Abstract
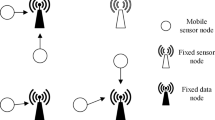
With the developing demands of massive-data services, the applications that rely on big geographic data play crucial roles in academic and industrial communities. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), combining with terrestrial wireless sensor networks (WSN), can provide sustainable solutions for data harvesting. The rising demands for efficient data collection in a larger open area have been posed in the literature, which requires efficient UAV trajectory planning with lower energy consumption methods. Currently, there are amounts of inextricable solutions of UAV planning for a larger open area, and one of the most practical techniques in previous studies is deep reinforcement learning (DRL). However, the overestimated problem in limited-experience DRL quickly throws the UAV path planning process into a locally optimized condition. Moreover, using the central nodes of the sub-WSNs as the sink nodes or navigation points for UAVs to visit may lead to extra collection costs. This paper develops a data-driven DRL-based game framework with two partners to fulfill the above demands. A cluster head processor (CHP) is employed to determine the sink nodes, and a navigation order processor (NOP) is established to plan the path. CHP and NOP receive information from each other and provide optimized solutions after the Nash equilibrium. The numerical results show that the proposed game framework could offer UAVs low-cost data collection trajectories, which can save at least 17.58% of energy consumption compared with the baseline methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Chen Q, Zhu H, Yang L, Chen X Q, Pollin S, Vinogradov E. Edge computing assisted autonomous flight for UAV: Synergies between vision and communications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(1): 28-33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.001.2000501.
Liu D X, Xu Y H, Wang J L, Chen J, Yao K L, Wu Q H, Anpalagan A. Opportunistic UAV utilization in wireless networks: Motivations, applications, and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(5): 62-68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.001.1900687.
Ma M, Yang Y Y, Zhao M. Tour planning for mobile data-gathering mechanisms in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology, 2013, 62(4): 1472-1483. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2012.2229309.
Zhan C, Zeng Y, Zhang R. Energy-efficient data collection in UAV enabled wireless sensor network. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(3): 328-331. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2017.2776922.
Chai C L, Liu J B, Tang N, Li G L, Luo Y Y. Selective data acquisition in the wild for model charging. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2022, 15(7): 1466-1478. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14778/3523210.3523223.
Chai C L, Cao L, Li G L, Li J, Luo Y Y, Madden S. Human-in-the-loop outlier detection. In Proc. the 2020 ACM SIG-MOD Int. Conf. Management of Data, June 2020, pp.19-33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3318464.3389772.
Dong M X, Ota K, Lin M, Tang Z Y, Du S G, Zhu H J. UAV-assisted data gathering in wireless sensor networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2014, 70(3): 1142-1155. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-014-1161-6.
Zhan C, Zeng Y. Aerial{ground cost tradeoff for multi-UAV-enabled data collection in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1937-1950. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2962479.
Asadi K, Kalkunte Suresh A, Ender A, Gotad S, Maniyar S, Anand S, Noghabaei M, Han K, Lobaton E, Wu T F. An integrated UGV-UAV system for construction site data collection. Automation in Construction, 2020, 112: Article No. 103068. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2019.103068.
Chai C L, Li G L, Li J, Deng D, Feng J H. Cost-effective crowdsourced entity resolution: A partial-order approach. In Proc. the 2016 International Conference on Management of Data, June 2016, pp.969-984. DOI: 10.1145/2882903.2915252.
Li G L, Chai C L, Fan J, Weng X P, Li J, Zheng Y D, Li Y B, Yu X, Zhang X H, Yuan H T. CDB: Optimizing queries with crowd-based selections and joins. In Proc. the 2017 International Conference on Management of Data, May 2017, pp.1463-1478. DOI: 10.1145/3035918.3064036.
Chai C L, Fan J, Li G L. Incentive-based entity collection using crowdsourcing. In Proc. the 34th International Conference on Data Engineering, April 2018, pp.341-352. DOI: 10.1109/ICDE.2018.00039.
Baek J, Han S I, Han Y. Energy-efficient UAV routing for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(2): 1741-1750. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2959808.
Zhao S L, Wang X K, Kong W W, Zhang D B, Shen L C. A novel data-driven control for fixed-wing UAV path following. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Apr. 2015, pp.3051-3056. DOI: 10.1109/ICInfA.2015.7279812.
Rossello N B, Carpio R F, Gasparri A, Garone E. Information-driven path planning for UAV with limited autonomy in large-scale field monitoring. IEEE Trans. Automation Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(3): 2450-2460. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2021.3085365.
Hydher H, Jayakody D N K, Hemachandra K T, Samaras-inghe T. Intelligent UAV deployment for a disaster-resilient wireless network. Sensors, 2020, 20(21): Article No. 6140. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216140.
Chen W C, Zhao S J, Zhang R Q, Chen Y, Yang L Q. UAV-assisted data collection with nonorthogonal multiple access. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(1): 501- 511. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3005271.
Xiong Z H, Zhang Y, Lim W Y B, Kang J W, Niyato D, Leung C, Miao C Y. UAV-assisted wireless energy and data transfer with deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(1): 85-99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCCN.2020.3027696.
Duo B, Wu Q Q, Yuan X J, Zhang R. Anti-jamming 3D trajectory design for UAV-enabled wireless sensor networks under probabilistic LoS channel. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 16288-16293. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2020.3040334.
