Abstract
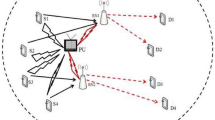
Imbalance and unfairness in resource allocation and utilization can lead to a degraded network environment where wireless network users experience poor quality of service (QoS) within the wireless networks. In multi-user wireless radio networks with constrained wireless network resources, such as power and bandwidth resources, uniform allocation of power or bandwidth may lead to unfairness in network resource management. The cooperative cognitive radio relay networks’ (CCRRN) radio resource allocation problem among multi-users is investigated in this paper through combined resource optimization. To facilitate fairness in the multi-user networks, the maxi–min criterion is employed. The max–min fairness ensures that when the wireless network attains max–min utility fairness, no user’s utility can be improved without degrading the utility performance of any other user. To maximize the worst-case user (max–min) capacity in the CCRRN using the power and bandwidth allocation strategy, a combined optimal resource allocation (COPBA) scheme is proposed. The max–min resource allocation optimization problem developed is observed to be convex. Efficient computer-based numerical optimization solver packages, such as SNOPT, exist that can solve convex optimization problems efficiently. The MATLAB software provides a robust integrated environment where the implementation of the SNOPT solver can be executed. Using the uniform bandwidth optimal power allocation (UBOPA) scheme as a benchmark, the fairness metric of the COPBA is evaluated and compared. Furthermore, the results showed the COPBA outperforming the UBOPA scheme.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Yes.
Change history
27 September 2024
The original version of this article was revised: In this article the author’s name Uyoata Uyoata was incorrectly written as Uyota Uyota. The original article has been corrected.
25 September 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11578-2
References
Li, F., Zhang, J., Liu, Z., Chan, K. Y., Yang, Y., & Xie, Y. (2023). Sum-rate maximization for cognitive relay NOMA systems with channel uncertainty. Computer Communications, 202, 183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2023.02.020
Subedi, P., Alsadoon, A., Prasad, P. W. C., Rehman, S., Giweli, N., Imran, M., & Arif, S. (2021). Network slicing: A next generation 5G perspective. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2021(1), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-021-01983-7
Rachakonda, L. P., Siddula, M., & Sathya, V. (2024). A comprehensive study on IoT privacy and security challenges with focus on spectrum sharing in next-generation networks (5G/6G/beyond). High-Confidence Computing, 4(2), 100220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hcc.2024.100220
Haghrah, A., Abdollahi, M. P., Azarhava, H., & Niya, J. M. (2023). A survey on the handover management in 5G-NR cellular networks: Aspects, approaches and challenges. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-023-02261-4
Suriya, M., & Sumithra, M. G. (2022). Overview of spectrum sharing and dynamic spectrum allocation schemes in cognitive radio networks. In 2022 8th International conference on advanced computing and communication systems (ICACCS), (Vol. 1, pp. 934–937). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCS54159.2022.9785048
Ahmad, W. S. H. M. W., Radzi, N. A. M., Samidi, F. S., Ismail, A., Abdullah, F., Jamaludin, M. Z., & Zakaria, M. N. (2020). 5G technology: Towards dynamic spectrum sharing using cognitive radio networks. IEEE Access, 8, 14460–14488. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2966271
Khasawneh, M., Azab, A., Alrabaee, S., Sakkal, H., & Bakhit, H. H. (2023). Convergence of IoT and cognitive radio networks: A survey of applications, techniques, and challenges. IEEE Access, 11, 71097–71112. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3294091
Musa, A., Salameh, H. B., Halloush, R., Bataineh, R., & Qasaymeh, M. M. (2024). Variable rate power-controlled batch-based channel assignment for enhanced throughput in cognitive radio networks. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 5, 175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijin.2024.04.001
Arteaga, A., Spedes, S. C., & Azurdia-Meza, C. A. (2022). Toward the coexistence of cognitive networks for vehicular communications on TVWS for IEEE std. 802.22. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 8(3), 1316–1331.
