Abstract
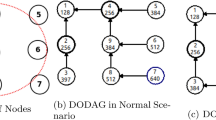
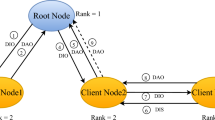
Routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks (RPL) is the standard routing protocol specified by the Internet engineering task force (IETF) for Low power and lossy Nnetworks (LLNs) based Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Although RPL gives many benefits to LLNs, due to the resource-constrained and easily tamperable nature of LLN devices, LLNs are vulnerable to a wide range of attacks that primarily alter the functioning of the RPL. One such attack is known as a Network partitioning attack (NPA). An NPA in RPL occurs when an attacker node intentionally divides a network into disjoint segments, preventing communication between nodes that may be previously able to communicate. This can happen when an attacker does not complete the route registration step at the root node, exploits the rank property of RPL, and continues the standard Destination advertisement object (DAO) forwarding technique of RPL during the node joining and DAG maintenance phase. Consequently, it segregates the section of nodes from the root node. In the literature, Enhanced-RPL (ERPL) is the only solution proposed to address NPA. However, our study shows that ERPL further induces fake Destination Advertisement Object Acknowledgement (DAO-ACK) and dropping DAO Attack, making it unsuitable for deployment in real-world applications. Our analysis indicates that the performance metrics of the network are not improved with the existing mitigation technique when the attacker unicasts fake DAO-ACK packets to victim client nodes. Our key idea is to improve the existing mitigation technique (ERPL) to incorporate an effective NPA detection approach that authenticates the DAO-ACK packet sent from parent nodes to client nodes. Our proposed approach, SecRPLNPA, has been integrated and thoroughly tested using the Cooja simulator. We have conducted a performance assessment of SecRPLNPA comparing it against standard RPL and ERPL. Our empirical results suggest that in both stationary and mobile scenarios, SecRPLNPA proficiently detects and mitigates Network Partitioning Attacks while causing only minimal impact on resource-constrained nodes.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors.
Abbreviations
- OSPF:
-
Open shortest path first
- IETF:
-
Internet engineering task force
- 6LoWPAN:
-
IPv6 over low-power wireless personal area networks
- IoT:
-
Internet of Things
- LLN:
-
Low-power and lossy network
- DIS:
-
DODAG information solicitation
- AODV:
-
Adhoc on-demand distance vector
- DODAG:
-
Destination oriented directed acyclic graph
- DAO:
-
Destination advertisement object
- RPL:
-
Routing protocol for low power and lossy networks
- DIO:
-
DODAG information object
- NPA:
-
Network partitioning attack
- ERPL:
-
Enhanced-RPL
- OF:
-
Objective functions
- DAO-ACK:
-
Destination advertisement object-acknowledgment
- MRHOF:
-
Minimum rank with hysteresis objective function
- NS:
-
Non-storing
References
Espinoza, H., Kling, G., McGroarty, F., O’Mahony, M., & Ziouvelou, X. (2020). Estimating the impact of the Internet of Things on productivity in Europe. Heliyon, 6(5), 03935.
Safaei, B., Monazzah, A. M. H., & Ejlali, A. (2021). ELITE: An elaborated cross-layer RPL objective function to achieve energy efficiency in Internet-of-Things devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(2), 1169–1182.
Napiah, M. N., Bin Idris, M. Y. I., Ramli, R., & Ahmedy, I. (2018). Compression header analyzer intrusion detection system (CHA - IDS) for 6LoWPAN communication protocol. IEEE Access, 6, 16623–16638.
Mayzaud, A., Badonnel, R., & Chrisment, I. (2016). A taxonomy of attacks in RPL-based Internet of Things. International Journal of Network Security, 18(3), 459–473.
Murali, S., & Jamalipour, A. (2020). A lightweight intrusion detection for Sybil attack under mobile RPL in the Internet of Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(1), 379–388.
Sharma, G., Grover, J., & Verma, A. (2023). Performance evaluation of mobile RPL-based IoT networks under version number attack. Computer Communications, 197, 12–22.
Airehrour, D., Gutierrez, J., & Ray, S. K. (2016). Secure routing for Internet of Things: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 66, 198–213.
Winter, T., Thubert, P., Brandt, A., Hui, J., Kelsey, R., Levis, P., Pister, K., Struik, R., Vasseur, J.-P., & Alexander, R. (2012). RPL: Ipv6 routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks. Technical report.
Musaddiq, A., Zikria, Y. B., Kim, S. W., et al. (2020). Routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks for heterogeneous traffic network. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2020(1), 1–23.
