Abstract
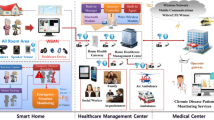
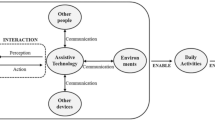
Current IT market has increased significantly boosted by the development of network technology and IT technology. As we move into an aging society, global people have paid attentions to the matters related to health while the many technologies related to health have been developed, too. Such a change of social paradigm has improved the quality of life but various mental diseases show its growing trend. The past mental disease matters were limited to the area of chronic mental disease patients, but recently light mental diseases including the stress caused by excessive work and internet addiction are included in this area. Especially there are many cases where early treatable depressions have been developed into the serious diseases as they had no chance to recognition and healing or missed the appropriate time for healing. Even if various health related mobile services to solve this show it gradual growing trend now, providing services which correspond to the needs of users, are difficult in the actual situation, while many researches are performed to provide the customized service by utilizing PHR but they are very vulnerable in the aspect of security. Therefore, in this paper, we proposed the context aware based user customized light therapy service using security framework. The proposed service applied the context aware based security framework to enhance the security of health service for PHR interlocking, which can protect the medical information by complying with standard based encryption, security guideline. For this purpose, we arranged that object group support component of DOGF should be existed in server system and components such as user information and distributed sources re-composed by smart health for service providing. Based on this, the user’s states was analyzed in real time through Personal Health Record and Galvanic Skin Response of users, the brightness and chromaticity of bulb was adjusted depending on the states of user for soothing effect, the real-time states was figured out through questionnaires for mental states analysis of smartphone application to provide the real-time treatment for users stress alleviating and concentration enhancement. Also focused on Psychological illness, we arranged to provide the real-time light therapy according to the states of users based on the data of patients collected from smart device in order to mental disease prevention and treatment caused from the stress of workers who work with computer for a long time such as office workers, program developer and home workers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kang, S.K., Chung, K.Y., Ryu, J.K., Rim, K.W., Lee, J.H.: Bio-interactive healthcare service system using lifelog based context computing. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 73(2), 341–351 (2013)
Jung, E.Y., Kim, J.H., Chung, K.Y., Park, D.K.: Home health gateway based healthcare services through u-health platform. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 73(2), 207–218 (2013)
Rahman, A.F.A., Ahmad, R., Ramli, S.N.: Forensics readiness for wireless body area network (WBAN) system. In: Proceedings of the 16th international conference on advanced communication technology (ICACT), pp. 177–180 (2014)
Liao, L.D., Wang, I.J., Chang, C.J., Lin, B.S.: Human cognitive application by using wearable mobile brain computer interface. In: Proceedings of IEEE region 10 conference TENCON 2010, vol. 1, pp. 346–351 (2010)
Park, C.Y., Lim, J.H., Park, S.: ISO/IEEE 11073 PHD standardization of legacy healthcare devices for home healthcare services. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on consumer electronics, vol. 1, pp. 547–548 (2011)
Elhadj, H.B., Chaari, L., Kamoun, L.: A survey of routing protocols in wireless body area networks for healthcare applications. Int. J. E Health Med. Commun. 3(2), 1–18 (2012)
Khan, P., Ullah, N., Ullah, S., Kwak, K.S.: Seamless interworking architecture for WBAN in heterogeneous wireless networks with QoS guarantees. J. Med. Syst. 35(5), 1313–1321 (2011)
Barua, M., Alam, M.S., Xiaohui, L., Xuemin, S.: Secure and quality of service assurance scheduling scheme for WBAN with application to E-health. In: Proceedings of the IEEE wireless communications and networking conference, vol. 1, pp. 1102–1106 (2011)
Ramli, S.N., Ahmad, R., Abdollah, M.F., Dutkiewicz, E.: Biometric-based security for data authentication in wireless body area network (WBAN). In: Proceedings of the 15th international conference on advanced communication technology (ICACT), pp. 998–1001 (2013)
