Abstract
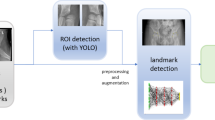
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is one of the most common diseases in children. Due to the experience-requiring medical image analysis work, online automatic diagnosis of DDH has intrigued the researchers. Traditional implementation of online diagnosis faces challenges with reliability and interpretability. In this paper, we establish an online diagnosis tool based on a multi-task hourglass network, which can accurately extract landmarks to detect the extent of hip dislocation and predict the age of the femoral head. Our method utilizes a multi-task hourglass network, which trains an encoder-decoder network to regress the landmarks and predict the developmental age for online DDH diagnosis. With the support of precise image analysis and fast GPU computing, our method can help overcome the shortage of medical resources and enable telehealth for DDH diagnosis. Applying this approach to a dataset of DDH X-ray images, we demonstrate 4.64 mean pixel error of landmark detection compared to the results of human experts. Moreover, we can improve the accuracy of the age prediction of femoral heads to 89%. Our online automatic diagnosis system has provided service to 112 patients, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Online service can be found at http://202.38.69.241:30128/ddh.php
References
Cheng, L., Shi, Y., Zhang, K.: Medical treatment migration behavior prediction and recommendation based on health insurance data. World Wide Web 23(3), 2023–2042 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-020-00781-3
Zhang, Y., Ou, W., Shi, Y., Deng, J., You, X., Wang, A.: Deep medical cross-modal attention hashing. World Wide Web, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-021-00881-8 (2021)
Yue, L., Tian, D., Chen, W., Han, X., Yin, M.: Deep learning for heterogeneous medical data analysis. World Wide Web 23(5), 2715–2737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00764-z
Dezateux, C., Rosendahl, K.: Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Lancet 369(9572), 1541–1552 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60710-7
Tönnis, D.: Indications and time planning for operative interventions in hip dysplasia in child and adulthood. Z. Orthop. Ihre. Grenzgeb. 123(4), 458–461 (1985)
Thieme, W.T., Thiersch, J.B.: Translation: Hilgenreiner on congenital hip dislocation. J. Pediatr. Orthop 6(2), 202–214 (1986)
Harris, N.H., Lloyd-Roberts, G., Gallien, R.: Acetabular development in congenital dislocation of the hip: with special reference to the indications for acetabuloplasty and pelvic or femoral realignment osteotomy. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. Vol. 57(1), 46–52 (1975)
Lindstrom, J.R., Ponseti, I., Wenger, D.R.: Acetabular development after reduction in congenital dislocation of the hip. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. Vol. 61(1), 112–118 (1979)
Gaffney, B.M., Hillen, T.J., Nepple, J.J., Clohisy, J.C., Harris, M.D.: Statistical shape modeling of femur shape variability in female patients with hip dysplasia. J. Orthop. Res.®; 37(3), 665–673 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.24214
El-Sayed, M., Ahmed, T., Fathy, S., Zyton, H.: The effect of dega acetabuloplasty and salter innominate osteotomy on acetabular remodeling monitored by the acetabular index in walking ddh patients between 2 and 6 years of age: short-to middle-term follow-up. J. Child.’s Orthop. 6 (6), 471–477 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-012-0451-x
Ertürk, C., Altay, M.A., Isikan, U.E.: A radiological comparison of salter and pemberton osteotomies to improve acetabular deformations in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 22(6), 527–532 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e32836337cd
Roposch, A., Ridout, D., Protopapa, E., Nicolaou, N., Gelfer, Y.: Osteonecrosis complicating developmental dysplasia of the hip compromises subsequent acetabular remodeling. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res.®; 471(7), 2318–2326 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-2804-2
Sublett, J.W., Dempsey, B.J., Weaver, A.C.: Design and implementation of a digital teleultrasound system for real-time remote diagnosis. In: Proceedings Eighth IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/CBMS.1995.465413, pp 292–298 (1995)
Kermany, D.S., Goldbaum, M., Cai, W., Valentim, C.C.S., Liang, H., Baxter, S.L., McKeown, A., Yang, G., Wu, X., Yan, F., Dong, J., Prasadha, M.K., Pei, J., Ting, M.Y.L., Zhu, J., Li, C., Hewett, S., Dong, J., Ziyar, I., Shi, A., Zhang, R., Zheng, L., Hou, R., Shi, W., Fu, X., Duan, Y., Huu, V.A.N., Wen, C., Zhang, E.D., Zhang, C.L., Li, O., Wang, X., Singer, M.A., Sun, X., Xu, J., Tafreshi, A., Lewis, M.A., Xia, H., Zhang, K.: Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 172(5), 1122–11319 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, pp 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015)
Xu, J., Xie, H., Liu, C., Yang, F., Zhang, S., Chen, X., Zhang, Y.: Hip landmark detection with dependency mining in ultrasound image. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(12), 3762–3774 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2021.3097355
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90, pp 770–778 (2016)
Wang, B., Qi, G.-J., Tang, S., Zhang, L., Deng, L., Zhang, Y.; Automated pulmonary nodule detection: high sensitivity with few candidates. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2018), LNCS 11071, pp 759–767, Sep. 16–20, Granada, Spain (2018)
Newell, A., Yang, K., Deng, J.: Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_29, pp 483–499. Springer, Cham (2016)
Al-Bashir, A.K., Al-Abed, M., Sharkh, F.M.A., Kordeya, M.N., Rousan, F.M.: Algorithm for automatic angles measurement and screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh). In: 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2015.7319854, pp 6386–6389. IEEE (2015)
