Abstract
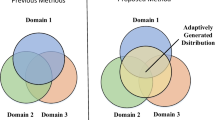
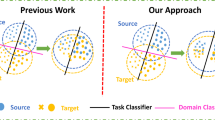
The domain adversarial neural network (DANN) methods have been successfully proposed and attracted much attention recently. In DANNs, a discriminator is trained to discriminate the domain labels of features generated by a generator, whereas the generator attempts to confuse it such that the distributions between domains are aligned. As a result, it actually encourages the whole alignment or transfer between domains, while the inter-class discriminative information across domains is not considered. In this paper, we present a Discrimination-Aware Domain Adversarial Neural Network (DA2NN) method to introduce the discriminative information or the discrepancy of inter-class instances across domains into deep domain adaptation. DA2NN considers both the alignment within the same class and the separation among different classes across domains in knowledge transfer via multiple discriminators. Empirical results show that DA2NN can achieve better classification performance compared with the DANN methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mansour Y, Mohri M, Rostamizadeh A. Domain adaptation: Learning bounds and algorithms. In Proc. the 22nd Annual Conference on Learning Theory, Jun. 2009, Article No. 3.
Özbulak G, Aytar Y, Ekenel H K. How transferable are CNN-based features for age and gender classification? In Proc. the 15th International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group, Sept. 2016, pp.39-50.
Pan S J, Yang Q, Engineering D. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345-1359.
Long M, Cao Y, Wang J. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In Proc. the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, July 2015, pp.97-105.
Long M, Zhu H, Wang J, Jordan M I. Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks. In Proc. the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Aug. 2017, pp.2208-2217.
Ganin Y, Ustinova E, Ajakan H et al. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17: Article No. 59.
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Darrell T et al. Simultaneous deep transfer across domains and tasks. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2015, pp.4068-4076.
Pei Z, Cao Z, Long M et al. Multi-adversarial domain adaptation. In Proc. the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Feb. 2018, pp.3934-3941.
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Saenko K et al. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In Proc. the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, July 2017, pp.2962-2971.
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Zhang N et al. Deep domain confusion: Maximizing for domain invariance. arXiv:1412.3474, 2014. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.3474.pdf, Nov. 2019.
Baktashmotlagh M, Harandi M T, Lovell B C et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation by domain invariant projection. In Proc. the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2013, pp.769-776.
Wang J, Chen Y, Hao S et al. Balanced distribution adaptation for transfer learning. In Proc. the 17th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Nov. 2017, pp.1129-1134.
Liang J, He R, Sun Z et al. Aggregating randomized clustering-promoting invariant projections for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2019, 41(5): 1027-1042.
Long M, Zhu H, Wang J, Jordan M I. Unsupervised domain adaptation with residual transfer networks. In Proc. the 30th Neural Information Processing Systems, Dec. 2016, pp.136-144.
Sohn K, Shang W, Yu X et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation for distance metric learning. In Proc. the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, May 2019.
Pan S J, Tsang IW, Kwok J T et al. Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(2): 199-210.
Long M, Wang J, Ding G et al. Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In Proc. the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2014, pp.2200-2207.
Ben-David S, Blitzer J, Crammer K et al. Analysis of representations for domain adaptation. In Proc. the 20th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Dec. 2006, pp.137-144.
Fernando B, Habrard A, Sebban M et al. Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In Proc. the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2013, pp.2960-2967.
Jing Z, Li W, Ogunbona P. Joint geometrical and statistical alignment for visual domain adaptation. In Proc. the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, July 2017, pp.5150-5158.
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proc. the 26th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Dec. 2012, pp.1106-1114.
Ghifary M, Kleijn W B, Zhang M. Domain adaptive neural networks for object recognition. In Proc. the 13th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Dec. 2014, pp.898-904.
Yu C, Wang J, Chen Y et al. Transfer learning with dynamic adversarial adaptation network. In Proc. the 19th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Nov. 2019.
Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M et al. Adapting visual category models to new domains. In Proc. the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2010, pp.213-226.
Gong B, Yuan S, Fei S et al. Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proc. the 25th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2012, pp.2066-2073.
Gretton A, Borgwardt K M, Rasch M et al. A kernel two-sample test. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2012, 13(1): 723-773.
Jia Y, Shelhamer E, Donahue J et al. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proc. the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Apr. 2014, pp.675-678.
Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O et al. DeCAF: A deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In Proc. the 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Jun. 2014, pp.647-655.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 368 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YY., Gu, JM., Wang, C. et al. Discrimination-Aware Domain Adversarial Neural Network. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 35, 259–267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-020-9969-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-020-9969-4