Abstract
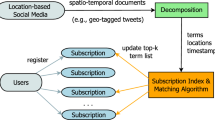
With the proliferation of location-based social media, it is of great importance to provide web users and mobile users with timely and high-quality information. In this light, we study the problem of continuous spatial keyword search over a stream of spatio-temporal messages by taking spatial relevance, textual relevance, and result diversification into consideration. We define a novel continuous query named Diversified Continuous Spatial Keyword (DCSK) query. A DCSK query consists of a spatial region, a set of query keywords, a similarity threshold 𝜃, and the number of query results k. Given a stream of spatio-temporal messages, the DCSK query continuously receive spatio-temporal messages such that: (1) they are located inside the query region and contain at least one query keyword, and (2) the similarities between each message and its previous k messages are all mess than 𝜃. Compared to traditional continuous spatial keyword query, the DCSK query can provide subscribers with spatio-temporal messages of higher quality because that the DCSK query takes both spatio-temporal relevance and query result diversification into consideration. We develop a Spatio-temporal Diversified Publish/Subscribe (STD-PS) framework to process a large number of DCSK queries efficiently. We conduct extensive experiments with real-world datasets. Our experimental results confirm the capability of our proposal in terms of result diversity, efficiency, and salability.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shraer, A., Gurevich, M., Fontoura, M., Josifovski, V.: Top-k publish-subscribe for social annotation of news. PVLDB 6(6), 385–396 (2013)
Chen, L., Cong, G., Cao, X., Tan, K.-L.: Temporal spatial-keyword top-k publish/subscribe. In: ICDE, pp. 255–266 (2015)
Zhao, K., Chen, L., Cong, G.: Topic exploration in spatio-temporal document collections. In: SIGMOD, pp. 985–998 (2016)
Manning, C.D., Raghavan, P., Schütze, H.: Introduction to information retrieval. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2008)
Felipe, I.D., Hristidis, V., Rishe, N.: Keyword search on spatial databases. In: ICDE, pp. 656–665 (2008)
Cong, G., Jensen, C.S., Wu, D.: Efficient retrieval of the top-k most relevant spatial Web objects. In: PVLDB, pp. 337–348 (2009)
Rocha-Junior, J.B., Gkorgkas, O., Jonassen, S., Nørvåg, K.: Efficient processing of top-k spatial keyword queries. In: SSTD, pp. 205–222 (2011)
Zhang, D., Tan, K.-L., Tung, A.K.H.: Scalable top-k spatial keyword search. In: EDBT, pp. 359–370 (2013)
Zhang, C., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Lin, X.: Inverted linear quadtree: efficient top k spatial keyword search. In: ICDE, pp. 901–912 (2013)
Yang, C., Chen, L., Shang, S., Zhu, F., Li, L., Shao, L.: Toward efficient navigation of massive-scale geo-textual streams. In: IJCAI, pp. 4838–4845 (2019)
Li, M., Chen, L., Cong, G., Gu, Y., Yu, G.: Efficient processing of location-aware group preference queries. In: CIKM, pp. 559–568. ACM (2016)
Chen, L., Cong, G., Jensen, C.S., WU, D.: Spatial keyword query processing: an experimental evaluation. In: PVLDB, pp. 217–228 (2013)
Chen, L., Shang, S., Yang, C., Li, J.: Spatial keyword search: a survey. GeoInformatica 24(1), 85–106 (2020)
Yao, B., Chen, Z., Gao, X., Shang, S., Ma, S., Guo, M.: Flexible aggregate nearest neighbor queries in road networks. In: ICDE, pp. 761–772. IEEE Computer Society (2018)
Shang, S., Lu, H., Pedersen, T.B., Xie, X.: Modeling of traffic-aware travel time in spatial networks. In: MDM, pp. 247–250. IEEE Computer Society (2013)
Shang, S., Chen, L., Wei, Z., Jensen, C.S., Wen, J.-R., Kalnis, P.: Collective travel planning in spatial networks. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 28(5), 1132–1146 (2016)
Shang, S., Chen, L., Wei, Z., Jensen, C.S., Zheng, K., Kalnis, P.: Parallel trajectory similarity joins in spatial networks. VLDB J. 27(3), 395–420 (2018)
Shang, S., Chen, L., Jensen, C.S., Wen, J.-R., Kalnis, P.: Searching trajectories by regions of interest. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(7), 1549–1562 (2017)
Shang, S., Chen, L., Wei, Z., Guo, D., Wen, J.-R.: Dynamic shortest path monitoring in spatial networks. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 31(4), 637–648 (2016)
