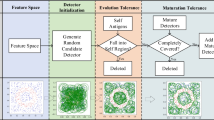
Abstract
To effectively improve the prediction precision of network security situation and prevent the large-scale network security attacks, an immunity-based time series prediction approach for network security situation (ITSPA) is proposed. In ITSPA, the concepts and formal definitions of antigen, antibody and affinity used for predicting network security situation are given; and meanwhile, the mathematical models of antibody evolution operators used for establishing the prediction model of network security situation are shown. For the time series of network security situation, its chaotic characteristics are analyzed and the corresponding sample space is reconstructed by phase space reconstruction method; then, the corresponding prediction model is constructed by artificial immune mechanism; finally, this prediction model is used for predicting the time series of network security situation. To demonstrate the predicting effectiveness of ITSPA, four typical time series (namely real-time network probe situation, real-time network situation, short-term network probe situation and short-term network situation) obtained from DARPA 1999 data set and long-term network security situation time series obtained from HoneyNet Project data set are used for simulating experiments. The experimental results show that ITSPA is an effective prediction approach for the time series of network security situation.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Xu JQ, Wang JF, Zhang J, Zhao H (2014) Virus spreading model based on degree correlation and its analysis. Sci China Ser F Inf Sci 66:793–810
Ou CM (2012) Host-based intrusion detection systems adapted from agent-based artificial immune systems. Neurocomputing 88:78–86
Chen XZ, Zheng QH, Guan XH, Lin CG (2006) Quantitative hierarchical threat evaluation model for network security. J Softw 17(4):885–897
Endsley MR (1988) Design and evaluation for situation awareness enhancement. In: Human factors society 32nd annual meeting. Anaheim, vol 1, p 97
Bass T (2000) Intrusion detection systems and multisensor data fusion. Commun ACM 43(4):99–105
Sun FX (2011) Artificial immune danger theory based model for network security evaluation. J Netw 6(2):255–262
Lau S (2004) The spinning cube of potential doom. Commun ACM 47(6):25–26
Carnegie Mellon’s SEI (2005) System for Internet Level Knowledge (SILK). http://silktools.sourceforge.net
Li T (2005) An immunity based network security risk estimation. Sci China Ser F Inf Sci 48(5):557–578
Wei Y, Lian YF (2009) A network security situational awareness model based on log audit and performance correction. Chin J Comput 32(4):763–772
Lai JB, Wang HQ, Liu XW, Liang Y, Zheng RJ, Zhao GS (2008) WNN-based network security situation quantitative prediction method and its optimization. J Comput Sci Technol 23(2):222–230
Szpiro GG (1997) Forecasting chaotic time series with genetic algorithms. Am Phys Soc 2557–2568:1997
Oliveira KD, Vannucci A, da Silva EC (2000) Using artificial neural networks to forecast chaotic time series. Phys A 284:393–404
Thissen U (2003) Using support vector machines for time series prediction. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 69:35–49
Liu B, Hu DP (1999) Studies on applying artificial neural networks to some forecasting problems. J Syst Eng 14(4):338–344
Miranian A, Abdollahzade M (2013) Developing a local least-squares support vector machines-based neuro-fuzzy model for nonlinear and chaotic time series prediction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(2):207–218
Aydin I, Karakose M, Akin E (2011) A multi-objective artificial immune algorithm for parameter optimization in support vector machine. Appl Soft Comput 11:120–129
Quan TW, Liu XM, Liu Q (2010) Weighted least squares support vector machine local region method for nonlinear time series prediction. Appl Soft Comput 10:562–566
De Castro LN, Timmis J (2002) Artificial immune systems: a new computational intelligence approach. Springer, London
Forrest S, Perelson AS, Allen L, Cherukuri R (1994) Self-nonself discrimination in a computer. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society symposium on research in security and privacy, USA, vol 1, pp 202–212
Timmis J, Hone A, Stibor T, Clark E (2008) Theoretical advances in artificial immune systems. Theor Comput Sci 403:11–32
Gong MG, Jiao LC, Zhang LN, Du HF (2009) Immune secondary response and clonal selection inspired optimizers. Prog Nat Sci 19:237–253
Haktanirlar Ulutas B, Kulturel-Konak S (2011) A review of clonal selection algorithm and its applications. Artif Intell Rev 36(2):117–138
Shang RH, Qi LP, Jiao LC, Stolkin R, Li YY (2014) Change detection in SAR images by artificial immune multi-objective clustering. Eng Appl Artif Intell 31:53–67
Khilwani N, Prakash A, Shankar R, Tiwari MK (2008) Fast clonal algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 21:106–128
Packard NH, Crutchfietd JP, Farmer JD, Shaw RS (1980) Geometry from a time series. Phys Rev Lett 45(9):712–716
Takens F (1981) Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. Lect Notes Math 898:361–381
Kim HS, Eykholt R, Salas JD (1999) Nonlinear dynamics delay times and embedding windows. Phys D 127:48–60
Yu SQ, Wang HH, Zhu NS, Ye R (2008) Introduction to immunology. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Puntambekar AA (2008) Data structures and algorithms. Technical Publications, Pune
George AJT, Grey D (1999) Receptor editing during affinity maturation. Immunol Today 20(4):196
Rudolph G (1994) Convergence analysis of canonical genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5:96–101
Zhang WX, Leung Y (2003) Mathematical foundation of genetic algorithms. Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, Xian
Lippmann RP, Haines JW, Fried DJ, Korba J, Das K (2000) The 1999 DARPA off-line intrusion detection evaluation. Comput Netw 34(4):579–595
HoneyNet P (2002) Know your enemy: statistics, USA. http://old.honeynet.org/papers/stats/honeynet_data.tar.gz
Rosenstein MT, Collins JJ, De Luca CJ (1993) A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Phys D 65:117–134
Cichocki A, Unbehauen R (1993) Neural networks for optimization and signal processing. Wiley, New York
Acknowledgments
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61173036, 61262077, 61462025, the Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Hunan Province of China under Grant No. 12B099, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2014M562102, Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 07JJ6140, and the Constructing Program of the Key Discipline in Huaihua University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Li, R., Zhang, Y. et al. An immunity-based time series prediction approach and its application for network security situation. Intel Serv Robotics 8, 1–22 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-014-0160-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-014-0160-z