Abstract
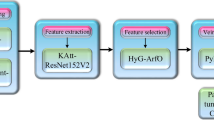
Contactless palm vein recognition plays a significant role in biometric application because of its high stability, non-intrusive, flexibility and unique nature. Thus, different neural approaches were proposed to identify and segment the vein from the contactless palm image. But the traditional techniques face challenging issues in vein tracking and segmentation. Thus, a novel hybrid optimized deep network named Monkey-based Elman Neural Vein Recognition Framework was developed in this article. First, the dataset is pre-processed, and the palm region is extracted. Then, the extracted features are matched with the saved ground truth features. Further, the veins are tracked and segmented in the classification phase. The spider monkey fitness function is integrated into the developed model, which tracks and segments the vein from the palm image. The presented work was implemented, and the results are estimated for the palm image dataset. Furthermore, the results are verified with a comparative analysis. The highest accuracy score for the Contactless Palm-Vein Recognition by the proposed model is 99.76, and the lowest error rate is 0.0089%. Hence, the comparative analysis shows that the developed model earned better outcomes than the existing approaches.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Singh, A., Prakash, S., Kumar, A., & Kumar, D. (2022). A proficient approach for face detection and recognition using machine learning and high-performance computing. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 34(3), e6582. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6582
Haidri, R. A., Alam, M., Shahid, M., Prakash, S., & Sajid, M. (2022). A deadline aware load balancing strategy for cloud computing. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 34(1), e6496. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6496
Srivastava, S., Kumar, A., Singh, A., Prakash, S., & Kumar, A. (2022). An improved approach towards biometric face recognition using artificial neural network. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 81(6), 8471–8497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11721-2
Yadav, R., Zhang, W., Elgendy, I. A., & Prakash, S. (2021). Smart healthcare: RL-based task offloading scheme for edge-enable sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 21(22), 24910–24918. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3096245
Dhawankar, P., Kumar, A., Crespi, N., Busawon, K., Prakash, S., & Kaiwartya, O. (2021). Next-generation indoor wireless systems: Compatibility and migration case study. IEEE Access, 9, 156915–156929. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3126827
Rajak, R., Kumar, S., Prakash, S., Rajak, N., & Dixit, P. (2023). A novel technique to optimize quality of service for directed acyclic graph (DAG) scheduling in cloud computing environment using heuristic approach. The Journal of Supercomputing, 79(2), 1956–1979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04729-4
Rajak, N., Rajak, R., & Prakash, S. (2022). A workflow scheduling method for cloud computing platform. Wireless Personal Communications, 126(4), 3625–3647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09882-w
Agrawal, A., Ghune, N., Prakash, S., & Ramteke, M. (2021). Evolutionary algorithm hybridized with local search and intelligent seeding for solving multi-objective Euclidian TSP. Expert Systems with Applications, 181, 115192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115192
Singh, A., Singh, S., & Prakash, S. (2023). Critical comparative analysis and recommendation in mac protocols for wireless mesh networks using multi-objective optimization and statistical testing. Wireless Personal Communications, 129, 2319–2344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10228-3
Singh, A., Prakash, S., & Singh, S. (2022). Optimization of reinforcement routing for wireless mesh network using machine learning and high-performance computing. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 34(15), e6960. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6960
Sukesh Adiga, V., & Sivaswamy, J. (2019). Fpd-m-net: Fingerprint image denoising and inpainting using m-net based convolutional neural networks. Inpainting and denoising challenges. Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-25614-2_4
Kumar, C., Bharti, T. S., & Prakash, S. (2023). A hybrid data-driven framework for spam detection in online social network. Procedia Computer Science, 218, 124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.408
Zhang, Y., Cai, X., Zhang, Y., Kang, H., Ji, X., & Yuan, X. (2021). TAU: Transferable attention U-Net for optic disc and cup segmentation. Knowledge-based Systems, 213, 106668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106668
Baumgartner, M., Jäger, P. F., Isensee, F., & Maier-Hein, K. H. (2021). nndetection: A self-conFiguring method for medical object detection. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87240-3_51
Azar, J., Tayeh, G. B., Makhoul, A., & Couturier, R. (2022). Efficient lossy compression for IoT using SZ and reconstruction with 1D U-Net. Mobile Networks and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-022-01918-6
Bigalke, A., Hansen, L., Diesel, J., & Heinrich, M. P. (2021). Seeing under the cover with a 3D U-Net: Point cloud-based weight estimation of covered patients. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 16(12), 2079–2087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-021-02476-0
Oh, S. L., Ng, E. Y. K., San Tan, R., & Acharya, U. R. (2019). Automated beat-wise arrhythmia diagnosis using modified U-Net on extended electrocardiographic recordings with heterogeneous arrhythmia types. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 105, 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.12.012
Tong, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, M., Meng, L., & Zhang, J. (2021). Improved U-Net MALF model for lesion segmentation in breast ultrasound images. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 68, 102721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102721
Adiraju, R. V., Masanipalli, K. K., Reddy, T. D., Pedapalli, R., Chundru, S., & Panigrahy, A. K. (2021). An extensive survey on finger and palm vein recognition system. Materials Today: Proceedings, 45, 1804–1808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.742
