4674-5
Irshad, M., Liu, W., Wang, L., & Khalil, M. U. R. (2019). Cogent machine learning algorithm for indoor and underwater localization using visible light spectrum. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06631-4
Sahana, S., & Singh, K. (2020). Cluster based localization scheme with backup node in underwater wireless sensor network. Wireless Personal Communications, 110(4), 1693–1706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06807-y
Beniwal, M., Singh, R. P., & Sangwan, A. (2016). A localization scheme for underwater sensor networks without time synchronization. Wireless Personal Communications, 88(3), 537–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3175-2
Goyal, N., Dave, M., & Verma, A. K. (2019). Protocol stack of underwater wireless sensor network: Classical approaches and new trends. Wireless Personal Communications, 104(3), 995–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-6064-z
Goyal, N., Dave, M., & Verma, A. K. (2016). Energy efficient architecture for intra and inter cluster communication for underwater wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 89(2), 687–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3302-0
Krishnaswamy, V., & Manvi, S. S. (2019). Fuzzy and PSO based clustering scheme in underwater acoustic sensor networks using energy and distance parameters. Wireless Personal Communications, 108(3), 1529–1546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06483-y
Artemenko, O., & Mitschele-Thiel, A. (2013). Localization in wireless networks with post-improvement using estimation of distances between unknown nodes: Simulation and experimental evaluation. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 20, 268–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-013-0228-2
Prashar, D., & Jyoti, K. (2019). Distance error correction-based hop localization algorithm for wireless sensor network. Wireless Personal Communications, 106(3), 1465–1488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06225-0
Goyal, N., Dave, M., & Verma, A. K. (2020). SAPDA: Secure authentication with protected data aggregation scheme for improving QoS in scalable and survivable UWSNs. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07175-8
Pandey, S., & Varma, S. (2016). A range based localization system in multihop wireless sensor networks: A distributed cooperative approach. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(2), 615–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2948-3
Sekar, K., Suganya Devi, K., & Srinivasan, P. (2021). Energy efficient data gathering using spatio-temporal compressive sensing for WSNs. Wireless Personal Communications, 117, 1279–1295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07922-x
Lee, S., & Kim, K. (2012). Localization with a mobile beacon in underwater acoustic sensor networks. Sensors (Switzerland), 12(5), 5486–5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120505486
Wang, J., Urriza, P., Han, Y., & Cabric, D. (2011). Weighted centroid localization algorithm: Theoretical analysis and distributed implementation. IEEE Transactions on wireless communications, 10(10), 3403–3413. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2011.081611.102209
Wang, J., Gao, Y., Yin, X., Li, F., & Kim, H. J. (2018). An enhanced PEGASIS algorithm with mobile sink support for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9472075
Wang, P., Xue, F., Li, H., Cui, Z., Xie, L., & Chen, J. (2019). A multi-objective DV-Hop localization algorithm based on NSGA-II in internet of things. Mathematics, 7(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7020184
Dong, P., Qian, H., Wei, X., et al. (2013). A beacon-less geographic multipath routing protocol for ad hoc networks. Mobile Netw Appl, 18, 500–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-012-0427-6
Wang, J., Gao, Y., Liu, W., Sangaiah, A. K., & Kim, H. J. (2019). Energy efficient routing algorithm with mobile sink support for wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 19(7), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071494
Wahid, A., Lee, S., Kim, D., & Lim, K. S. (2014). MRP: A localization-free multi-layered routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks. Wireless personal communications, 77(4), 2997–3012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1690-6
Kumari, S., Mishra, P. K., & Anand, V. (2020). Integrated load balancing and void healing routing with cuckoo search optimization scheme for underwater wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 111, 1787–1803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06957-z
Singh, A., & Nagaraju, A. (2020). Low latency and energy efficient routing-aware network coding-based data transmission in multi-hop and multi-sink WSN. Ad Hoc Networks, 107, 102182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2020.102182
Sohn, I., Lee, J. H., & Lee, S. H. (2016). Low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy using affinity propagation for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 20(3), 558–561. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2517017
He, F. H., Yu, Z. J., & Liu, H. T. (2012). Multiple target localization via compressed sensing in wireless sensor networks. Dianzi Yu Xinxi Xuebao (Journal of Electronics and Information Technology), 34(3), 716–721.
Lin, Y., Tao, H., Tu, Y., & Liu, T. (2019). A node self-localization algorithm with a mobile anchor node in underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Access, 7, 43773–43780. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904725
Han, G., Zhang, C., Liu, T., & Shu, L. (2016). MANCL: A multi-anchor nodes collaborative localization algorithm for underwater acoustic sensor networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 16(6), 682–702. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcm.2561
Fazel, F., Fazel, M., & Stojanovic, M. (2011). Random access compressed sensing for energy-efficient underwater sensor networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 29(8), 1660–1670. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2011.110915
Yu, K., Hao, K., Li, C., Du, X., Wang, B., & Liu, Y. (2019, May). An improved TDoA localization algorithm based on AUV for underwater acoustic sensor networks. In International conference on artificial intelligence for communications and networks (pp. 419–434). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22968-9_38.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sachin Kumar Gupta and Nitin Goyal conceived the idea, designed the experiments and analysed the data; Madhumitha Kulandaive, Arulanand Natarajan performed the experiments and conducted the analysis; Sathiyamoorthi Velayutham and Ashutosh Srivastava analysed the methods, interpreted the results and drew the conclusions; Suresh P proofread the paper. All the authors agree with the above contribution details.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulandaivel, M., Natarajan, A., Velayutham, S. et al. Compressive Sensing Node Localization Method Using Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Network. Wireless Pers Commun 126, 2781–2799 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09841-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09841-5