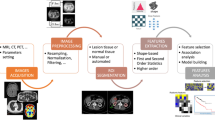
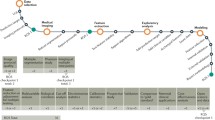
Abstract
Radiomics is a domain of biomedical and bioengineering research that analyzes large-scale radiological images associated with biology. Radiomics is dependent on feature extraction and is one of the extensions in the applications of Computer aided diagnosis (CAD). The number of features used in diagnosis are comparatively more in radiomics, making it one of the best approaches to be used in image analysis. The features that are extracted can be used in multiple modalities making the models more feasible and increasing their overall utility. Thus, this paper analyzes and showcases recent work being done on radiomics that is emerging rapidly in the field of medical applications. This paper mainly focused on oncology and presents a detailed literature review of radiomics. Further, various gaps and challenges that this field of radiomics faces while emerging as one of the most used approaches for future development are also presented in this study.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Doi, K. (2007). Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: historical review, current status and future potential. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 31(4–5), 198–211.
Gillies, R. J., Kinahan, P. E., & Hricak, H. (2016). Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology, 278(2), 563–577.
Yip, S. S., & Aerts, H. J. (2016). Applications and limitations of radiomics. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 61(13), R150.
Nam, D., Barrack, R. L., & Potter, H. G. (2014). What are the advantages and disadvantages of imaging modalities to diagnose wear-related corrosion problems? Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 472(12), 3665–73.
Lambin, P., Rios-Velazquez, E., Leijenaar, R., Carvalho, S., Van Stiphout, R. G., Granton, P., Zegers, C. M., Gillies, R., Boellard, R., Dekker, A., & Aerts, H. J. (2012). Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. European Journal of Cancer, 48(4), 441–446.
Arber, N. J., Wu, Y., Zou, L., Belani, P., & Singer, E. A. (2015). Challenges in RCC imaging: renal insufficiency, post-operative surveillance, and the role of radiomics. Kidney Cancer Journal: Official Journal of the Kidney Cancer Association., 13(4), 84.
Rizzo, S., Botta, F., Raimondi, S., Origgi, D., Fanciullo, C., Morganti, A. G., & Bellomi, M. (2018). Radiomics: The facts and the challenges of image analysis. European Radiology Experimental, 2(1), 1–8.
Grossmann, P., Stringfield, O., El-Hachem, N., Bui, M. M., Velazquez, E. R., Parmar, C., Leijenaar, R. T., Haibe-Kains, B., Lambin, P., Gillies, R. J., & Aerts, H. J. (2017). Defining the biological basis of radiomic phenotypes in lung cancer. eLife, 6, e23421.
Shaikh, F., Franc, B., Allen, E., Sala, E., Awan, O., Hendrata, K., Halabi, S., Mohiuddin, S., Malik, S., Hadley, D., & Shrestha, R. (2018). Translational radiomics: Defining the strategy pipeline and considerations for application—Part 1: From methodology to clinical implementation. Journal of the American College of Radiology, 15(3), 538–542.
Zwanenburg, A., Vallières, M., Abdalah, M. A., Aerts, H. J., Andrearczyk, V., Apte, A., Ashrafinia, S., Bakas, S., Beukinga, R. J., Boellaard, R., & Bogowicz, M. (2020). The image biomarker standardization initiative: Standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping. Radiology, 295(2), 328–338.
Ergen, B., & Baykara, M. (2014). Texture based feature extraction methods for content based medical image retrieval systems. Bio-Medical Materials And Engineering, 24(6), 3055–3062.
Haralick, R. M., Shanmugam, K., & Dinstein, I. H. (1973). Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 6, 610–621.
Balagurunathan, Y., Kumar, V., Gu, Y., Kim, J., Wang, H., Liu, Y., Goldgof, D. B., Hall, L. O., Korn, R., Zhao, B., & Schwartz, L. H. (2014). Test–retest reproducibility analysis of lung CT image features. Journal of Digital Imaging, 27(6), 805–823.
Galloway, M. M. (1975). Texture classification using gray level run length. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 4(2), 172–179.
