Abstract
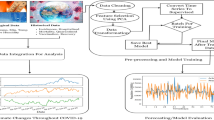
Coronavirus has been avowed world epidemic by the Organisation Mondiale de la Santé on March 11th 2020. Formerly, numerous investigators have endeavoured to envisage divergent periods of covid-19 malady and their possessions. Several have contemplate the temporal order of the events as primary factor which will contribute to the onset of infectious ailment including flu, influenza, etc. During this research analysis, total daily corroborated infested cases basedprognostication models for the time-series database of India for 30 days are estimated by applying extremely boosted neural network (XBNet). The main objective to introduce this XBNet model is to build an efficient and accurate time series deep learning model. Further, the performance of this model with previously developed time series models including logistic regression, facebook prophet, and sarimax is contrasted. To compare performance, numerous performance parameters like MAPE, RMSE, MAE, and MSE are employed to examine the consequence of model-fitting. This research also shows analysis of coronavirus cases based on three factors namely mortality rate, discharge rate, and the growth factor during different phases of lockdown. Also, projected the prediction of the cumulative number of confirmed COVID-19 cases for various time periods. This work presented the forecasts by applying the dataset that was attainable upto August 11th, 2021. The XBNet model showed a 99.27 percent precision accuracy and relatively less MSE, MAPE, RMSE, and MAE than other models. The results confirm superiority of the proposed approach over prevailing approaches.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abbasimehr, H., & Paki, R. (2021). Prediction of COVID-19 confirmed cases combining deep learning methods and Bayesian optimization. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 142, 110511.
ain, A., Sukhdeve, T., Gadia, H., Sahu, S. P., & Verma, S. (2021). COVID19 prediction using time series analysis. In 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Systems (ICAIS). IEEE, pp. 1599–1606.
Alali, Y., Harrou, F., & Sun, Y. (2022). A proficient approach to forecast COVID-19 spread via optimized dynamic machine learning models. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 2467.
Alassafi, M. O., Jarrah, M., & Alotaibi, R. (2022). Time series predicting of COVID-19 based on deep learning. Neurocomputing, 468, 335–344.
Alazab, M., Awajan, A., Mesleh, A., Abraham, A., Jatana, V., & Alhyari, S. (2020). COVID-19 prediction and detection using deep learning. International Journal of Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications, 12(June), 168–181.
AlJame, M., Ahmad, I., Imtiaz, A., & Mohammed, A. (2020). Ensemble learning model for diagnosing COVID-19 from routine blood tests. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 21, 100449.
Arunraj, N. S., Ahrens, D., & Fernandes, M. (2016). Application of SARIMAX model to forecast daily sales in food retail industry. International Journal of Operations Research and Information Systems (IJORIS), 7(2), 1–21.
Bacaër, N. (2011). A short history of mathematical population dynamics (Vol. 618). Springer.
Bansal, H., Bhatt, G., Malhotra, P., & Prathosh, A. P. (2021). Systematic generalization in neural networks-based multivariate time series forecasting models. In 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE, pp. 1–8.
Banyal, S., Dwivedi, R., Datta Gupta, K., Kumar Sharma, D., Al-Turjman, F., et al. (2021). Technology landscape for epidemiological prediction and diagnosis of covid-19. Computers, Materials & Continua, 67(2), 1679–1696.
Huchinson, G. E. (1978). An introduction to population ecology, JSTOR, 1–260.
Batcha, B. B. C., Singaravelu, R., Ramachandran, M., Muthusamy, S., Panchal, H., Thangaraj, K., & Ravindaran, A. (2023). A novel security algorithm RPBB31 for securing the social media analyzed data using machine learning algorithms. Wireless Personal Communications, 131, 581–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10446-9
Bennet, M. A., Mishra, O. P., & Muthusamy, S. (2023). "Modeling of upper limb and prediction of various yoga postures using artificial neural networks. In 2023 International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Data Communication Systems (ICSCDS), IEEE, pp. 503–508.
Bhimala, K. R., Patra, G. K., Mopuri, R., & Mutheneni, S. R. (2021). Prediction of COVID‐19 cases using the weather integrated deep learning approach for India. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 69(3),1349–1363.
Cecaj, A., Lippi, M., Mamei, M., & Zambonelli, F. (2020). Comparing deep learning and statistical methods in forecasting crowd distribution from aggregated mobile phone data. Applied Sciences, 10(18), 6580.
Chatfield, C. (1978). The Holt-winters forecasting procedure. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series C (Applied Statistics), 27(3), 264–279.
Chimmula, V. K. R., & Zhang, L. (2020). Time series forecasting of COVID-19 transmission in Canada using LSTM networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 135, 109864.
COVID-19 in India (2019). Kaggle, accessed 12 October 2021. Web Link: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sudalairajkumar/covid19-in-india
Dahiya, S., Gosain, A., & Mann, S. (2021). Experimental analysis of fuzzy clustering algorithms. In Intelligent data engineering and analytics. Springer, pp. 311–320.