Gaddour, O., & Koubâa, A. (2012). RPL in a nutshell: A survey. Computer Networks, 56(14), 3163–3178.
Vasseur, J. P., Agarwal, N., Hui, J., Shelby, Z., Bertrand, P., & Chauvenet, C. (2011). RPL the IP routing protocol designed for low power and lossy networks. Internet Protocol for Smart Objects (IPSO) Alliance, 36, 1–20.
Lamaazi, H., & Benamar, N. (2020). A comprehensive survey on enhancements and limitations of the RPL protocol: A focus on the objective function. Ad Hoc Networks, 96, 102001.
Muzammal, S. M., Murugesan, R. K., & Jhanjhi, N. (2020). A comprehensive review on secure routing in Internet of Things: Mitigation methods and trust-based approaches. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(6), 4186–4210.
Butun, I., Österberg, P., & Song, H. (2019). Security of the Internet of Things: Vulnerabilities, attacks, and countermeasures. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 22, 616–644.
Bang, A. O., & Rao, U. P. (2022). EMBOF-RPL: Improved RPL for early detection and isolation of rank attack in RPL-based internet of things. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 15(1), 642–665.
Verma, A., & Ranga, V. (2020). Security of RPL based 6LoWPAN networks in the internet of things: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20(11), 5666–5690.
Sahay, R., Geethakumari, G., & Mitra, B. (2021). A novel network partitioning attack against routing protocol in internet of things. Ad Hoc Networks, 121, 102583.
Verma, A., & Ranga, V. (2020). Mitigation of DIS flooding attacks in RPL-based 6LoWPAN networks. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 31(2), 3802.
Pu, C., & Choo, K.-K.R. (2022). Lightweight Sybil attack detection in IoT based on bloom filter and physical unclonable function. Computers & Security, 113, 102541.
Ghaleb, B., Al-Dubai, A., Ekonomou, E., Qasem, M., Romdhani, I., & Mackenzie, L. (2018). Addressing the DAO insider attack in RPL’s Internet of Things networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(1), 68–71.
Kiran, U. (2022). Ids to detect worst parent selection attack in RPL-based IoT network. In 2022 14th International Conference on COMmunication Systems & NETworkS (COMSNETS), pp. 769–773. IEEE.
Pu, C., & Song, T. (2018). Hatchetman attack: A denial of service attack against routing in low power and lossy networks. In 2018 5th IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud)/2018 4th IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing and Scalable Cloud (EdgeCom), pp. 12–17. IEEE.
Perazzo, P., Vallati, C., Anastasi, G., & Dini, G. (2017). DIO suppression attack against routing in the internet of things. IEEE Communications Letters, 21(11), 2524–2527.
Cam-Winget, N., Hui, J., & Popa, D. (2017). Applicability statement for the routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks (RPL) in advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) networks. Technical report.
Verma, A., & Ranga, V. (2020). CoSec-RPL: Detection of copycat attacks in RPL based 6LoWPANs using outlier analysis. Telecommunication Systems, 75(1), 43–61.
Kaliyar, P., Jaballah, W. B., Conti, M., & Lal, C. (2020). Lidl: localization with early detection of Sybil and wormhole attacks in IoT networks. Computers & Security, 94, 101849.
Challa, S., Wazid, M., Das, A. K., Kumar, N., Reddy, A. G., Yoon, E.-J., & Yoo, K.-Y. (2017). Secure signature-based authenticated key establishment scheme for future IoT applications. IEEE Access, 5, 3028–3043.
Park, M.-H. (2012). Challenge-response based ACK message authentication. Electronics Letters, 48(16), 1021–1023.
Sharma, G., Grover, J., & Verma, A. (2023). Performance evaluation of mobile RPL-based IoT networks under version number attack. Computer Communications, 197, 12–22.
Alexander, R., Brandt, A., Vasseur, J., Hui, J., Pister, K., Thubert, P., Levis, P., Struik, R., Kelsey, R., & Winter, T. (2012). RPL: IPv6 Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks. RFC Editor. https://doi.org/10.17487/RFC6550. https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc6550.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shefali Goel and Abhishek Verma wrote the main manuscript text. Abhishek Verma and Vinod Kumar Jain supervised the implementation. Shefali Goel prepared the figures, graphs. Vinod Kumar Jain proofread the manuscript and revised it critically to include technical content. All authors reviewed and did proofreading.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, S., Verma, A. & Jain, V. Design and Implementation of a Lightweight Mitigation Solution for Addressing Network Partitioning Attack Against RPL Protocol. Wireless Pers Commun 139, 2027–2050 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11704-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11704-0