Abstract
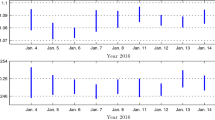
Traditional econometrics has long employed “points” to measure time series data. In real life situations, however, it suffers the loss of volatility information, since many variables are bounded by intervals in a given period. To address this issue, this paper provides a new methodology for interval time series analysis. The concept of “interval stochastic process” is formally defined as a counterpart of “stochastic process” in point-based econometrics. The authors introduce the concepts of interval stationarity, interval statistics (including interval mean, interval variance, etc.) and propose an interval linear model to investigate the dynamic relationships between interval processes. A new interval-based optimization approach for estimation is proposed, and corresponding evaluation criteria are derived. To demonstrate that the new interval method provides valid results, an empirical example on the sterling-dollar exchange rate is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. E. Moore, Interval Analysis, Prentice-Hall Press, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 1966.
E. Hansen and W. Walster, Global Optimization Using Interval Analysis, Marcel Dekker, New York, 2003.
G. F. Corliss and R. B. Kearfortt, Rigorous global search: Industrial applications, in Developments in Reliable Computing, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1999: 1–16.
R. B. Kearfott, Interval computations: Introduction, uses, and resources, Euromath Bulletin, 1996, 2(1): 95–112.
A. Korvin, C. Hu, and P. Chen, Generating and applying rule for interval valued fuzzy oservations, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2005, 3177: 279–284.
D. J. Berleant, M. P. Cheong, C. Chu, Y. Guan, A. Kamal, G. Shedbl, S. Ferson, and J. F. Peters, Dependable handling of uncertainty, Reliable Computing, 2003, 9(6): 407–418.
Z. H. Hu, Reliable optimal production control with Cobb-Douglas model, Reliable Computing, 1998, 4(1): 63–69.
M. E. Jerrell, Interval arithmetic for input-output models with inexact data, Computational Economics, 1997, 10(1): 89–100.
C. Y. Hu and L. T. He, An application of interval methods to stock market forecasting, Reliable Computing, 2007, 13(5): 423–434.
J. D. Hamilton, Time Series Analysis, Princeton University Press, New Jersey, 1994.
D. J. Berleant, Automatically verified reasoning with both intervals and probability density functions, Interval Computations, 1993, 2: 48–70.
D. J. Berleant and C. Goodman-Strauss, Bounding the results of arithmetic operations on random variables of unknown dependency using intervals, Reliable Computing, 1998, 4(2): 147–165.
D. J. Berleant, F. G. Cozman, O. Kosheleva, and V. Kreinovich, Dealing with imprecise probabilities, interval-related talks at ISIPTA’05, Reliable Computing, 2006, 12(2): 153–165.
D. J. Berleant and J. Z. Zhang, Using pearson correlation to improve envelopes around the distributions of functions, Reliable Computing, 2004, 10(2): 139–161.
D. J. Berleant, L. Z. Xie, and J. Z. Zhang, Statool: A tool for distribution envelope (DEnv), an interval-based algorithm for arithmetic on random variables, Reliable Computing, 2003, 9(2): 91–108.
D. J. Berleant, M. Ceberio, G. Xiang, and V. Kreinovich, Towards adding probabilities and correlations to interval computations, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2007, 46(3): 499–510.
D. J. Berleant, O. Kosheleva, V. Kreinovich, and H. T. Nguyen Unimodality, Independence lead to NP-hardness of interval probability problems, Reliable Computing, 2007, 13(3): 261–282.
O. Kosheleva and V. Kreinovich, Error estimation for indirect measurements: interval computation problem is (slightly) harder than a similar probabilistic computational problem, Reliable Computing, 1999, 5(1): 81–95.
S. Ferson, L. Ginzburg, V. Kreinovich, L. Longpr, and M. Aviles, Exact bounds on finite populations of interval data, Reliable Computing, 2005, 11(3): 207–233.
S. Ferson, L. Ginzburg, V. Kreinovich, L. Longpr, and M. Aviles, Computing variance for interval data is NP-hard, ACM SIGACT News, 2002, 33(2): 108–118.
V. Kreinovich, D. J. Berleant, S. Ferson, and W. A. Lodwick, Combining interval and probabilistic uncertainty: Foundations, algorithms, challenges{An overview, Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Systems Neural Networks, and Genetic Algorithms FNG'05, Tijuana, Mexico, 2005: 1–10.
V. Kreinovich and S. Ferson, Computing best-possible bounds for the distribution of a sum of several variables is NP-hard, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2006, 41(3): 331–342.
V. Kreinovich, L. Longpre, S. A. Starks, G. Xiang, J. Beck, R. Kandathi, A. Nayak, S. Ferson, and J. Hajagos, Interval versions of statistical techniques, with applications to environmental analysis, bioinformatics, and privacy in statistical databases, Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2007, 199(2): 418–423.
B. Hayes, A lucid interval, American Scientist, 2003, 91(6): 484–488.
L. T. He and C. Y. Hu, Impacts of interval measurement on studies of economic variability: Evidence from stock market variability forecasting, Risk Finance, 2007, 8(5): 489–507.
R. E. Moore, Methods and Applications of Interval Analysis, SIAM, Philadelphia, 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Research Granting Committee of Hong Kong.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HAN, A., HONG, Y., LAI, K.K. et al. Interval Time Series Analysis with an Application to the Sterling-Dollar Exchange Rate. J Syst Sci Complex 21, 558–573 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-008-9135-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-008-9135-5