Shehadeh, H. A., Jebril, I. H., Wang, X., Chu, S.-C., & Idna, M. I. Y. (2023). Optimal topology planning of electromagnetic waves communication network for underwater sensors using multi-objective optimization algorithms (MOOAs). Automatika, 64(2), 315–326. https://doi.org/10.1080/00051144.2022.2123761
Mwaimu, M. P., Majham, M., Ronoh, K. K., Michael, K., & Sinde, R. S. (2022). Improved resource allocation model for reducing interference among secondary users in TV white space for broadband services. IEEE Access, 10, 118981–118991. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3220628
Ahmad, W. .S. .H. .M. .W., Radzi, N. .A. .M., Samidi, F. .S., Ismail, A., Abdullah, F., Jamaludin, M. .Z., & Zakaria, M. .N. (2020). 5G technology: Towards dynamic spectrum sharing using cognitive radio networks. IEEE Access, 8, 14460–14488. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2966271
Azdemir, T. (2019). Performance evaluation of NOMA-based cooperative communications over cascaded Rician fading channels. In 2019 27th signal processing and communications applications conference (SIU), (pp. 1– 4). https://doi.org/10.1109/SIU.2019.8806273
Huaizhou, S. H. I., Prasad, R. V., Onur, E., & Niemegeers, I. G. M. M. (2014). Fairness in wireless networks: Issues, measures and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. https://doi.org/10.1109/SURV.2013.050113.00015
Uppal, N., Gangadharappa, M. (2021). A survey on spectral and energy efficient next-generation wireless networks. In 2021 8th International conference on computing for sustainable global development (INDIACom), (pp. 155–160). https://doi.org/10.1109/INDIACom51348.2021.00028
Siddiqi, M. Z., Wuttisittikulkij, L., Mirza, I. S., Chaudhary, S., Paranianifard, A. (2022). Adaptive modulation and power allocation in green cognitive radio networks. In 2022 19th International conference on electrical engineering/electronics, computer, telecommunications and information technology (ECTI-CON), (pp. 1–4) . https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTI-CON54298.2022.9795490
Liu, C., Yin, J., Xu, Y. (2023). Adaptive live streaming for multi-user access with fairness guarantee. In 2023 IEEE International symposium on broadband multimedia systems and broadcasting (BMSB), (pp. 1–6) . https://doi.org/10.1109/BMSB58369.2023.10211604
Di, Z., Zhong, Z., Pengfei, Q., Hao, Q., & Bin, S. (2024). Resource allocation in multi-user cellular networks: A transformer-based deep reinforcement learning approach. China Communications. https://doi.org/10.23919/JCC.ea.2021-0665.202401
Panayiotou, T., & Ellinas, G. (2024). Balancing efficiency and fairness in resource allocation for optical networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 21(1), 389–401. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSM.2023.3304426
Rezaeinia, N., Gez, J., & Guajardo, M. (2023). On efficiency and the Jain’s fairness index in integer assignment problems. Computational Management Science, 20(1), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10287-023-00477-9
Trankatwar, S., & Wali, P. (2024). Power allocation scheme for sum rate and fairness trade-off in downlink NOMA networks. Computer Communications, 221, 78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2024.04.018. . ID: 271515.
