Abstract
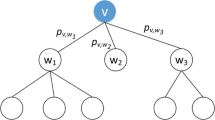
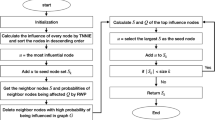
In the study of influence maximization in social networks, the speed of information dissemination decreases with increasing time and distance. The investigation of the characteristics of information dissemination is of great significance to the management and control of public opinion. A three-hop velocity decay propagation model is proposed to determine the propagation speed in information dissemination and the time and distance attenuation factors of information dissemination were modeled. We simulated the three-hop information propagation and developed an influence maximization algorithm based on the rate attenuation propagation model (IMMRA). Experiments using two example data sets showed that the proposed algorithm had higher accuracy and time efficiency than a greedy algorithm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kempe D, Kleinberg J, Tardos E. Maximizing the spread of influence in a social network .Proceeding s of the 9th AC M SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Washington, 2003:137–146
Goyal A,Wei Lu,Lakshmanan L V S.CELF++:optimizing the greedy algorithm for influence maximization in social networks. Proc of the 20th International Conference Companion on World Wide Web, 2011:47–48
Wei Chen,Yajun Wang,Siyu Yang. Efficient Influence Maximization in Social Networks. Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Paris, France, 2009:199–207
Chen, H., Wang, Y.: Threshold-based heuristic algorithm for influence maximization. Journal of Computer Research and Development. 49(10), 2181–2188 (2012)
Wang, J., Wang, Y., Feng, X.: A new hybrid algorithm for influence maximization in social networks. Chinese Journal of Computer. 34(10), 1956–1965 (2011)
Kyomin Jung,Wooram Heo,Wei Chen.IRIE: Scalable and Robust Influence Maximization in Social Networks. Data Mining(ICDM),2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on.2012:918–923, ISSN 1550-4786
Wang, W., Street, W.N.: Modeling and maximizing influence diffusion in social networks for viral marketing. Applied network science. 3(1), 6 (2018)
Kempe D, Kleinberg J, Tardos E. Maximizing the spread of influence in a social network .Proceeding s of the 9th AC M SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Washington, 2003:137–146
Song, G., Li, Y., Chen, X., He, X., Tang, J.: Influential node tracking on dynamic social network: an interchange greedy approach. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering. 99, 1–1 (2017)
Liu, B., Gao, C., Zeng, Y., Xu, D., Chee, Y.M.: Influence spreading path and its application to the time constrained social influence maximization problem and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science & Engineering. 26(8), 1904–1917 (2014)
Nguyen, H., Zheng, R.: On budgeted influence maximization in social networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications. 31(6), 1084–1094 (2013)
Lee J R , Chung C W . A Fast Approximation for Influence Maximization in Large Social Networks [J]. 2014
Gong, M., Song, C., Duan, C., et al.: An efficient Memetic algorithm for influence maximization in social networks [J]. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 11(3), 22–33 (2016)
Zheng H , Wu J . Friend Recommendation in Online Social Networks: Perspective of Social Influence Maximization[C]// 2017 26th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN). IEEE, 2017
J. Leskovec, A. Krause, C. Guestrin, C. Faloutsos, J. VanBriesen, and N. S. Glance, “Cost-effective outbreak detection in networks.” in KDD, 2007, pp. 420–429
Zhou, C., Zhang, P., Guo, J., Zhu, X., Guo, L.: Ublf: an upper bound based approach to discover influential nodes in social networks. In: ICDM (2013)
M. G. Rodriguez and B. Scholkopf, “Influence maximization in continuous time diffusion networks,” arXiv preprint arXiv: 1205.1682, 2012
Chen, W., Lin, T., Tan, Z., Zhao, M., & Zhou, X.. Robust influence maximization. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (pp. 795–804). ACM.2016
Y. Tang, Y. Shi, and X. Xiao, “Influence maximization in near linear time: a martingale approach,” in Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. ACM, 2015, pp. 1539–1554
Shi, Q., Wang, C., Chen, J., et al.: Location driven influence maximization: online spread via offline deployment [J]. Knowl.-Based Syst. 166, 30–41 (2019)
Sun, L., Huang, W., Yu, P.S., et al.: Multi-round influence maximization[C]//proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. ACM. 2249–2258 (2018)
Barabási, A.-L.: The origin of bursts and heavy tails in human dynamics [J]. Nature. (2005)
Vazquez A,Oliveira J G,DezseZ,et al. Modeling burst and heavy tails in human dynamics[J]. Physical Review E,2006,73(3):036127
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFE0117500) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61762002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Smart Computing and Cyber Technology for Cyberization
Guest Editors: Xiaokang Zhou, Flavia C. Delicato, Kevin Wang, and Runhe Huang
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Fan, Y., Mo, J. et al. Three-hop velocity attenuation propagation model for influence maximization in social networks. World Wide Web 23, 1261–1273 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00750-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00750-5