Nie, K., Al-Hallaq, H., Li, X. A., Benedict, S. H., Sohn, J. W., Moran, J. M., Fan, Y., Huang, M., Knopp, M. V., Michalski, J. M., & Monroe, J. (2019). NCTN assessment on current applications of radiomics in oncology. International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics, 104(2), 302–15.
Zhao, B., Tan, Y., Tsai, W. Y., Qi, J., Xie, C., Lu, L., & Schwartz, L. H. (2016). Reproducibility of radiomics for deciphering tumor phenotype with imaging. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–7.
Parmar, C., Velazquez, E. R., Leijenaar, R., Jermoumi, M., Carvalho, S., Mak, R. H., Mitra, S., Shankar, B. U., Kikinis, R., Haibe-Kains, B., & Lambin, P. (2014). Robust radiomics feature quantification using semiautomatic volumetric segmentation. PLoS ONE, 9(7), e102107.
Leijenaar, R. T., Nalbantov, G., Carvalho, S., Van Elmpt, W. J., Troost, E. G., Boellaard, R., Aerts, H. J., Gillies, R. J., & Lambin, P. (2015). The effect of SUV discretization in quantitative FDG-PET Radiomics: The need for standardized methodology in tumor texture analysis. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 1.
Aerts, H. J., Grossmann, P., Tan, Y., Oxnard, G. R., Rizvi, N., Schwartz, L. H., & Zhao, B. (2016). Defining a radiomic response phenotype: A pilot study using targeted therapy in NSCLC. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1.
Lao, J., Chen, Y., Li, Z. C., Li, Q., Zhang, J., Liu, J., & Zhai, G. (2017). A deep learning-based radiomics model for prediction of survival in glioblastoma multiforme. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–8.
Parmar, C., Leijenaar, R. T., Grossmann, P., Velazquez, E. R., Bussink, J., Rietveld, D., Rietbergen, M. M., Haibe-Kains, B., Lambin, P., & Aerts, H. J. (2015). Radiomic feature clusters and prognostic signatures specific for lung and head & neck cancer. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 1.
Coroller, T. P., Grossmann, P., Hou, Y., Velazquez, E. R., Leijenaar, R. T., Hermann, G., Lambin, P., Haibe-Kains, B., Mak, R. H., & Aerts, H. J. (2015). CT-based radiomic signature predicts distant metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 114(3), 345–350.
Limkin, E. J., Sun, R., Dercle, L., Zacharaki, E. I., Robert, C., Reuzé, S., Schernberg, A., Paragios, N., Deutsch, E., & Ferté, C. (2017). Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Annals of Oncology, 28(6), 1191–1206.
Huang, Y., Liu, Z., He, L., Chen, X., Pan, D., Ma, Z., Liang, C., Tian, J., & Liang, C. (2016). Radiomics signature: A potential biomarker for the prediction of disease-free survival in early-stage (I or II) non—small cell lung cancer. Radiology, 281(3), 947–957.
Giesel, F., Schneider, F., Kratochwil, C., Rath, D., Holland-Letz, T., Moltz, J., Kauczor, H.U., Schwartz, L., Haberkorn, U., Flechsig, P. (2016) CT radiomic analysis using lymph-node-density profile in correlation to SUV-value for PET/CT based N-staging. Journal of Nuclear Medicine jnumed-116.
McNitt-Gray, M. F., Hart, E. M., Wyckoff, N., Sayre, J. W., Goldin, J. G., & Aberle, D. R. (1999). A pattern classification approach to characterizing solitary pulmonary nodules imaged on high resolution CT: Preliminary results. Medical Physics, 26(6), 880–888.
Ganeshan, B., Abaleke, S., Young, R. C., Chatwin, C. R., & Miles, K. A. (2010). Texture analysis of non-small cell lung cancer on unenhanced computed tomography: Initial evidence for a relationship with tumor glucose metabolism and stage. Cancer Imaging, 10(1), 137.
Ganeshan, B., Goh, V., Mandeville, H. C., Ng, Q. S., Hoskin, P. J., & Miles, K. A. (2013). Non–small cell lung cancer: Histopathologic correlates for texture parameters at CT. Radiology, 266(1), 326–336.
