Abstract
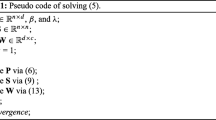
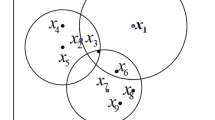
Spectral clustering is an important component of clustering method, via tightly relying on the affinity matrix. However, conventional spectral clustering methods 1). equally treat each data point, so that easily affected by the outliers; 2). are sensitive to the initialization; 3). need to specify the number of cluster. To conquer these problems, we have proposed a novel spectral clustering algorithm, via employing an affinity matrix learning to learn an intrinsic affinity matrix, using the local PCA to resolve the intersections; and further taking advantage of a robust clustering that is insensitive to initialization to automatically generate clusters without an input of number of cluster. Experimental results on both artificial and real high-dimensional datasets have exhibited our proposed method outperforms the clustering methods under comparison in term of four clustering metrics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias-Castro, E., Lerman, G., Zhang, T.: Spectral clustering based on local PCA. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18, 9:1–9:57 (2017)
Kang, S.H., Sandberg, B., Yip, A.M.: A regularized k-means and multiphase scale segmentation. Inverse Probl. Imaging 5(2), 407–429 (2017)
Kanungo, T., Mount, D.M., Netanyahu, N.S., Piatko, C.D., Silverman, R., Wu, A.Y.: An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(7), 881–892 (2002)
Lei, C., Zhu, X.: Unsupervised feature selection via local structure learning and sparse learning, p. 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042--017--5381--7 (2017)
Nie, F., Wang, X., Huang, H.: Clustering and projected clustering with adaptive neighbors. In: SIGKDD, pp. 977–986 (2014)
Nie, F., Zhu, W., Li, X.: Unsupervised feature selection with structured graph optimization. In: AAAI, pp. 1302–1308 (2016)
Pedrycz, W., Waletzky, J.: Fuzzy clustering with partial supervision. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 27(5), 787–795 (1997)
Rongyao, H.U., Zhu, X., Cheng, D., He, W., Yan, Y., Song, J., Zhang, S.: Graph self-representation method for unsupervised feature selection. Neurocomputing 220, 130–137 (2017)
Shah, S.A., Koltun, V.: Robust continuous clustering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114(37), 9814 (2017)
Stella, X., Shi, J.: Multiclass spectral clustering. In: ICCV, pp. 313–319 (2003)
von Luxburg, U.: A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat. Comput. 17(4), 395–416 (2007)
Yu, C.-Y., Li, Y., Liu, A.-L., Liu, J.-H.: A novel modified kernel fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm on image segementation. In: CSE, pp. 621–626 (2011)
Zhang, S., Li, X., Zong, M., Zhu, X., Wang, R.: Efficient knn classification with different numbers of nearest neighbors. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29 (5), 1774–1785 (2018)
Zhang, S., Li, X., Zong, M., Zhu, X., Cheng, D.: Learning k for kNN classification. ACM TIST 8(3), 43:1–43:19 (2017)
Zhang, T., Liu, B.: Spectral clustering ensemble based on synthetic similarity. In: ISCID, pp. 252–255 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Zhao, Q., Jin, J., Wang, X., Cichocki, A.: A novel bci based on erp components sensitive to configural processing of human faces. J. Neural Eng. 9 (2), 026018 (2012)
Zhang, Y.U., Jin, J., Qing, X., Wang, B., Wang, X.: Lasso based stimulus frequency recognition model for ssvep bcis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 7(2), 104–111 (2012)
Zheng, W., Zhu, X., Wen, G., Zhu, Y., Yu, H., Gan, J.: Unsupervised feature selection by self-paced learning regularization. Pattern Recognition Letters. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.06.029 (2018)
Zheng, W., Zhu, X., Zhu, Y., Hu, R., Lei, C.: Dynamic graph learning for spectral feature selection. Multimedia Tools and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042--017--5272--y (2017)
Zhu, X., Huang, Z., Yang, Y., Shen, H.T., Xu, C., Luo, J.: Self-taught dimensionality reduction on the high-dimensional small-sized data. Pattern Recogn. 46 (1), 215–229 (2013)
Zhu, X., Li, X., Zhang, S.: Block-row sparse multiview multilabel learning for image classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(2), 450–461 (2016)
Zhu, X., Li, X., Zhang, S., Chunhua, J.U., Wu, X.: Robust joint graph sparse coding for unsupervised spectral feature selection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(6), 1263–1275 (2017)
Zhu, X., Li, X., Zhang, S., Zongben, X.U., Litao, Y.U., Wang, C.: Graph PCA hashing for similarity search. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 19(9), 2033–2044 (2017)
Zhu, X., Zhang, S., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Yang, L., Fang, Y: Low-rank sparse subspace for spectral clustering. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2018.2858782 (2018)
Zhu, X., Suk, H.-I., Huang, H., Shen, D.: Low-rank graph-regularized structured sparse regression for identifying genetic biomarkers. IEEE Trans. Big Data 3(4), 405–414 (2017)
Zhu, X., Suk, H.-I., Lee, S.-W., Shen, D.: Subspace regularized sparse multitask learning for multiclass neurodegenerative disease identification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(3), 607–618 (2016)
Zhu, X., Suk, H.-I., Wang, L., Lee, S.-W., Shen, D.: A novel relational regularization feature selection method for joint regression and classification in AD diagnosis. Med. Image Anal. 38, 205–214 (2017)
Zhu, X., Zhang, L., Zi, H.: A sparse embedding and least variance encoding approach to hashing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(9), 3737–3750 (2014)
Zhu, X., Zhang, S., Hu, R., Zhu, Y., Song, J.: Local and global structure preservation for robust unsupervised spectral feature selection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 30(3), 517–529 (2018)
Zhu, X., Zhang, S., Jin, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhuoming, X.U.: Missing value estimation for mixed-attribute data sets. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 23(1), 110–121 (2011)
Zhu, Y., Kim, M., Zhu, X., Yan, J., Kaufer, D., Guorong, W.U.: Personalized diagnosis for alzheimer’s disease. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 205–213 (2017)
Zhu, Y., Lucey, S.: Convolutional sparse coding for trajectory reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(3), 529–540 (2015)
Zhu, Y., Zhu, X., Kim, M., Kaufer, D., Guorong, W.U.: A novel dynamic hyper-graph inference framework for computer assisted diagnosis of neuro-diseases. In: International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the China Key Research Program (Grant No: 2016YFB1000905); the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No: 61573270 and 6167217); the Project of Guangxi Science and Technology (GuiKeAD17195062); the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Grant No: 2015GXNSFCB139011); Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (Grant No: YCSW2018093); the Guangxi Collaborative Innovation Center of Multi-Source Information Integration and Intelligent Processing; the Guangxi High Institutions Program of Introducing 100 High-Level Overseas Talents; and the Research Fund of Guangxi Key Lab of Multisource Information Mining & Security (18-A-01-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Deep Mining Big Social Data
Guest Editors: Xiaofeng Zhu, Gerard Sanroma, Jilian Zhang, and Brent C. Munsell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, G., Zhu, Y., Cai, Z. et al. Self-tuning clustering for high-dimensional data. World Wide Web 21, 1563–1573 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-018-0622-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-018-0622-x