Kang, S.K., Chung, K.Y., Lee, J.H.: Development of head detection and tracking systems for visual surveillance. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 18(3), 515–522 (2014)
David, M., Thaddeus, R.F., Fulford, J., Matt, W.: CodeBlue: An ad hoc sensor network infrastructure for emergency medical care. Mobisys 2004 workshop on applications of mobile embedded systems, pp. 12–14 (2004)
Han, K.W.: To study the success of mayo clinic by use of systems ethics. In: 2010 International conference on system science and engineering (ICSSE), pp. 1–2 (2010)
Park, R., Jung, H., Shin, D.K., Kim, G.J., Yoon, K.H.: M2M-based smart health service for human UI/UX using motion recognition. Cluster Comput. 18(1), 221–232 (2015)
Burkhard, J.: Heterogeneous Network Quality of Service Systems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston (2011)
Jung, H., Chung, K.: Sequential pattern profiling based bio-detection for smart health service. Cluster Comput. 18(1), 209–219 (2015)
Park, R.C., Jung, H., Shin, D.K., Cho, Y.H., Lee, K.D.: Telemedicine health service using LTE-advanced relay antenna. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. (2014). doi:10.1007/s00779-013-0734-3
Park, R.C., Jung, H., Chung, K., Yoon, K.H.: Picocell based telemedicine health service for human UX/UI. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11042-014-1964-8
Park, R.C., Jung, H., Shin, D.K., Kim, G.J., Yoon, K.H.: M2M-based smart health service for human UI/UX. Cluster Comput. 18(1), 221–232 (2015)
Park, R.C., Jung, H., Jo, S.M.: ABS scheduling technique for interference mitigation of M2M based medical WBAN service. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 79(4), 2685–2700 (2014)
Chung, K., Kim, J.C., Park, R.C.: Knowledge-based health service considering user convenience using hybrid Wi-Fi P2P. Inf. Technol. Manag. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10799-015-0241-5
Jung, H., Chung, K.: Knowledge based dietary nutrition recommendation for obesity management. Inf. Technol. Manag. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10799-015-0218-4
Ayyildiz, C., Erman, K., Ozgul, M.E., Erman, A.T., Gungor, C.: TeleHealth: intelligent healthcare with M2M communication module. In: Proceedings of the Second ACM Workshop on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services for HealthCare (2012). doi:10.1145/2396276.2396285
Park, D., Kim, J., Kim, J., Jung, E., Lee, Y.: U-health service model for managing health of chronic patients in multi-platform environment. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 11(8), 23–32 (2011)
Park, R., Jung, H., Jo, S.M.: ABS scheduling technique interference mitigation of M2M based medical WBAN service. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 79(4), 2685–2699 (2014)
Kim, J.C., Chung, K.: Depression index service using knowledge based crowdsourcing in smart health. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 93(1), 255–268 (2017)
Yoo, H., Chung, K.: PHR based diabetes index service model using life behavior analysis. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 93(1), 161–174 (2017)
Kim, S.H., Chung, K.: Emergency situation monitoring service using context motion tracking of chronic disease patients. Cluster Comput. 18(2), 747–759 (2015)
Jung, H., Chung, K.Y., Lee, Y.H.: Decision supporting method for chronic disease patients based on mining frequent pattern. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2013). doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1730-3
Chung, K.Y.: Recent trends on convergence and ubiquitous computing. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 18(6), 1291–1293 (2014)
Kim, H., Jo, J., Choi, Y., Oh, J., Lee, J., Yoon, K.: Ubiquitous health care system for chronic disease management. J. Korea Inf. Commun. Mag. 27(9), 3–8 (2010)
Tu, Y., Huang, Y., Yi, F.: Chronic disease management system design based on cloud storage architecture. In: Proceedings of the international conference on information science and control engineering (ICISCE), pp. 654–658 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2016R1C1B1014849).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, H., Kim, JC., Kim, KW. et al. Context aware based user customized light therapy service using security framework. J Comput Virol Hack Tech 13, 279–288 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11416-017-0298-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11416-017-0298-2