Karlo, C. A., Di Paolo, P. L., Chaim, J., Hakimi, A. A., Ostrovnaya, I., Russo, P., Hricak, H., Motzer, R., Hsieh, J. J., & Akin, O. (2014). Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Associations between CT imaging features and mutations. Radiology, 270(2), 464–471.
Traverso, A., Wee, L., Dekker, A., & Gillies, R. (2018). Repeatability and reproducibility of radiomic features: a systematic review. International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics., 102(4), 1143–58.
Panth, K. M., Leijenaar, R. T., Carvalho, S., Lieuwes, N. G., Yaromina, A., Dubois, L., & Lambin, P. (2015). Is there a causal relationship between genetic changes and radiomics-based image features? An in vivo preclinical experiment with doxycycline inducible GADD34 tumor cells. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 116(3), 462–466.
Ypsilantis, P. P., Siddique, M., Sohn, H. M., Davies, A., Cook, G., Goh, V., & Montana, G. (2015). Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with PET imaging using convolutional neural networks. PLoS ONE, 10(9), e0137036.
Dhingra, V. K., Mahajan, A., & Basu, S. (2015). Emerging clinical applications of PET based molecular imaging in oncology: The promising future potential for evolving personalized cancer care. The Indian Journal of Radiology & Imaging, 25(4), 332.
Capobianco, E., & Dominietto, M. (2020). From medical imaging to radiomics: Role of data science for advancing precision health. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(1), 15.
Lu, L., Lv, W., Jiang, J., Ma, J., Feng, Q., Rahmim, A., & Chen, W. (2016). Robustness of radiomic features in [11 C] choline and [18 F] FDG PET/CT imaging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Impact of segmentation and discretization. Molecular Imaging and Biology, 18(6), 935–945.
El Naqa, I. (2014). The role of quantitative PET in predicting cancer treatment outcomes. Clinical and Translational Imaging, 2(4), 305–320.
Grigsby, P. W., Siegel, B. A., Dehdashti, F., Rader, J., & Zoberi, I. (2004). Posttherapy [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in carcinoma of the cervix: Response and outcome. Journal of Clinical Oncology., 22(11), 2167–2171.
Yoon, H.J., Sohn, I., Cho, J.H., Lee, H.Y., Kim, J.H., Choi, Y.L., Kim, H., Lee, G., Lee, K.S., Kim, J. (2015) Decoding tumor phenotypes for ALK, ROS1, and RET fusions in lung adenocarcinoma using a radiomics approach. Medicine 94 (41).
Berghmans, T., Dusart, M., Paesmans, M., Hossein-Foucher, C., Buvat, I., Castaigne, C., Scherpereel, A., Mascaux, C., Moreau, M., Roelandts, M., & Alard, S. (2008). Primary tumor standardized uptake value (SUVmax) measured on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) is of prognostic value for survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A systematic review and meta-analysis (MA) by the European lung cancer working party for the IASLC lung cancer staging project. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 3(1), 6–12.
Hatt, M., Tixier, F., Pierce, L., Kinahan, P. E., Le Rest, C. C., & Visvikis, D. (2017). Characterization of PET/CT images using texture analysis: The past, the present any future? European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 44(1), 151–165.
Scrivener, M., de Jong, E. E., van Timmeren, J. E., Pieters, T., Ghaye, B., & Geets, X. (2016). Radiomics applied to lung cancer: A review. Transl Cancer Res., 5(4), 398–409.
Hatt, M., Parmar, C., Qi, J., & El Naqa, I. (2019). Machine (deep) learning methods for image processing and radiomics. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 3(2), 104–108.
Cameron, A., Khalvati, F., Haider, M. A., & Wong, A. (2015). MAPS: A quantitative radiomics approach for prostate cancer detection. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering., 63(6), 1145–1156.
Kumar, V., Gu, Y., Basu, S., Berglund, A., Eschrich, S. A., Schabath, M. B., Forster, K., Aerts, H. J., Dekker, A., Fenstermacher, D., & Goldgof, D. B. (2012). Radiomics: The process and the challenges. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 30(9), 1234–1248.
Li, H., Zhu, Y., Burnside, E. S., Huang, E., Drukker, K., Hoadley, K. A., Fan, C., Conzen, S. D., Zuley, M., Net, J. M., & Sutton, E. (2016). Quantitative MRI radiomics in the prediction of molecular classifications of breast cancer subtypes in the TCGA/TCIA data set. NPJ Breast Cancer, 2(1), 1.
