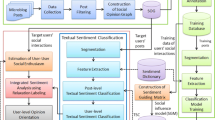
Abstract
Recently, more and more researchers have focused on the problem of analyzing people’s sentiments and opinions in social media. The sentiment lexicon plays a crucial role in most sentiment analysis applications. However, the existing thesaurus based lexicon building methods suffer from the coverage problems when faced with the new words and new meanings in social media. On the other hand, the previous learning based methods usually need intensive expert efforts for annotating training datasets or designing extraction patterns. In this paper, we observe that the graphical emoticons are good natural sentiment labels for the corresponding microblog posts and a word-emoticon mutual reinforcement ranking model is proposed to learn the sentiment lexicon from the massive collection of microblog data. We integrate the emoticons and candidate sentiment words in the microblogs to construct a two-layer graph, on which a random walk is run for extracting the top ranked words as a sentiment lexicon. Extensive experiments were conducted on a benchmark dataset with various topics. The results validate the effectiveness of the proposed methods in building sentiment lexicon from microblog data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baccianella, S., Esuli, A., Sebastiani, F.: SentiWordNet 3.0: an enhanced lexical resource for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC), pp. 2200–2204 (2010)
Barbosa, L., Feng, J.: Robust sentiment detection on twitter from biased and noisy data. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING), pp. 36–44 (2010)
Bermingham, A., Smeaton, A.F.: Classifying sentiment in microblogs: is brevity an advantage? In: Proceedings of the the 19th ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), pp. 1833–1836 (2010)
Bollegala, D., Weir, D., Carroll, J.: Using multiple sources to construct a sentiment sensitive thesaurus for cross-domain sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 132–141 (2011)
Brody, S., Diakopoulos, N.: Cooooooooooooooollllllllllllll!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Using word lengthening to detect sentiment in microblogs. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 562–570 (2011)
Choi, Y., Cardie, C.: Adapting a polarity lexicon using integer linear programming for domain-specific sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 590–598 (2009)
Cui, H., Mittal, V., Datar, M.: Comparative experiments on sentiment classification for online product reviews. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-First National Conference on Artificial Intelligence and the Eighteenth Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference (AAAI), pp. 1265–1270 (2006)
Davidov, D., Tsur, O., Rappoport, A.: Enhanced sentiment learning using twitter hashtags and smileys. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING), pp. 241–249 (2010)
Diakopoulos, N., Shamma, D.A.: Characterizing debate performance via aggregated twitter sentiment. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), pp. 1195–1198 (2010)
Esuli, A., Sebastiani, F.: PageRanking wordnet synsets: an application to opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the 45th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 424–431 (2010)
Feldman, R.Commun. ACM. 56(4), 82–89 (2013)
Gao, D., Wei, F., Li, W., Liu, X., Zhou, M.: Co-training based bilingual sentiment lexicon learning. In: Proceedings of the 27th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), pp. 26–28 (2013)
Hassan, A., Radev, D.: Identifying text polarity using randomWalks. In: Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 395–403 (2010)
Hong, Y., Kwak, H., Baek, Y., Moon, S.: Tower of Babel: a crowdsourcing game building sentiment lexicons for resource-scarce languages. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International World Wide Web Conference (WWW), pp. 549–556 (2013)
HowNet. http://www.keenage.com Accessed 1 Mar 2012
Hu, M., Liu, B.: Mining and summarizing customer review. In: Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), pp. 168–177 (2004)
Jiang, L., Yu, M., Zhou, M., Liu, X., Zhao, T.: Target-dependent twitter sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 151–160 (2011)
Jijkoun, V., Rijke, M., Weerkamp, W.: Generating focused topic-specific sentiment lexicons. In: Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 151–160 (2010)
Jin, W., Ho, H.H., Srihari, R.K.: OpinionMiner: a novel machine learning system for web opinion mining and extraction. In: Proceedings of the the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), pp. 1195–1204 (2009)
