Abstract
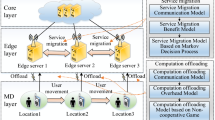
Mobile edge computing (MEC) has been envisioned as a promising distributed computing paradigm where mobile users offload their tasks to edge nodes to decrease the cost of energy and computation. However, most of the existing studies only consider the congestion of wireless channels as a crucial factor affecting the strategy-making process, while ignoring the impact of offloading among edge nodes. In addition, centralized task offloading strategies result in enormous computation complexity in center nodes. Along this line, we take both the congestion of wireless channels and the offloading among multiple edge nodes into consideration to enrich users’ offloading strategies and propose the Parallel User Selection Algorithm (PUS) and Single User Selection Algorithm (SUS) to substantially accelerate the convergence. More practically, we extend the users’ offloading strategies to take into account idle devices and cloud services, which considers the potential computing resources at the edge. Furthermore, we construct a potential game in which each user selfishly seeks an optimal strategy to minimize its cost of latency and energy based on acceptable latency, and find the potential function to prove the existence of Nash equilibrium (NE). Additionally, we update PUS to accelerate its convergence and illustrate its performance through the experimental results of three real datasets, and the updated PUS effectively decreases the total cost and reaches Nash equilibrium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Kim S, Visotsky E, Moorut P, Bechta K, Ghosh A, Dietrich C. Coexistence of 5G with the incumbents in the 28 and 70 GHz bands. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(6): 1254-1268. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2017.2687238.
Ding C, Tao D. Trunk-branch ensemble convolutional neural networks for video-based face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 40(4): 1002-1014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2700390.
Zong Z, Hong C. On application of natural language processing in machine translation. In Proc. the 3rd International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering, Sept. 2018, pp.506-510. DOI: 10.1109/ICMCCE.2018.00112.
Meng H J, Wang D C. Robust design for game-based instruction using interactive whiteboards. In Proc. the 4th IEEE International Conference on Digital Game and Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning, Mar. 2012, pp.250-253. DOI: 10.1109/DIGITEL.2012.66.
Zhang Z, Weng D, Jiang H, Liu Y, Wang Y. Inverse augmented reality: A virtual agent's perspective. arXiv:1808.03413, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.03413-v1, Aug. 2021.
Abbas N, Yan Z, Taherkordi A, Skeie T. Mobile edge computing: A survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 5(1): 450-465. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2017.2750180.
Satyanarayanan M. The emergence of edge computing. Computer, 2017, 50(1): 30-39. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MC.2017.9.
Niu Z,Wu Y, Gong J, Yang Z. Cell zooming for cost-efficient green cellular networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2010, 48(11): 74-79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2010.5621970.
Asadi A, Wang Q, Mancuso V. A survey on device-todevice communication in cellular networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2014, 16(4): 1801-1819. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2014.2319555.
Kumar K, Lu Y H. Cloud computing for mobile users: Can offloading computation save energy? Computer, 2010, 43(4): 51-56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MC.2010.98.
Chen Y, Li Z, Yang B, Nai K, Li K. A Stackelberg game approach to multiple resources allocation and pricing in mobile edge computing. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 108: 273-287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.02.045.
Zhou A, Wang S, Wan S, Qi L. LMM: Latency-aware microservice mashup in mobile edge computing environment. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(19): 15411-15425. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04693-w.
Yang Y, Long C, Wu J, Peng S, Li B. D2D-enabled mobile-edge computation offloading for multi-user IoT network. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(16): 12490-12504. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3068722.
Ding Y, Li K, Liu C, Li K. A potential game theoretic approach to computation offloading strategy optimization in end-edge-cloud computing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2022, 33(6): 1503-1519. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2021.3112604.
Wang E, Dong P, Xu Y, Li D, Wang L, Yang Y. Distributed game-theoretical task offloading for mobile edge computing. In Proc. the 18th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Smart Systems (MASS), Oct. 2021, pp. 216-224. DOI: 10.1109/MASS52906.2021.00037.
Baron B, Spathis P, Rivano H, De Amorim M D, Viniotis Y, Ammar M H. Centrally controlled mass data offloading using vehicular traffic. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2017, 14(2): 401-415. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSM.2017.2672878.