Parmar, C., Grossmann, P., Bussink, J., Lambin, P., & Aerts, H. J. (2015). Machine learning methods for quantitative radiomic biomarkers. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 1–1.
Antunes, J., Viswanath, S., Rusu, M., Valls, L., Hoimes, C., Avril, N., & Madabhushi, A. (2016). Radiomics analysis on FLT-PET/MRI for characterization of early treatment response in renal cell carcinoma: A proof-of-concept study. Translational Oncology, 9(2), 155–162.
Barucci, A., Baccini, M., Carpi, R., Giannetti, A., Olmastroni, M., Pini, R., Pujol, S., Ratto, F., Zatelli, G., Esposito, M. (2017) Prostate cancer radiomics using multiparametric MR imaging. Technical, Scientific and Research Reports (TSRR) 9.
Reuzé, S., Orlhac, F., Chargari, C., Nioche, C., Limkin, E., Riet, F., Escande, A., Haie-Meder, C., Dercle, L., Gouy, S., & Buvat, I. (2017). Prediction of cervical cancer recurrence using textural features extracted from 18F-FDG PET images acquired with different scanners. Oncotarget, 8(26), 43169.
Tanadini-Lang, S., Bogowicz, M., Veit-Haibach, P., Huellner, M., Pauli, C., Shukla, V., Guckenberger, M., & Riesterer, O. (2018). Exploratory radiomics in computed tomography perfusion of prostate cancer. Anticancer Research, 38(2), 685–690.
Theek, B., Opacic, T., Magnuska, Z., Lammers, T., & Kiessling, F. (2018). Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound data. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–9.
Khalvati, F., Zhang, J., Chung, A. G., Shafiee, M. J., Wong, A., & Haider, M. A. (2018). MPCaD: A multi-scale radiomics-driven framework for automated prostate cancer localization and detection. BMC Medical Imaging, 18(1), 1–4.
Chiang, G. C., Kovanlikaya, I., Choi, C., Ramakrishna, R., Magge, R., & Shungu, D. C. (2018). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy, positron emission tomography and radiogenomics: Relevance to glioma. Frontiers in Neurology, 5(9), 33.
Toivonen, J., Montoya Perez, I., Movahedi, P., Merisaari, H., Pesola, M., Taimen, P., Boström, P. J., Pohjankukka, J., Kiviniemi, A., Pahikkala, T., & Aronen, H. J. (2019). Radiomics and machine learning of multisequence multiparametric prostate MRI: Towards improved non-invasive prostate cancer characterization. PLoS ONE, 14(7), e0217702.
Kickingereder, P., Burth, S., Wick, A., Götz, M., Eidel, O., Schlemmer, H. P., Maier-Hein, K. H., Wick, W., Bendszus, M., Radbruch, A., & Bonekamp, D. (2016). Radiomic profiling of glioblastoma: Identifying an imaging predictor of patient survival with improved performance over established clinical and radiologic risk models. Radiology, 280(3), 880–889.
Zhang, L., Fried, D. V., Fave, X. J., Hunter, L. A., Yang, J., & Court, L. E. (2015). IBEX: An open infrastructure software platform to facilitate collaborative work in radiomics. Medical physics, 42(3), 1341–1353.
Fang, Y. H., Lin, C. Y., Shih, M. J., Wang, H. M., Ho, T. Y., Liao, C. T., & Yen, T. C. (2014). Development and evaluation of an open-source software package “CGITA” for quantifying tumor heterogeneity with molecular images. BioMed Research International, 2014, 1.
Szczypiński, P. M., Strzelecki, M., Materka, A., & Klepaczko, A. (2009). MaZda—a software package for image texture analysis. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 94(1), 66–76.
El Naqa, I., Grigsby, P. W., Apte, A., Kidd, E., Donnelly, E., Khullar, D., Chaudhari, S., Yang, D., Schmitt, M., Laforest, R., & Thorstad, W. L. (2009). Exploring feature-based approaches in PET images for predicting cancer treatment outcomes. Pattern Recognition, 42(6), 1162–1171.