Kaji, N., Kitsuregawa, M.: Building lexicon for sentiment analysis from massive collection of html documents. In: Proceedings of the 2007 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning (EMNLP), pp. 1075–1083 (2007)
Kanayama, H., Nasukawa, T.: Fully automatic lexicon expansion for domain-oriented sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 355–363 (2006)
Kim, S.M., Hovy, E.H.: Determining the sentiment of opinions. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING), pp. 1367–1373 (2004)
Ku, L., Chen, H.: Mining opinions from the web: beyond relevance retrieval. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 58(12), 1838–1850 (2007)
Leung, C., Chan, S., Chung, F., Ngai, G.: A probabilistic rating iference framework for mining user preferences from reviews. World Wide Web 14(2), 187–215 (2011)
Li, F., Han, C., Huang, M., Zhu, X., Xia, Y.J., Zhang, S., Yu, H.: Structure-aware review mining and summarization. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING), pp. 653–661 (2010)
Liu, Y., Yu, X., An, A., Huang, X.: Riding the tide of sentiment change: Sentiment analysis with evolving online reviews. World Wide Web 16(4), 477–496 (2013)
Lu, Y., Castellanos, M., Dayal, U., Zhai, C.: Automatic construction of a context-aware sentiment lexicon: an optimization approach. In: Proceedings of the the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW), pp. 347–356 (2011)
Mohammad, S., Dunne, C., Dorr, B.: Generating high-coverage semantic orientation lexicons from overtly marked words and a thesaurus. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 599–608 (2009)
Pang, B., Lee, L.: Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Found. Trends Inf. Retr. 2(1–2), 1–135 (2007)
Pak, A., Paroubek, P.: Twitter as a corpus for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC), pp. 1320–1326 (2010)
Qiu, G., Liu, B., Bu, J., Chen, C.: Expanding domain sentiment lexicon through double propagation. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Joint Conference on Artificial intelligence (IJCAI), pp. 1199–1204 (2009)
Rao, Y., Quan, X., Wenyin, L., Li, Q., Chen, M.: Building word-emotion mapping dictionary for online news. In: Proceedings of the first International Workshop on Sentiment Discovery from Affective Data (SDAD), pp. 28–39 (2012)
Si, J., Mukherjee, A., Liu, B., Li, Q., Li, H., Deng, X.: Exploiting topic based twitter sentiment for stock prediction. In: Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 24–29 (2013)
Speriosu, M., Sudan, N., Upadhyay, S., Baldridge, J.: Twitter polarity classification with label propagation over lexical links and the follower graph. In: Proceedings of 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 53–63 (2011)
Turney, P.D.: Thumbs up or thumbs down? Semantic orientation applied to unsupervised classification of reviews. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pp. 417–424 (2002)
Yang, J., Leskovec, J.: Patterns of temporal variation in online media. In: Proceedings of the Forth International Conference on Web Search and Web Data Mining (WSDM), pp. 177–186 (2011)
Velikovich, L., Blair-Goldensohn, S., Hannan, K., McDonald, R.T.: The viability of web-derived polarity lexicons. In: Proceedings of the North American Chapter of the Association of Computational Linguistics (NAACL), pp. 777–785 (2010)
Zhang, J., Kawai, Y., Kumamoto, T., Tanaka, K.: A novel visualization method for distinction of web news sentiment. In: Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering (WISE), pp. 181–194 (2009)
Zhang, X., Zhou, Y.: Holistic approaches to identifying the sentiment of blogs using opinion words. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering (WISE), pp. 15–28 (2011)
Zhang, R., Tran, T., Mao, Y.: Opinion helpfulness prediction in the presence of “Words of Few Mouths”. World Wide Web J. 15(2), 117–138 (2012)
Zhao, J., Dong, L., Wu, J., Xu, K.: MoodLens: an emoticon-based sentiment analysis system for chinese tweets. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), pp. 1528–1531 (2012)
Zhu, X., Ghahramani, Z.: Learning from labeled and unlabeled data with label propagation. Technical report, CMU-CALD-02 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S., Song, K., Wang, D. et al. A word-emoticon mutual reinforcement ranking model for building sentiment lexicon from massive collection of microblogs. World Wide Web 18, 949–967 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-014-0289-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-014-0289-x