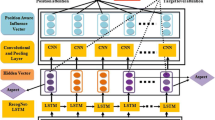
Abstract
The current digitalized world has emerged with the advances of big data, such as online learning, business, marketing, etc. So reviewing the customer opinion in each field is more critical in enabling smart services. Several neural models are implemented diversely to characterize the customer opinion from the gained review of the user or customer. But, those models have met some difficulties detecting the aspect terms and sentiment values. So, this proposed article has planned to design a novel Strawberry Deep Belief Neural Mechanism (SDBNM) to classify the aspect and sentiment values from the trained datasets. In addition, to evaluate the performance of the designed approach, three datasets are adopted: product, trip review, and Twitter data. Initially, after the data training process, the error is extracted from the database in the preprocessing model of SDBNM. Hereafter, the error-free data is imported to the dense frame of the SDBNM to specify the aspect terms and sentiment values. At last, the parameters are estimated and compared with old approaches and have earned the best results for classification rate.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Change history
21 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-10115-3
References
Gandhi, U. D., Malarvizhi Kumar, P., Chandra Babu, G., & Karthick, G. (2021). Sentiment analysis on twitter data by using convolutional neural network (CNN) and long short term memory (LSTM). Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08580-3
Mahalakshmi, P., & Fatima, N. S. (2021). Ensembling of text and images using deep convolutional neural networks for intelligent information retrieval. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08211-x
BalaAnand, M., Karthikeyan, N., & Karthik, S. (2019). Envisioning social media information for big data using big vision schemes in wireless environment. Wireless Personal Communications, 109, 777–796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06590-w
Das, D. (2018). Positive and negative link prediction algorithm based on sentiment analysis in large social networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 102, 2183–2198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5499-6
Poria, S., Hazarika, D., Majumder, N., & Mihalcea, R. (2020). Beneath the tip of the iceberg: Current challenges and new directions in sentiment analysis research. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2020.3038167
Liu, B. (2020). Text sentiment analysis based on CBOW model and deep learning in big data environment. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 11(2), 451–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1095-6
Kushwah, S., & Das, S. (2020). Sentiment analysis of big-data in healthcare: issue and challenges. In 2020 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation (ICCCA), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCA49541.2020.9250841
Sun, X., & He, J. (2020). A novel approach to generate a large scale of supervised data for short text sentiment analysis. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 79(9), 5439–5459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5748-4
Xia, R., Jiang, J., & He, H. (2017). Distantly supervised lifelong learning for large-scale social media sentiment analysis. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 8(4), 480–491. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2771234
Muhammad, A., Wiratunga, N., & Lothian, R. (2016). Contextual sentiment analysis for social media genres. Knowledge-based Systems, 108, 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.05.032
Geetha, R., & Thilagam, T. (2021). A review on the effectiveness of machine learning and deep learning algorithms for cyber security. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 28(4), 2861–2879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-020-09478-2
Sohangir, S., Wang, D., Pomeranets, A., & Khoshgoftaar, T. M. (2018). Big data: Deep Learning for financial sentiment analysis. Journal of Big Data, 5(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-017-0111-6
Agüero-Torales, M. M., Salas, J. I. A., & López-Herrera, A. G. (2021). Deep learning and multilingual sentiment analysis on social media data: An overview. Applied Soft Computing, 107, 107373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107373
Ruz, G. A., Henríquez, P. A., & Mascareño, A. (2020). Sentiment analysis of Twitter data during critical events through Bayesian networks classifiers. Future Generation Computer Systems, 106, 92–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.01.005
Naseem, U., Razzak, I., Khushi, M., Eklund, P. W., & Kim, J. (2021). Covidsenti: A large-scale benchmark Twitter data set for COVID-19 sentiment analysis. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 8(4), 1003–1015. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSS.2021.3051189
Khan, M., & Malviya, A. (2020). Big data approach for sentiment analysis of twitter data using Hadoop framework and deep learning. In 2020 International Conference on Emerging Trends in Information Technology and Engineering (ic-ETITE), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ic-ETITE47903.2020.201
Meškelė, D., & Frasincar, F. (2020). ALDONAr: A hybrid solution for sentence-level aspect-based sentiment analysis using a lexicalized domain ontology and a regularized neural attention model. Information Processing & Management, 57(3), 102211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102211
Nandal, N., Tanwar, R., & Pruthi, J. (2020). Machine learning based aspect level sentiment analysis for Amazon products. Spatial Information Research, 28(5), 601–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-020-00320-2