Dastider, A. G., Sadik, F., & Fattah, S. A. (2021). An integrated autoencoder-based hybrid CNN-LSTM model for COVID-19 severity prediction from lung ultrasound. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 132, 104296.
Gnanadesigan, N. S., Dhanasegar, N., Ramasamy, M. D., Muthusamy, S., Mishra, O. P., Pugalendhi, G. K., Sundararajan, S. C. M., & Ravindaran, A. (2023). An integrated network topology and deep learning model for prediction of Alzheimer disease candidate genes. Soft Computing, 1–15.
Harvey, A. C., & Peters, S. (1990). Estimation procedures for structural time series models. Journal of Forecasting, 9(2), 89–108.
Hooda, S., & Mann, S. (2020). A focus on the ICU’s mortality prediction using a CNN-LSTM model. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 24(6), 8045–8050.
Hosseiny, M., Kooraki, S., Gholamrezanezhad, A., Reddy, S., & Myers, L. (2020). Radiology perspective of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Lessons from severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology, 214(5), 1078–1082.
Jamal, M., Shah, M., Almarzooqi, S. H., Aber, H., Khawaja, S., El Abed, R., & Samaranayake, L. P. (2021). Overview of transnational recommendations for COVID-19 transmission control in dental care settings. Oral Diseases, 27, 655–664.
Jude, M. Joseph Auxilius, V. C. Diniesh, M. Shivaranjani, Suresh Muthusamy, Hitesh Panchal, Suma Christal Mary Sundararajan, and Kishor Kumar Sadasivuni (2023). On minimizing TCP traffic congestion in vehicular internet of things (VIoT). Wireless Personal Communications, 128(3), 1873–1893.
Kafieh, R., Arian, R., Saeedizadeh, N., Amini, Z., Serej, N. D., Minaee, S., & Haghjooy Javanmard, S. (2021). COVID-19 in Iran: Forecasting pandemic using deep learning. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.
Kathamuthu, N. D., Subramaniam, S., Le, Q. H., Muthusamy, S., Panchal, H., Sundararajan, S. C. M., Alrubaie, A. J., & Zahra, M. M. A. (2023). A deep transfer learning-based convolution neural network model for COVID-19 detection using computed tomography scan images for medical applications. Advances in Engineering Software, 175, 103317.
Katrakazas, C., Michelaraki, E., Sekadakis, M., Ziakopoulos, A., Kontaxi, A., & Yannis, G. (2021). Identifying the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on driving behavior using naturalistic driving data and time series forecasting. Journal of Safety Research, 78, 189–202.
Krishnasamy, K. G., Periasamy, S., Periasamy, K., Prasanna Moorthy, V., Thangavel, G. , Lamba, R., & Muthusamy, S. (2023). A pair-task heuristic for scheduling tasks in heterogeneous multi-cloud environment. Wireless Personal Communications, 1–32.
Kukar, M., Gunčar, G., Vovko, T., Podnar, S., Černelč, P., Brvar, M., & Notar, M. (2021). COVID-19 diagnosis by routine blood tests using machine learning. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 10738.
Luo, J., Zhongliang Z., Yao F., & Feng R. (2021). Time series prediction of COVID-19 transmission in America using LSTM and XGBoost algorithms. Results in Physics, 27, 104462.
Manojkumar, P., Suresh, M., Ahmed, A. A. A., Panchal, H., Rajan, C. A., Dheepanchakkravarthy, A., Geetha, A., Gunapriya, B., Mann, S., & Sadasivuni, K. K. (2022). A novel home automation distributed server management system using Internet of Things. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 43(1), 5478–5483.
Omran, N. F., Abd-el Ghany, S. F., Saleh, H., Ali, A. A., Gumaei, A., & Al-Rakhami, M. (2021). Applying deep learning methods on time-series data for forecasting COVID-19 in Egypt, Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia. Complexity.
Periyasamy, K., Rathinam, V., Ganesan, K., Ramachandran, M., Muthusamy, S., Lamba, R., Panchal, H., Shanmugam, M., Jalajakumari, S. P. S. N., & Kottapalli, R. (2023). A novel method for analyzing the performance of free space optical communication in WDM using EDFA. Wireless Personal Communications, 131, 679–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10452-x
Raghavendran, P. S., Ragul, S., Asokan, R., Loganathan, A. K., Muthusamy, S., Mishra, O. P., Ramamoorthi, P., & Sundararajan, S. C. M. (2023). A new method for chest X-ray images categorization using transfer learning and CovidNet_2020 employing convolution neural network. Soft Computing, 27(19), 14241–14251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08874-7
Rakkiannan, T., Ekambaram, G., Palanisamy, N., Ramasamy, R. R., Muthusamy, S., Loganathan, A. K., Panchal, H., Thangaraj, K., & Ravindaran, A. (2023). An automated network slicing at edge with software defined networking and network function virtualization: a federated learning approach. Wireless Personal Communications, 131(1), 639–658.