Vallières, M., Freeman, C. R., Skamene, S. R., & El Naqa, I. (2015). A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 60(14), 5471.
Aerts, H. J., Velazquez, E. R., Leijenaar, R. T., Parmar, C., Grossmann, P., Carvalho, S., Bussink, J., Monshouwer, R., Haibe-Kains, B., Rietveld, D., & Hoebers, F. (2014). Decoding tumor phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nature Communications, 5(1), 1–9.
Coroller, T. P., Agrawal, V., Narayan, V., Hou, Y., Grossmann, P., Lee, S. W., Mak, R. H., & Aerts, H. J. (2016). Radiomic phenotype features predict pathological response in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 119(3), 480–486.
Van Timmeren, J. E., Cester, D., Tanadini-Lang, S., Alkadhi, H., & Baessler, B. (2020). Radiomics in medical imaging—“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Into Imaging, 11(1), 1–6.
Scapicchio, C., Gabelloni, M., Barucci, A., Cioni, D., Saba, L., & Neri, E. (2021). A deep look into radiomics. La Radiologia Medica, 126(10), 1296–1311.
Reginelli, A., Nardone, V., Giacobbe, G., Belfiore, M. P., Grassi, R., Schettino, F., Del Canto, M., Grassi, R., & Cappabianca, S. (2021). Radiomics as a new frontier of imaging for cancer prognosis: A narrative review. Diagnostics, 11(10), 1796.
Feng, Q., Liang, J., Wang, L., Ge, X., Ding, Z., & Wu, H. (2022). A diagnosis model in nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on PET/MRI radiomics and semiquantitative parameters. BMC Medical Imaging, 22(1), 1–9.
Chung, A. G., Khalvati, F., Shafiee, M. J., Haider, M. A., & Wong, A. (2015). Prostate cancer detection via a quantitative radiomics-driven conditional random field framework. IEEE Access, 3, 2531–2541.
Ma, J., Wang, Q., Ren, Y., Hu, H., Zhao, J. (2016) Automatic lung nodule classification with radiomics approach. In Medical Imaging 2016: PACS and Imaging Informatics: Next Generation and Innovations (Vol. 9789, p. 978906). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Lambin, P., Leijenaar, R. T., Deist, T. M., Peerlings, J., De Jong, E. E., Van Timmeren, J., Sanduleanu, S., Larue, R. T., Even, A. J., Jochems, A., & van Wijk, Y. (2017). Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 14(12), 749–762.
Van Griethuysen, J. J., Fedorov, A., Parmar, C., Hosny, A., Aucoin, N., Narayan, V., Beets-Tan, R. G., Fillion-Robin, J. C., Pieper, S., & Aerts, H. J. (2017). Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Research, 77(21), e104–e107.
Leger, S., Zwanenburg, A., Pilz, K., Lohaus, F., Linge, A., Zöphel, K., Kotzerke, J., Schreiber, A., Tinhofer, I., Budach, V., & Sak, A. (2017). A comparative study of machine learning methods for time-to-event survival data for radiomics risk modelling. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–1.
Buizza, G. (2017) Classifying patients' response to tumor treatment from PET/CT data: A machine learning approach.
Wang, J., Wu, C. J., Bao, M. L., Zhang, J., Wang, X. N., & Zhang, Y. D. (2017). Machine learning-based analysis of MR radiomics can help to improve the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS v2 in clinically relevant prostate cancer. European Radiology, 27(10), 4082–4090.
Ginsburg, S. B., Algohary, A., Pahwa, S., Gulani, V., Ponsky, L., Aronen, H. J., Boström, P. J., Böhm, M., Haynes, A. M., Brenner, P., & Delprado, W. (2017). Radiomic features for prostate cancer detection on MRI differ between the transition and peripheral zones: Preliminary findings from a multi-institutional study. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging., 46(1), 184–193.
Aerts, H. J. (2018). Data science in radiology: A path forward. Clinical Cancer Research, 24(3), 532–534.
Algohary, A., Viswanath, S., Shiradkar, R., Ghose, S., Pahwa, S., Moses, D., Jambor, I., Shnier, R., Böhm, M., Haynes, A. M., & Brenner, P. (2018). Radiomic features on MRI enable risk categorization of prostate cancer patients on active surveillance: Preliminary findings. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging., 48(3), 818–828.