Phan, M. H., & Ogunbona, P. O. (2020). Modelling context and syntactical features for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 3211–3220). https://aclanthology.org/2020.acl-main.293
Kundu, S., & Chakraborti, S. (2020). A comparative study of online consumer reviews of Apple iPhone across Amazon, Twitter and MouthShut platforms. Electronic Commerce Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-020-09429-w
Kothalawala, M., & Thelijjagoda, S. (2020). Aspect-based sentiment analysis on hair care product reviews. In: 2020 International Research Conference on Smart Computing and Systems Engineering (SCSE), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/SCSE49731.2020.9313040
Maheswari, S. U., & Dhenakaran, S. S. (2020). Aspect based Fuzzy Logic Sentiment Analysis on Social Media Big Data. In: 2020 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSP48568.2020.9182174
Tammina, S., & Annareddy, S. (2020). Sentiment analysis on customer reviews using convolutional neural network. In: 2020 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCI48352.2020.9104086
Yadav, A., Agarwal, A., & Vishwakarma, D. K. (2019). XRA-net framework for visual sentiments analysis. In: 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigMM.2019.00-22
Yadav, A., & Vishwakarma, D. K. (2020). A deep learning architecture of RA-DLNet for visual sentiment analysis. Multimedia Systems, 26(4), 431–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-020-00656-7
Yadav, A., & Vishwakarma, D. K. (2020). A deep multi-level attentive network for multimodal sentiment analysis. ACM Transactions on Multimidia Computing Communications and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1145/3517139
Mowlaei, M. E., Abadeh, M. S., & Keshavarz, H. (2020). Aspect-based sentiment analysis using adaptive aspect-based lexicons. Expert Systems with Applications, 148, 113234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113234
Alamanda, M. S. (2020). Aspect-based sentiment analysis search engine for social media data. CSI Transactions on ICT, 8, 193–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-020-00295-3
Kastrati, Z., Imran, A. S., & Kurti, A. (2020). Weakly supervised framework for aspect-based sentiment analysis on students’ reviews of MOOCs. IEEE Access, 8, 106799–106810. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3000739
Li, N., Chow, C. Y., & Zhang, J. D. (2020). SEML: A semi-supervised multi-task learning framework for aspect-based sentiment analysis. IEEE Access, 8, 189287–189297. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3031665
Jia, Z., Bai, X., & Pang, S. (2020). Hierarchical gated deep memory network with position-aware for aspect-based sentiment analysis. IEEE Access, 8, 136340–136347. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3011318
Truşcǎ, M. M., Wassenberg, D., Frasincar, F., & Dekker, R. (2020). A hybrid approach for aspect-based sentiment analysis using deep contextual word embeddings and hierarchical attention. In International Conference on Web Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50578-3_25
Zhou, J., Huang, J. X., Hu, Q. V., & He, L. (2020). Is position important? Deep multi-task learning for aspect-based sentiment analysis. Applied Intelligence, 50, 3367–3378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01760-x
Xu, Q., Zhu, L., Dai, T., & Yan, C. (2020). Aspect-based sentiment classification with multi-attention network. Neurocomputing, 388, 135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.01.024
Jiang, N., Tian, F., Li, J., Yuan, X., & Zheng, J. (2020). MAN: Mutual attention neural networks model for aspect-level sentiment classification in SIoT. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(4), 2901–2913. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2963927
Afzaal, M., Usman, M., & Fong, A. (2019). Tourism mobile app with aspect-based sentiment classification framework for tourist reviews. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 65(2), 233–242. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2019.2908944
Kumar, R., Pannu, H. S., & Malhi, A. K. (2020). Aspect-based sentiment analysis using deep networks and stochastic optimization. Neural Computing and Applications, 32(8), 3221–3235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04105-z
Alamoudi, E. S., & Alghamdi, N. S. (2021). Sentiment classification and aspect-based sentiment analysis on yelp reviews using deep learning and word embeddings. Journal of Decision Systems. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2020.1864106
Behera, R. K., Jena, M., Rath, S. K., & Misra, S. (2021). Co-LSTM: Convolutional LSTM model for sentiment analysis in social big data. Information Processing & Management, 58(1), 102435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102435
Phan, H. T., Tran, V. C., Nguyen, N. T., & Hwang, D. (2020). Improving the performance of sentiment analysis of tweets containing fuzzy sentiment using the feature ensemble model. IEEE Access, 8, 14630–14641. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963702
Yang, L., Li, Y., Wang, J., & Sherratt, R. S. (2020). Sentiment analysis for E-commerce product reviews in Chinese based on sentiment lexicon and deep learning. IEEE Access, 8, 23522–23530. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2969854
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
In this article the affiliation of the first author contained an incorrect location. The original article has been corrected.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmidevi, N., Vamsikrishna, M. & Nayak, S.S. An Optimized Deep Neural Aspect Based Framework for Sentiment Classification. Wireless Pers Commun 128, 2953–2979 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-10081-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-10081-w