Anis, F., Hussein, M., Diasty, S. E., Elazeem, M. H. A. (2024). On dynamic resource allocation schemes for D2D communications over ultra-dense 5G cellular networks. In 2024 6th International Youth conference on radio electronics, electrical and power engineering (REEPE), (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/REEPE60449.2024.10479760
Awoyemi, B. S., Maharaj, J. T. B., & Alfa, A. S. (2016). Solving resource allocation problems in cognitive radio networks: A survey. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0673-6
Zheng, H., Li, H., Hou, S., & Song, Z. (2018). Joint resource allocation with weighted max-min fairness for NOMA-enabled V2X communications. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877199
Sokun, H. U., Bedeer, E., Gohary, R. H., Yanikomeroglu, H. (2018). Fairness-oriented resource allocation for energy efficiency optimization in uplink OFDMA networks. In 2018 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/WCNC.2018.8377327
Gautam, S., Lagunas, E., Chatzinotas, S., & Ottersten, B. (2021). Feasible point pursuit and successive convex approximation for transmit power minimization in SWIPT-multigroup multicasting systems. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking., 5, 884. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGCN.2021.3050736
Noorivatan, N., Mahboobi, B. (2020). Joint user association and power-bandwidth allocation in heterogeneous cellular networks. In 2020 10th International symposium on telecommunications (IST), (pp. 96–102). https://doi.org/10.1109/IST50524.2020.9345814
Wu, J., Shim, B. (2021). Power minimization of intelligent reflecting surface-aided uplink IoT networks. In 2021 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/WCNC49053.2021.9417397
Ahmed, S., Chowdhury, M. Z., & Jang, Y. M. (2020). Energy-efficient UAV-to-user scheduling to maximize throughput in wireless. Networks. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2969357
Zhu, Y., Hu, Y., Chang, Z., Schmeink, A. (2019). Throughput maximization of low-latency communication with imperfect CSI in finite blocklength regime. In 2019 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/WCNC.2019.8885564
Sun, X., & Dai, L. (2020). Towards fair and efficient spectrum sharing between LTE and WiFi in unlicensed bands: Fairness-constrained throughput maximization. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 19, 2713. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2020.2967702
Xie, R., Ji, H., Si, P., Li, M., Li, Y. (2010). Optimal joint power and transmission time allocation in cognitive radio networks. In 2010 IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference, (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/WCNC.2010.5506153
Naeem, M., Anpalagan, A., Jaseemuddin, M., & Lee, D. C. (2014). Resource allocation techniques in cooperative cognitive radio. Networks. https://doi.org/10.1109/SURV.2013.102313.00272
Shah, S. M. T., Hamood, M. A., Arslan, H. (2021). Efficient spectral access in distributed cooperative cognitive radio networks. In 2021 IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Fall), (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/VTC2021-Fall52928.2021.9625274
Tang, J., Hincapie, R., Xue, G., Zhang, W., & Bustamante, R. (2010). Fair bandwidth allocation in wireless mesh networks with cognitive radios. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology., 59, 1487. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2009.2038478
Tang, L., Wang, H., Chen, Q. (2010). Power allocation with max-min fairness for cognitive radio networks. In 2010 Global Mobile Congress, (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/GMC.2010.5634564
Boyd, S., Kim, S. J., Vandenberghe, L., & Hassibi, A. (2007). A tutorial on geometric programming. Optimization and Engineering, 8(1), 67–127.
Li, L., Pal, M., Yang, Y. R. (2008). Proportional fairness in multi-rate wireless LANS. In IEEE INFOCOM 2008-The 27th Conference on Computer Communications, (pp. 1004–1012). https://doi.org/10.1109/INFOCOM.2008.154
Tran, L., Cha, H., & Park, W. (2017). RF power harvesting: A review on designing methodologies and applications. Micro and Nano Systems Letters, 5(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40486-017-0051-0
Poposka, M., Hadzi-Velkov, Z., & Pejoski, S. (2020). Fairness optimization of fixed-rate wireless networks with RF energy harvesting transmitters. IEEE Communications Letters., 24, 2859. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3020876
Dai, L., Wang, B., Ding, Z., Wang, Z., Chen, S., & Hanzo, L. (2018). A survey of non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials., 20, 2294. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2835558
Khales, F. A., Hodtani, G. A. (2017). An evaluation of the coverage region for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) based on power allocation factor. In 2017 Iran Workshop on Communication and Information Theory (IWCIT), (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/IWCIT.2017.7947675
Ding, H., Zhao, F., Tian, J., & Zhang, H. (2020). Fairness-driven energy efficient resource allocation in uplink MIMO enabled HetNets. IEEE Access., 8, 37229. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975301
Gu, B., Zhang, C., Wang, H., Yao, Y., & Tan, X. (2019). Power control for cognitive M2M communications underlaying cellular with fairness concerns. IEEE Access., 7, 80789. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2914157
Saif, R., Pourgharehkhan, Z., ShahbazPanahi, S., Bavand, M., & Boudreau, G. (2023). Underlay spectrum sharing in massive MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 9(3), 647–663. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCCN.2023.3252542
Thakur, S., & Singh, A. (2021). Underlay cognitive radio with instantaneous interference constraint: A secrecy performance. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology., 70, 7839. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2021.3093071
Sharmila, A., Dananjayan, P. (2019). Spectrum sharing techniques in cognitive radio networks: A survey. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking (ICSCAN), (pp. 1–4). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSCAN.2019.8878714
Alemdar, T. Z., Onur, E. (2021). Max-min fair bandwidth allocation in millimeter-wave radio clusters. In 2021 17th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), (pp. 77–83). https://doi.org/10.23919/CNSM52442.2021.9615530
Funding
No funding or grants were received by the authors for the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Uyoata Uyoata and Oluwafemi Ipinnimo have contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests in the preparation of this manuscript.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: In this article the author’s name Uyoata Uyoata was incorrectly written as Uyota Uyota. The original article has been corrected.