Jiang F, Ma R, Sun C, Gu Z. Dueling Deep Q-Network learning based computing offloading scheme for F-RAN. In Proc. the 31st IEEE Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Aug. 31-Sept.3, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/PIMRC48278.2020.9217355.
Hong Z, Chen W, Huang H, Guo S, Zheng Z. Multihop cooperative computation offloading for industrial IoTedge- cloud computing environments. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2019, 30(12): 2759-2774. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2019.2926979.
Wang Y, Ge H, Feng A, Li W, Liu L, Jiang H. Computation offloading strategy based on deep reinforcement learning in cloud-assisted mobile edge computing. In Proc. the 5th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics, Apr. 2020, pp.108-113. DOI: 10.1109/ICCCBDA49378.2020.9095689.
Yu S, Langar R, Wang X. A D2D-multicast based computation offloading framework for interactive applications. In Proc. the 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Dec. 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7841490.
Fabiani F, Grammatico S. Multi-vehicle automated driving as a generalized mixed-integer potential game. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 21(3): 1064-1073. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2019.2901505.
Liu H, Jia H, Chen J, Ge X, Li Y, Tian L, Shi J. Computing resource allocation of mobile edge computing networks based on potential game theory. arXiv:1901.00233, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.00233, Jan. 2022.
Raschellá A, Bouhafs F, Mackay M, Shi Q, Ortin J, Gallego J. R, Canales M. AP selection algorithm based on a potential game for large IEEE 802.11 WLANs. In Proc. the 2018 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Apr. 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/NOMS.2018.8406147.
He Q, Cui G, Zhang X, Chen F, Yang Y. A gametheoretical approach for user allocation in edge computing environment. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2020, 31(3): 515-529. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2019.2938944.
Wu B, Zeng J, Ge L, Tang Y, Su X. A gametheoretical approach for energy-efficient resource allocation in MEC network. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, May 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICC.2019.8761727.
Zhu T, Li J, Cai Z, Li Y, Gao H. Computation scheduling for wireless powered mobile edge computing networks. In Proc. the 2020 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Jul. 2020, pp.596-605. DOI: 10.1109/INFOCOM41043.2020.9155418.
Monderer D, Shapley L. Potential games. Games and Economic Behavior, 1996, 14(1): 124-143. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/game.1996.0044.
Roughgarden T. Algorithmic game theory. Communications of the ACM, 2010, 53(7): 78-86. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/1785414.1785439.
Xia X, Chen F, He Q, Grundy J, Abdelrazek M, Jin H. Online collaborative data caching in edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2020, 32(2): 281-294. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2020.3016344.
Li B, He Q, Cui G, Xia X, Yang Y. READ: Robustnessoriented edge application deployment in edge computing environment. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2022, 15(3): 1746-1759. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2020.3015316.
Wang S, Zhao Y, Xu J, Yuan J, Hsu C H. Edge server placement in mobile edge computing. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2019, 127: 160-168. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2018.06.008.
Guo Y, Wang S, Zhou A, Xu J, Yuan J, Hsu C. H. User allocation-aware edge cloud placement in mobile edge computing. Software: Practice and Experience, 2020, 50(5): 489-502. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/spe.2685.
Gedeon J, Krisztinkovics J, Meurisch C, Stein M, Wang L, Mühlhaüser M. A multi-cloudlet infrastructure for future smart cities: An empirical study. In Proc. the 1st International Workshop on Edge Systems, Analytics and Networking, Jun. 2018, pp.19-24. DOI: 10.1145/3213344.3213348.
Pu L, Chen X, Xu J, Fu X. D2D fogging: An energy efficient and incentive-aware task offloading framework via network-assisted D2D collaboration. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3887-3901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2016.2624118.
Wang E, Luan D, Yang Y, Wang Z, Dong P, Li D, Liu W, Wu J. Distributed game-theoretical route navigation for vehicular crowdsensing. In Proc. the 50th International Conference on Parallel Processing, Aug. 2021, pp.1-11. DOI: 10.1145/3472456.3472498.
Jain R K, Chiu D M W, Hawe W R. A quantitative measure of fairness and discrimination for resource allocation in shared computer systems. arXiv:cs/9809099, 1998. https://arxiv.org/abs/cs/9809099, Sept. 2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 173 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, E., Wang, H., Dong, PM. et al. Distributed Game-Theoretical D2D-Enabled Task Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 37, 919–941 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-022-2063-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-022-2063-3