Korman, S., Reichman, D., Tsur, G., Avidan, S.: Fast-match: Fast affine template matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.302, pp 2331–2338 (2013)
Liu, C., Xie, H., Zhang, S., Xu, J., Sun, J., Zhang, Y.: Misshapen pelvis landmark detection by spatial local correlation mining for diagnosing developmental dysplasia of the hip. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3008382, pp 441–449. Springer (2019)
Bier, B., Goldmann, F., Zaech, J.-N., Fotouhi, J., Hegeman, R.A., Grupp, R., Armand, M., Osgood, G.M., Navab, N., Maier, A.K., Unberath, M.: Learning to detect anatomical landmarks of the pelvis in x-rays from arbitrary views. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg., 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-019-01975-5(2019)
Craig, J., Petterson, V.: Introduction to the practice of telemedicine. J. Telemed. Telecare 11 (1), 3–9 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1177/1357633X0501100102. PMID: 15829036
Hollander, J.E., Carr, B.G.: Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for COVID-19. New Engl. J. Med. 382(18), 1679–1681 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp2003539
Ekeland, A.G., Bowes, A., Flottorp, S.: Effectiveness of telemedicine: A systematic review of reviews. Int. J. Med. Inform. 79(11), 736–771 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.08.006
Esteva, A., Kuprel, B., Novoa, R.A., Ko, J., Swetter, S.M., Blau, H.M., Thrun, S.: Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639), 115–118 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21056
Long, E., Lin, H., Liu, Z., Wu, X., Wang, L., Jiang, J., An, Y., Lin, Z., Li, X., Chen, J., et al: An artificial intelligence platform for the multihospital collaborative management of congenital cataracts. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 1 (2), 1–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-016-0024
Laina, I., Rieke, N., Rupprecht, C., Vizcaíno, J.P., Eslami, A., Tombari, F., Navab, N.: Concurrent segmentation and localization for tracking of surgical instruments. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00764-z, pp 664–672. Springer (2017)
Payer, C., Štern, D., Bischof, H., Urschler, M.: Regressing heatmaps for multiple landmark localization using cnns. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_27, pp 230–238. Springer (2016)
Cai, X., Li, S., Liu, X., Han, G.: Vision-based fall detection with multi-task hourglass convolutional auto-encoder. IEEE Access 8, 44493–44502 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2978249
Xu, Z., Huang, Q., Park, J., Chen, M., Xu, D., Yang, D., Liu, D., Zhou, S.K.: Supervised action classifier: Approaching landmark detection as image partitioning. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_39, pp 338–346. Springer (2017)
Zhang, J., Liu, M., Shen, D.: Detecting anatomical landmarks from limited medical imaging data using two-stage task-oriented deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(10), 4753–4764 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2721106
Kordon, F., Fischer, P., Privalov, M., Swartman, B., Schnetzke, M., Franke, J., Lasowski, R., Maier, A., Kunze, H.: Multi-task localization and segmentation for x-ray guided planning in knee surgery. In: Shen, D., Liu, T., Peters, T.M., Staib, L.H., Essert, C., Zhou, S., Yap, P.-T., Khan, A. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_69, pp 622–630. Springer, Cham (2019)
Wan, J., Lai, Z., Liu, J., Zhou, J., Gao, C.: Robust face alignment by multi-order high-precision hourglass network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 121–133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3032029
Duan, K., Bai, S., Xie, L., Qi, H., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Centernet: Keypoint triplets for object detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00667, pp 6568–6577 (2019)
Law, H., Deng, J.: Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_45, pp 734–750 (2018)
Liu, A.-A., Su, Y.-T., Nie, W.-Z., Kankanhalli, M.: Hierarchical clustering multi-task learning for joint human action grouping and recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(1), 102–114 (2017)
Li, G., Xu, F., Li, H., Yuan, Y., An, M.: Dra-odm: a faster and more accurate deep recurrent attention dynamic model for object detection. World Wide Web. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-021-00971-7 (2021)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965, pp 3431–3440. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA, USA (2015)
Lin, T.-Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(2), 318–327 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826
Zhou, X., Wang, D., Krähenbühl, P.: Objects as points. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1904.07850 (2019)
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Chintala, S., Chanan, G., Yang, E., DeVito, Z., Lin, Z., Desmaison, A., Antiga, L., Lerer, A.: Automatic differentiation in pytorch (2017)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, May 7-9, 2015, Conference Track Proceedings (2015)
Xu, N., Zhang, H.-W., Liu, A.-A., Nie, W.-Z., Su, Y.-T., Nie, J., Zhang, Y.-D.: Multi-level policy and reward-based deep reinforcement learning framework for image captioning. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 22(5), 1372–1383 (2019)
Deng, L., Tang, S., Fu, H., Wang, B., Zhang, Y.: Spatiotemporal breast mass detection network (MD-Net) in 4D DCE-MRI images. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2019), LNCS 11767, pp 271–279, Oct. 13–17, Shenzhen, China (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (62022076, 61972105, 61976008, U19A2057), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M703081), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Xie, H., Tan, Q. et al. Multi-task hourglass network for online automatic diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. World Wide Web 26, 539–559 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-022-01051-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-022-01051-0