Abstract
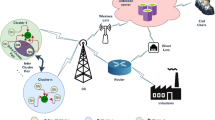
Wireless sensor networks occupy a prominent role in industrial as well as scientific applications. Lifetime enhancement and coverage are the major factors considered while designing the network. Various research models are evolved by considering the scheduling and routing process to solve the network lifetime issues. However, coverage and connectivity is another important factor that affects the lifetime of the remaining nodes. When a large number of sensors are deployed randomly, scheduling is preferred to enhance the network lifetime, but it leads to coverage issues. Other than scheduling, node damage, battery exhaustion, software and hardware failures might lead to coverage issues. Preserving the network connectivity while maximizing the network coverage is a crucial task in wireless sensor networks. To preserve the network connectivity and improve the wireless sensor networks coverage this research work presents a hybrid deep learning approach using a deep neural network and reinforcement learning algorithm. The Proposed model is experimentally verified and compared with conventional deep neural network and reinforcement learning algorithms to demonstrate the better balancing characteristics between network coverage and lifetime.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable—no new data generated.
References
Han, G., Liu, L., Jiang, J., Shu, L., & Hancke, G. (2017). Analysis of energy-efficient connected target coverage algorithms for industrial wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 13(1), 135–143.
Boukerche, A., & Sun, P. (2018). Connectivity and coverage based protocols for wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 80, 54–69.
Farsi, M., Elhosseini, M. A., Badawy, M., Ali, H. A., & Eldin, H. Z. (2019). Deployment techniques in wireless sensor networks, coverage and connectivity: A survey. IEEE Access, 7, 28940–28954.
Tripathi, A., Gupta, H. P., Dutta, T., Mishra, R., Shukla, K. K., & Jit, S. (2018). Coverage and connectivity in WSNs: A survey, research issues and challenges. IEEE Access, 6, 26971–26992.
Elhabyan, R., Shi, W., & St-Hilaire, M. (2019). Coverage protocols for wireless sensor networks: Review and future directions. Journal of Communications and Networks, 21(1), 45–60.
Chakraborty, S., Goyal, N. K., & Soh, S. (2020). On area coverage reliability of mobile wireless sensor networks with multistate nodes. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20(9), 4992–5003.
Suparna Chakraborty, N. K., & Goyal, S. S. (2019). A Monte-Carlo Markov chain approach for coverage-area reliability of mobile wireless sensor networks with multistate nodes. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 193, 1–14.
Qin, D., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., Feng, P., Ji, P., & Berhane, T. M. (2018). Study on connected target coverage algorithm for wireless sensor network. IEEE Access, 6, 69415–69425.
Yang, C., & Chin, K.-W. (2017). On nodes placement in energy harvesting wireless sensor networks for coverage and connectivity. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 13(1), 27–36.
Le Nguyen, P., Hanh, N. T., & Ji, Y. (2019). Node placement for connected target coverage in wireless sensor networks with dynamic sinks. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 59, 1–21.
Zishan, A. A., Karim, I., & Rahman, A. (2018). Maximizing heterogeneous coverage in over and under provisioned visual sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 124, 44–62.
Kibria, M. G., Nguyen, K., Villardi, G. P., Liao, W.-S., Ishizu, K., & Kojima, F. (2018). A stochastic geometry analysis of multiconnectivity in heterogeneous wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(10), 9734–9746.
Olasupo, T. O., & Otero, C. E. (2018). A framework for optimizing the deployment of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 15(3), 1105–1118.
Oroza, C. A., Zhang, Z., Watteyne, T., & Glaser, S. D. (2017). A machine-learning-based connectivity model for complex terrain large-scale low-power wireless deployments. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 3(4), 576–584.
Khalifa, B., Al Aghbari, Z., Khedr, A. M., & Abawajy, J. H. (2017). Coverage hole repair in WSNs using cascaded neighbor intervention. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(21), 7209–7216.
Sun, G., Liu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2017). A novel connectivity and coverage algorithm based on shortest path for wireless sensor networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 71, 1025–1039.
Gupta, H. P., Rao, S. V., & Venkatesh, T. (2016). Analysis of stochastic coverage and connectivity in three-dimensional heterogeneous directional wireless sensor networks. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 29, 38–56.
Senouci, M. R., & Mellouk, A. (2019). A robust uncertainty-aware cluster-based deployment approach for WSNs: Coverage, connectivity, and lifespan. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 146, 1–12.
Keshmiri, H., & Bakhshi, H. (2020). A new 2-phase optimization-based guaranteed connected target coverage for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20(13), 7472–7486.
Charr, J.-C., Deschinkel, K., & Hakem, M. (2020). Lifetime optimization for partial coverage in heterogeneous sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 107, 1–16.
Kabakulak, B. (2018). Sensor and sink placement, scheduling and routing algorithms for connected coverage of wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 86, 83–102.
Chakravarthi, S. S., & Kumar, G. H. (2020). Optimization of network coverage and lifetime of the wireless sensor network based on pareto optimization using non-dominated sorting genetic approach. Procedia Computer Science, 172, 225–228.
Hanh, N. T., Binh, H. T. T., & Palaniswami, M. S. (2019). An efficient genetic algorithm for maximizing area coverage in wireless sensor networks. Information Sciences, 488, 58–75.
Movassagh, M., & Aghdasi, H. S. (2017). Game theory based node scheduling as a distributed solution for coverage control in wireless sensor networks. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 65, 137–146.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrasekar, V., Bashar, A., Kumar, T.S. et al. Hybrid Deep Learning Approach for Improved Network Connectivity in Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 128, 2473–2488 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-10052-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-10052-1