Abstract
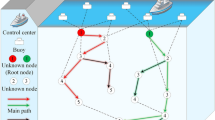
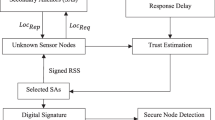
In Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks, ensuring precise localization of sensor nodes is crucial. Existing localization algorithms heavily rely on pre-deployed and known anchor nodes to compute and determine the positions of other nodes. However, anchor nodes may be compromised or misled in practical scenarios, resulting in localization inaccuracies. To address this challenge, a proficient iterative localization algorithm is proposed in Garg and Varna (IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 7: 717–730, 2012), which selects known nodes as reference anchors to locate unknown nodes and analyzes their performance under non-collaborative attacks. Therefore, a novel localization algorithm is introduced to counter collaborative attacks, utilizing time difference of arrival ranging mapping and selective minimum gradient principles from the AdaDelta Gradient Descent (AGD) algorithm to iteratively eliminate deceptive information transmitted by interfering nodes, thereby enhancing localization accuracy. Validations demonstrate its efficacy in combating collaborative network attacks under certain conditions and significantly improving localization performance. Simulation experiments confirm its robustness even under network attacks, ensuring the reliable operation of UWSNs.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Garg, R., & Varna, L. A. (2012). An efficient gradient descent approach to secure localization in resource constrained wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7, 717–730.
Yan, J., Meng, Y., Yang, X., Luo, X., & Guan, X. (2020). Privacy-preserving localization for underwater sensor networks via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on information forensics and security, 16, 1880–1895.
Toky, A., Singh, R. P., & Das, S. (2020). Localization schemes for underwater acoustic sensor networks - a review. Computer Science Review, 37, 100241.
Su, X., Ullah, I., Liu, X., & Choi, D. (2020). A review of underwater localization techniques, algorithms, and challenges. Journal of Sensors, 2020(1), 6403161.
Han, Y., Sun, D., Zheng, C., & Zhang, J. (2018). Centralized underwater node localization using range based multilateral accumulation method (RBMAM). Applied Acoustics, 138, 115–120.
Misra, S., & Ojha, T. (2021). SecRET: Secure range-based localization with evidence theory for underwater sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems (TAAS), 15, 1–26.
Xu, X., Wang, G., Ren, Y., & Liu, X. (2017). a secure localization algorithm based on confidence constraint for underwater wireless sensor networks. In International conference on information science and applications (pp. 46–49).
Das, A. P., & Thampi, S. M. (2015). Secure communication in mobile underwater wireless sensor networks. In 2015 international conference on advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI) (pp. 2164–2173).
Wang, S., Lin, Y., Tao, H., Sharma, P. K., & Wang, J. (2019). Underwater acoustic sensor networks node localization based on compressive sensing in water hydrology. Sensors, 19, 4552–4565.
Sabra, A., & Fung, W. K. (2020). A fuzzy cooperative localisation framework for underwater robotic swarms. Sensors, 20(19), 5496.
Zhang, R., & Zhang, Y. (2010). Wormhole-resilient secure neighbor discovery in underwater acoustic networks. In 2010 proceedings IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1–9).
Han, G., Liu, L., Jiang, J., Shu, L., & Rodrigues, J. J. (2016). A collaborative secure localization algorithm based on trust model in underwater wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 16, 229–241.
Liu, Z., Deng, X., & Li, J. (2017). A secure localization algorithm based on reputation against wormhole attack in UWSNS. In 2017 international symposium on intelligent signal processing and communication systems (ISPACS) (pp. 695–700).
Su, Y., Li, L., Fan, R., Liu, Y., & Jin, Z. (2022). A secure transmission scheme with energy-efficient cooperative jamming for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 22(21), 21287–21298.
Han, Y., Zheng, C., & Sun, D. (2015). Localization of large scale underwater sensor networks based on recursive position estimation. In OCEANS 2015-MTS/IEEE Washington (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Zhou, Z., Cui, J. H., & Zhou, S. (2007). Localization for large-scale underwater sensor networks. In International conference on research in networking (pp. 108–119).
Sun, S., Qin, S., Hao, Y., Zhang, G., & Zhao, C. (2020). Underwater acoustic localization of the black box based on generalized second-order time difference of arrival (gstdoa). IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 59(9), 7245–7255.
Zhou, Z., Cui, J. H., & Zhou, S. (2010). Efficient localization for large-scale underwater sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 8, 267–279.
Cheng, X., Shu, H., Liang, Q., & Du, D. H. C. (2008). Silent positioning in underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57, 1756–1766.
Cheng, W., Thaeler, A., Cheng, X., Liu, F., Lu, X., & Lu, Z. (2009). Time-synchronization free localization in large scale underwater acoustic sensor networks. In 2009 29th IEEE international conference on distributed computing systems workshops (pp. 80–87).
Li, S., Sun, H., & Esmaiel, H. (2020). Underwater TDOA acoustical location based on majorization-minimization optimization. Sensors, 20, 1–19.
Ma, Y. (2020, May). A simulation of the TDOA chan localization used in the train station and indoor location system. In 13th Asia Pacific transportation development conference (pp. 450–459). Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers.
Dang, B., Li, J., & Liao, G. (2012). Taylor polynomial expansion based waveform correlation cancellation for bistatic MIMO radar localization. Signal Processing, 92, 1404–1410.
Shi, X., Mao, G., Yang, Z., & Chen, J. (2017). MLE-based localization and performance analysis in probabilistic LOS/NLOS environment. Neurocomputing, 270, 101–109.
Liu, Y., Guo, F., Yang, L., & Jiang, W. (2015). An improved algebraic solution for TDOA localization with sensor position errors. IEEE Communications Letters, 19, 2218–2221.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant number (52171337), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, Grant number (RZ2100000416), and supported in part by the key project of Hainan Province under the Grant (ZDYF2020199).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no Conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Zhou, X., Xing, G. et al. Localization of Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks for Ranging Interference based on the AdaDelta Gradient Descent Algorithm. Wireless Pers Commun 137, 1189–1216 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11458-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11458-9