Bonekamp, D., Kohl, S., Wiesenfarth, M., Schelb, P., Radtke, J. P., Götz, M., Kickingereder, P., Yaqubi, K., Hitthaler, B., Gählert, N., & Kuder, T. A. (2018). Radiomic machine learning for characterization of prostate lesions with MRI: Comparison to ADC values. Radiology, 289(1), 128–137.
Choyke, P. L. (2018). Quantitative MRI or machine learning for prostate MRI: Which should you use? Radiology, 289, 138.
Peeken, J. C., Bernhofer, M., Wiestler, B., Goldberg, T., Cremers, D., Rost, B., Wilkens, J. J., Combs, S. E., & Nüsslin, F. (2018). Radiomics in radiooncology–challenging the medical physicist. Physica Medica, 48, 27–36.
Morin, O., Vallières, M., Jochems, A., Woodruff, H. C., Valdes, G., Braunstein, S. E., Wildberger, J. E., Villanueva-Meyer, J. E., Kearney, V., Yom, S. S., & Solberg, T. D. (2018). A deep look into the future of quantitative imaging in oncology: a statement of working principles and proposal for change. International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics, 102(4), 1074–82.
Banerjee, S., Mitra, S., Masulli, F., Rovetta, S. (2019) Deep radiomics for brain tumor detection and classification from multi-sequence MRI. arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.09240..
Chen, T., Li, M., Gu, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, S., Wei, C., Wu, J., Li, X., Zhao, W., & Shen, J. (2019). Prostate cancer differentiation and aggressiveness: assessment with a radiomic-based model vs. PI-RADS v2. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 49(3), 875–84.
Varghese, B., Chen, F., Hwang, D., Palmer, S.L., De Castro Abreu, A.L., Ukimura, O., Aron, M., Aron, M., Gill, I., Duddalwar, V., Pandey, G. (2020) Objective risk stratification of prostate cancer using machine learning and radiomics applied to multiparametric magnetic resonance images. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics (pp. 1–10).
Afshar, P., Mohammadi, A., Plataniotis, K. N., Oikonomou, A., & Benali, H. (2019). From handcrafted to deep-learning-based cancer radiomics: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 36(4), 132–160.
Dreyer, K. J., & Geis, J. R. (2017). When machines think: Radiology’s next frontier. Radiology, 285(3), 713–718.
Sanduleanu, S., Woodruff, H. C., De Jong, E. E., Van Timmeren, J. E., Jochems, A., Dubois, L., & Lambin, P. (2018). Tracking tumor biology with radiomics: A systematic review utilizing a radiomics quality score. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 127(3), 349–360.
Wu, J., Tha, K. K., Xing, L., & Li, R. (2018). Radiomics and radiogenomics for precision radiotherapy. Journal of Radiation Research., 59(Suppl_1), i25-31.
Robinson, K., Li, H., Lan, L., Schacht, D., & Giger, M. (2019). Radiomics robustness assessment and classification evaluation: A two-stage method demonstrated on multivendor FFDM. Medical physics, 46(5), 2145–2156.
Rogers, W., Thulasi Seetha, S., Refaee, T. A., Lieverse, R. I., Granzier, R. W., Ibrahim, A., Keek, S. A., Sanduleanu, S., Primakov, S. P., Beuque, M. P., & Marcus, D. (2020). Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. The British Journal of Radiology, 93(1108), 20190948.
Hong, J. H., Jung, J. Y., Jo, A., Nam, Y., Pak, S., Lee, S. Y., Park, H., Lee, S. E., & Kim, S. (2021). Development and validation of a radiomics model for differentiating bone islands and osteoblastic bone metastases at abdominal CT. Radiology, 30, 203783.
Funding
Funding is provided by Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), Govt. of India under the Project “Design Innovation Centre (DIC) sub-theme Medical Devices and Restorative Technologies” with grant number 17-11/2015-PN-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have equally contributed in the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, S.K., Thakur, N. & Juneja, M. Radiomics Based Diagnosis with Medical Imaging: A Comprehensive Study. Wireless Pers Commun 130, 481–514 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10295-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10295-6