Appendix
Appendix
For notation simplicity, we rewrite the lower bound constraints C1 and C2 of \( \textbf{P2} \) as;
and
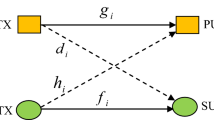
respectively. The concave functions are negative semi-definite functions. In the optimization problem P2, the \(Q_1(b_1,p_1)\) and \( Q_2(b_2,p_2)\) bound the epigraph function of the optimization objective function. Our goal is to prove that they are concave functions with the facts that the functions are negative semi-definite. The function Q(x, y) is said to be negative semi-definite, if and only if the Hessian of Q(x, y) has eigenvalues ( \(\psi _l \)) that are non-positive. That is \( \psi _l \le 0, l=1,2,...L. \), where the Hessian matrix F(x, y) is of dimension L. Also, \(R^i_{SR_k} = b_1 \log \left( 1+ \frac{p_1 g_1}{N_0b_1}\right) \) and \( R^i_{R_kD_i} = b_2 \log \left( 1+ \frac{p_2 g_2}{N_0b_2}\right) \).
Firstly, for the negative semi-definite proof of \( Q_1(b_1, p_1)\), we define the Hessian matrix \( H_{Q_1(b_1,p_1)} \) as;
Therefore, we have the Hessian matrix \( H_{Q_1(b_1,p_1)} \) as;
The eigenvalues \( \psi _1 \) and \(\psi _2 \) of \( H_{Q_1(b_1,p_1)}\) are the first principal minors of \( H_{Q_1(b_1,p_1)} \). Hence,
The Hessian matrix determinant is the last eigenvalue \( \psi _3 \).
Therefore, with \( \psi _1 <0 \), \( \psi _2 <0 \) and \( \psi _3 = 0 \). Consequently, \( H_{Q_1(b_1,p_1)} \) is negative semi-definite. Thus in \( B^i_S \) and \( P^i_S \), \( R^i_{SR_k} \) is a concave function.
Secondly, for the negative semi-definite proof of \( Q_2 (b_2, p_2)\), we the Hessian matrix \( H_{Q_2(b_2,p_2)} \) as;
Thus, the Hessian matrix \( H_{Q_2(b_2,p_2)} \) is;
The corresponding eigenvalues \( \psi _1 \) and \(\psi _2 \) of \( H_{Q_2(b_2,p_2)}\) are the first principal minors of \( H_{Q_2(b_2,p_2)} \). Hence,
while the Hessian matrix determinant is the eigenvalue \( \psi _3 \).
Therefore, with \( \psi _1 <0 \), \( \psi _2 <0 \) and \( \psi _3 = 0 \), thus \( Q_2(b_2,p_2) \) is negative semi-definite. Since both \(R^i_{S R_k}\) and \(R^i_{R_k D_i} \) are concave functions, thus the objective function of optimization problem \( \textbf{ P2} \) is a concave function.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Obayiuwana, E., Uyoata, U. & Ipinnimo, O. Radio Resource Allocation Fairness in Cooperative Cognitive Radio Relay Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 136, 2595–2619 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11422-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11422-7