Ren, H., Sun, L., Guo, J., Han, C., & Wu, F. (2021). Finger vein recognition system with template protection based on convolution neural network. Knowledge-based Systems, 227, 107159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107159
Ahmad, F., Cheng, L. M., & Khan, A. (2019). Lightweight and privacy-preserving template generation for palm-vein-based human recognition. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15, 184–194. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2019.2917156
Jia, W., Ren, Q., Zhao, Y., Li, S., Min, H., & Chen, Y. (2022). EEPNet: An Efficient and Effective Convolution Neural Network for Palm print Recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters, 159, 140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2022.05.015
Horng, S. J., Vu, D. T., Nguyen, T. V., Zhou, W., & Lin, C. T. (2021). Recognizing Palm Vein in Smartphone Using RGB Images. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(9), 5992–6002. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3134016
Sharma, H., Hazrati, G., & Bansal, J. C. (2019). Spider monkey optimization algorithm. Evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms (pp. 43–59). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91341-4_4
Xu, L., Yu, X., & Gulliver, T. A. (2021). Intelligent outage probability prediction for mobile IoT networks based on an IGWO-Elman neural network. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(2), 1365–1375. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2021.3051966
Zhang, J., Lu, Z., & Li, M. (2020). Active contour-based method for finger-vein image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 69(11), 8656–8665. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2020.2995485
Ma, H., & Zhang, S. Y. (2019). Contactless finger-vein verification based on oriented elements feature. Infrared Physics and Technology, 97, 149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2018.12.021
Chen, Y. Y., Hsia, C. H., & Chen, P. H. (2021). Contactless multispectral palm-vein recognition with lightweight convolutional neural network. IEEE Access, 9, 149796–149806. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3124631
Wu, W., Wang, Q., Yu, S., Luo, Q., Lin, S., Han, Z., & Tang, Y. (2021). Outside box and contactless palm vein recognition based on a wavelet denoising ResNet. IEEE Access, 9, 82471–82484. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3086811
Aydemir, E., & Alalawi, R. T. E. (2023). Classification of hand images by person, age and gender with the median robust extended local binary model. Balkan Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 11(1), 78–87. https://doi.org/10.17694/bajece.1171905
Bhatti, U. A., Nizamani, M. M., & Mengxing, H. (2022). Climate change threatens Pakistan’s snow leopards. Science, 377(6606), 585–586. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.add9065
Bhatti, U. A., Zeeshan, Z., Nizamani, M. M., Bazai, S., Yu, Z., & Yuan, L. (2022). Assessing the change of ambient air quality patterns in Jiangsu Province of China pre-to post-COVID-19. Chemosphere, 288, 132569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132569
Bhatti, U. A., WuBazai, G. S. U., Nawaz, S. A., Baryalai, M., Bhatti, M. A., Hasnain, A., & Nizamani, M. M. (2022). A pre- to post-COVID-19 change of air quality patterns in Anhui Province using path analysis and regression. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 31(5), 4029–4042. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/148065
Aamir, M., Li, Z., Bazai, S., Wagan, R. A., Bhatti, U. A., Nizamani, M. M., & Akram, S. (2021). Spatiotemporal change of air-quality patterns in Hubei Province—a pre- to post-covid-19 analysis using path analysis and regression. Atmosphere, 12, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101338
Nawaz, S. A., Li, J., Bhatti, U. A., Bazai, S. U., Zafar, A., Bhatti, M. A., Mehmood, A., Ain, Q., & Shoukat, M. U. (2021). A hybrid approach to forecast the COVID-19 epidemic trend. PLoS ONE, 16(10), e0256971. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256971
Cervantes Galvan, L. P., Aslam Bhatti, U., Carmona, C. J., & Simancas Trujillo, R. A. (2022). The nexus between CO2 emission, economic growth, trade openness: Evidences from middle-income trap countries. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.938776
Unhelkar, B., Joshi, S., Sharma, M., Prakash, S., Mani, A. K., & Prasad, M. (2022). Enhancing supply chain performance using RFID technology and decision support systems in the industry 4.0–a systematic literature review. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 2(2), 100084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjimei.2022.100084
Kaiwartya, O., Abdullah, A. H., Cao, Y., Lloret, J., Kumar, S., Shah, R. R., Prasad, M., & Prakash, S. (2017). Virtualization in wireless sensor networks: Fault tolerant embedding for internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(2), 571–580. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2017.2717704
Trivedi, V., Prakash, S., & Ramteke, M. (2017). Optimized online control of MMA polymerization using fast multi-objective DE. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 32(10), 1144–1151. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2016.1257802
Prakash, S., Trivedi, V., & Ramteke, M. (2016). An elitist non-dominated sorting bat algorithm NSBAT-II for multi-objective optimization of phthalic anhydride reactor. International Journal of Systems Assurance Engineering and Management, 7, 299–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0467-6
Chen, Y., Zhong, J., Mumtaz, J., Zhou, S., & Zhu, L. (2023). An improved spider monkey optimization algorithm for multi-objective planning and scheduling problems of PCB assembly line. Expert Systems with Applications, 229, 120600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120600
Hao, Y. (2023). Numerical simulation of regional air pollution characteristics based on meteorological factors and improved Elman neural network algorithm. Applied Nanoscience, 13(5), 3383–3391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02201-y
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both the authors have contributed equally to the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sandhya, T., Reddy, G.S. An Optimized Elman Neural Network for Contactless Palm-Vein Recognition Framework. Wireless Pers Commun 131, 2773–2795 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10579-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10579-x