Rathee, D., & Mann, S. (2022). Detection of E-mail phishing attacks–using machine learning and deep learning. International Journal of Computer Applications, 975, 8887.
Sarkar, T. (2021). XBNet: An Extremely Boosted Neural Network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.05239.
Senthil Kumar, R., Gerald Raj, I., Suresh, K. P., Leninpugalhanthi, P., Suresh, M., Panchal, H., Meenakumari, R., & Sadasivuni, K. K. (2022). A method for broken bar fault diagnosis in three phase induction motor drive system using Artificial Neural Networks. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 43(1), 5138–5144.
Shahid, F., Zameer, A., & Muneeb, M. (2020). Predictions for COVID-19 with deep learning models of LSTM, GRU and Bi-LSTM. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 140, 110212.
Shastri, S., Singh, K., Kumar, S., Kour, P., & Mansotra, V. (2020). Time series forecasting of Covid-19 using deep learning models: India-USA comparative case study. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 140, 110227.
Sinnaswamy, R. A., Palanisamy, N., Subramaniam, K., Muthusamy, S., Lamba, R., & Sekaran, S. (2023). An extensive review on deep learning and machine learning intervention in prediction and classification of types of aneurysms. Wireless Personal Communications, 1–26.
Subramaniam, K., Palanisamy, N., Sinnaswamy, R. A., Muthusamy, S., Mishra, O. P., Loganathan, A. K., Ramamoorthi, P., Gnanakkan, C. A. R. C., Thangavel, G., & Sundararajan, S. C. M. (2023). A comprehensive review of analyzing the chest X-ray images to detect COVID-19 infections using deep learning techniques. Soft Computing, 27, 14219–14240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08561-7
Suji Prasad, S. J., Thangatamilan, M., Suresh, M., Panchal, H., Rajan, C. A., Sagana, C., Gunapriya, B., Sharma, A., Panchal, T., & Sadasivuni, K. K. (2022). An efficient LoRa-based smart agriculture management and monitoring system using wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 43(1), 5447–5450. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2021.1953591
Suresh, M., Meenakumari, R., Panchal, H., Priya, V., Agouz, E. S. E., & Israr, M. (2022). An enhanced multiobjective particle swarm optimisation algorithm for optimum utilisation of hybrid renewable energy systems. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 43(1), 2540–2548.
Taylor, S. J., Letham, B. (2017). Forecasting at scale. URL: https://facebookincubator.github.io/prophet
Taylor, S. J., & Letham, B. (2018). Forecasting at scale. The American Statistician, 72(1), 37–45.
Thangavel, K., Palanisamy, N., Muthusamy, S., Mishra, O. P., Sundararajan, S. C. M., Panchal, H., Loganathan, A. K., & Ramamoorthi, P. (2023). A novel method for image captioning using multimodal feature fusion employing mask RNN and LSTM models. Soft Computing, 1–14.
Tomar, A., & Gupta, N. (2020). Prediction for the spread of COVID-19 in India and effectiveness of preventive measures. Science of The Total Environment, 728, 138762.
Wu, K., Darcet, D., Wang, Q., & Sornette, D. (2020). Generalized logistic growth modeling of the COVID-19 outbreak: Comparing the dynamics in the 29 provinces in China and in the rest of the world. Nonlinear dynamics, 101(3), 1561–1581.
Zain, Z. M., & Alturki, N. M. (2021). COVID-19 pandemic forecasting using CNN-LSTM: a hybrid approach. Journal of Control Science and Engineering.
Zhou, G., & Yan, G. (2003). Severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic in Asia. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 9(12), 1608–1610.
Funding
There was no financial support received from any organization for carrying out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally for the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
To the best of my knowledge and belief any actual, perceived or potential conflicts between my duties as an employee and my private and/or business interests have been fully disclosed in this form in accordance with the requirements of the journal.
Consent to Participate
I have been informed of the risks and benefits involved, and all my questions have been answered to my satisfaction. Furthermore, I have been assured that any future questions I may have will also be answered by a member of the research team. I voluntarily agree to take part in this study.
Consent to Publish
Individuals may consent to participate in a study, but object to having their data published in a journal article.
Ethical Approval
This material is the authors' own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The paper reflects the authors' own research and analysis in a truthful and complete manner.
Human Participants and/or Animals
The authors hereby assure that this research does not involves any human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mann, S., Yadav, D., Muthusamy, S. et al. A Novel Method for Prediction and Analysis of COVID 19 Transmission Using Machine Learning Based Time Series Models. Wireless Pers Commun 133, 1935–1961 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10836-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10836-z