Challita U, Saad W, Bettstetter C. Interference management for cellular-connected UAVs: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(4): 2125-2140. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2019.2900035.
Xie H, Yang D C, Xiao L, Lyu J B. Connectivity-aware 3D UAV path design with deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(12): 13022-13034. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2021.3121747.
Mukherjee A, Misra S, Chandra V S P, Obaidat M S. Resource-optimized multiarmed bandit-based offload path selection in edge UAV swarms. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 4889-4896. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2879459.
Zhu B T, Bedeer E, Nguyen H H, Barton R, Henry J. UAV trajectory planning in wireless sensor networks for energy consumption minimization by deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(9): 9540-9554. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2021.3102161.
Zhang S T, Li Y B, Dong Q H. Autonomous navigation of UAV in multi-obstacle environments based on a deep reinforcement learning approach. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 115: 108194. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108194.
Shi T, Li J Z, Gao H, Cai Z P. A novel framework for the coverage problem in battery-free wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(3): 783-798. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2020.3019470.
Zhang L P, Li F Q, Wang P C, Su R, Chi Z Z. A blockchain-assisted massive IoT data collection intelligent framework. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 9(16): 14708-14722. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3049674.
Wang K, Xu L, Perrault A, Reiter M K, Tambe M. Co-ordinating followers to reach better equilibria: End-to-end gradient descent for stackelberg games. In Proc. the 36th AAAI Conf. Artificial Intelligence, 2022, pp.5219-5227. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i5.20457.
van Hasselt H, Guez A, Silver D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. In Proc. the 30th AAAI Conf. Artificial Intelligence, February 2016, pp.2094-2100. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v30i1.10295.
Liu J B, Chai C L, Luo Y Y, Lou Y, Feng J H, Tang N. Feature augmentation with reinforcement learning. In Proc. the 38th Int. Conf. Data Engineering, May 2022, pp.3360-3372. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE53745.2022.00317.
Watkins C J C H, Dayan P. Q-learning. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3): 279-292. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00992698.
Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Graves A, Antonoglou I, Wierstra D, Riedmiller M. Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1312.56022013, 2013. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.5602, Nov. 2022.
Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Tassa Y, Silver D, Wierstra D. Continuous control with deep re-inforcement learning. In Proc. the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, May 2016.
Barto A G, Sutton R S, Anderson C W. Neuronlike adaptive elements that can solve difficult learning control problems. IEEE Trans. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1983, SMC-13(5): 834-846. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1983.6313077.
BianWW,Wei J, Huang K H,Wang J X, Lv X, YuanWN. Intelligent decision algorithm of target compound interception based on A2C-PPO. In Proc. the 2021 International. Conference on Cyber-Physical Social Intelligence, December 2021. DOI: 10.1109/ICCSI53130.2021.9736236.
Mnih V, Badia A P, Mirza M, Graves A, Harley T, Lillicrap T P, Silver D, Kavukcuoglu K. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In Proc. the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Jun 2016, pp.1928-1937.
Schaul T, Quan J, Antonoglou I, Silver D. Prioritized experience replay. In Proc. the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, May 2016.
Wang Z Y, Schaul T, Hessel M, Van Hasselt H, Lanctot M, De Freitas N. Dueling network architectures for deep rein-forcement learning. In Proc. the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, June 2016, pp.1995-2003.DOI: 10.5555/3045390.3045601.
Su Z, Qi N, Yan Y J, Du Z Y, Chen J X, Feng Z B, Wu Q H. Guarding legal communication with smart jammer: Stackelberg game based power control analysis. China Communications, 2021, 18(4): 126-136. DOI: https://doi.org/10.23919/JCC.2021.04.010.
Bansal G, Sikdar B. Security service pricing model for UAV swarms: A stackelberg game approach. In Proc. the 2021 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, May 2021, pp.126-136. DOI: 10.1109/INFO-COMWKSHPS51825.2021.9484577.
Shi C G, Qiu W, Wang F, Salous S, Zhou J J. Cooperative LPI performance optimization for multistatic radar system: A stackelberg game. In Proc. the 2019 International. Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium, Aug. 2019. DOI: 10.23919/ACES48530.2019.9060749.
Su J T, Yang S S, Xu H T, Zhou X W. A stackelberg differential game based bandwidth allocation in satellite communication network. China Communications, 2018, 15(8): 205-214. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CC.2018.8438284.
Zhang X B, Wang H, Xu Y F, Feng Z B, Zhang Y P. Put others before itself: A multi-leader one-follower anti-jamming stackelberg game against tracking jammer. China Communications, 2021, 18(11): 168-181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.23919/JCC.2021.11.012.
Ghorbel M B, Rodríguez-Duarte D, Ghazzai H, Hossain M J, Menouar H. Joint position and travel path optimization for energy efficient wireless data gathering using unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(3): 2165-2175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2893374.
Hulens D, Verbeke J, Goedemé T. How to choose the best embedded processing platform for on-board UAV image processing? In Proc. the 10th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, Mar. 2015, pp.377-386. DOI: 10.5220/0005359403770386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, T., Liu, N., Yan, ZM. et al. An Efficient Reinforcement Learning Game Framework for UAV-Enabled Wireless Sensor Network Data Collection. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 37, 1356–1368 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-022-2419-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-022-2419-8