Cao, X., Cong, G., Jensen, C.S., Yiu, M.L.: Retrieving regions of interest for user exploration. PVLDB 7(9), 733–744 (2014)
Shang, S., Guo, D., Liu, J., Zheng, K., Wen, J.-R.: Finding regions of interest using location based social media. Neurocomputing 173, 118–123 (2016)
Zhao, Y., Xia, J., Liu, G., Su, H., Lian, D., Shang, S., Zheng, K.: Preference-aware task assignment in spatial crowdsourcing. In: AAAI, pp. 2629–2636. AAAI Press (2019)
Liu, A., Wang, W., Shang, S., Li, Q., Zhang, X.: Efficient task assignment in spatial crowdsourcing with worker and task privacy protection. GeoInformatica 22(2), 335–362 (2018)
Han, J., Zheng, K., Sun, A., Shang, S., Wen, J.-R.: Discovering neighborhood pattern queries by sample answers in knowledge base. In: ICDE, pp. 1014–1025. IEEE Computer Society (2016)
Zheng, K., Zheng, Y., Yuan, N.J., Shang, S., Zhou, X.: Online discovery of gathering patterns over trajectories. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26 (8), 1974–1988 (2014)
Chen, L., Cong, G., Cao, X.: An efficient query indexing mechanism for filtering geo-textual data. In: SIGMOD, pp. 749–760 (2013)
Li, G., Wang, Y., Wang, T., Feng, J.: Location-aware publish/subscribe. In: KDD, pp. 802–810 (2013)
Chen, L., Cui, Y., Cong, G., Cao, X.: SOPS: a system for efficient processing of spatial-keyword publish/subscribe. PVLDB 7(13), 1601–1604 (2014)
Chen, L., Shang, S., Jensen, C.S., Xu, J., Kalnis, P., Yao, B., Shao, L.: Top-k term publish/subscribe for geo-textual data streams. VLDB J. 29(5), 1101–1128 (2020)
Chen, L., Shang, S.: Approximate spatio-temporal top-k publish/subscribe. World Wide Web 22(5), 2153–2175 (2019)
Chen, L., Shang, S., Zhang, Z., Cao, X., Jensen, C. S., Kalnis, P.: Location-aware top-k term publish/subscribe. In: ICDE, pp. 749–760. IEEE Computer Society (2018)
Chen, Z., Cong, G., Zhang, Z., Fu, T.Z.J., Chen, L.: Distributed publish/subscribe query processing on the spatio-textual data stream. In: ICDE, pp. 1095–1106. IEEE Computer Society (2017)
Wang, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., Lin, X., Huang, Z.: Top-k spatial-keyword publish/subscribe over sliding window. VLDB J. 26(3), 301–326 (2017)
Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Lin, X., Wang, W.: Ap-tree: efficiently support location-aware publish/subscribe. VLDB J. 24(6), 823–848 (2015)
Xiao, K., Ye, Z., Zhang, L., Zhou, W., Ge, Y., Deng, Y.: Multi-user mobile sequential recommendation for route optimization. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 14(5), 52:1–52:28 (2020)
Li, K., Chen, L., Shang, S., Kalnis, P., Yao, B.: Traffic congestion alleviation over dynamic road networks: continuous optimal route combination for trip query streams. In: IJCAI, pp. 3656–3662. ijcai.org (2021)
Li, K., Chen, L., Shang, S.: Towards alleviating traffic congestion: optimal route planning for massive-scale trips. In: IJCAI, pp. 3400–3406. ijcai.org (2020)
Li, K., Chen, L., Shang, S., Wang, H., Liu, Y., Kalnis, P., Yao, B.: Towards controlling the transmission of diseases: continuous exposure discovery over massive-scale moving objects. In: IJCAI, pp. 3891–3897. ijcai.org (2022)
Liu, A., Shen, X., Li, Z., Liu, G., Xu, J., Zhao, L., Zheng, K., Shang, S.: Differential private collaborative web services qos prediction. World Wide Web 22(6), 2697–2720 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Fujian Province (No. 2020H0023, 2020Y9064).
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Fujian Province (No. 2020H0023, 2020Y9064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ying Zhong: Algorithm development and paper writing. Jianmin Li: Experimental study. Shunzhi Zhu: Algorithm design and paper proofreading. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Spatiotemporal Data Management and Analytics for Recommend
Guest Editors: Shuo Shang, Xiangliang Zhang and Panos Kalnis
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Y., Li, J. & Zhu, S. Continuous spatial keyword search with query result diversifications. World Wide Web 26, 1935–1948 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-022-01118-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-022-01118-y