Abstract
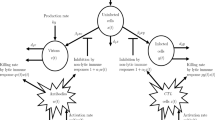
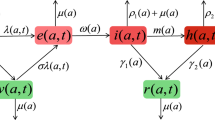
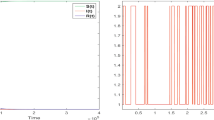
This paper discusses the application of a pulse vaccination strategy to prevent and control some infectious diseases, which is described by age-structured SIR model in which susceptible and recovered individuals are structured by chronological age, while infected individuals are structured by infection age (duration since infection). The time dependent disease-free equilibrium is determined, for which an explicit expression exists. The analytical results show that there exists a globally stable infection-free situation if the impulsive period T and proportion p satisfy R 0(p, T) < 1. Optimal problem is discussed: Pulse vaccination strategy with minimal costs at given R 0(p, T) < 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. O. Kermack and A. G. McKendrick, Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics, part 1, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A, 1927, 115(772): 700–721.
C. Castillo-Chavez, W. H. Hethcote, V. Andreasen, et al., Epidemiological models with age structure, proportionate mixing, and cross-immunity, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 1989, 27(3): 233–258.
D. Greenhalgh, Analytical threshold and stability results on age-structured epidemic models with vaccination, Theoretical Population Biology, 1988, 33(3): 266–290.
D. Greenhalgh, Vaccination campaigns for common childhood diseases, Mathematical Biosciences, 1990, 100(22): 201–240.
C. Castillo-Chavez and Z. Feng, Global stability of an age-structure model for tb and its applications to optimal vaccination strategies, Mathematical Biosciences, 1998, 151(2): 135–154.
Z. Agur, L. Cojocaru, R. M. Anderson, and Y. L. Danon, Pulse mass measles vaccination across age cohorts, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1993, 90(24): 11698–11702.
V. Lakshmikantham, D. D. Bainov, and P. S. Simeonov, Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations, World Scientific: Singapore, 1989.
A. D’Onofri, Stability properties of pulse vaccination strategy in SEIR epidemic model, Mathematical Biosciences, 2002, 179(1): 57–72.
Y. Zhou and H. Liu, Stability of periodic solutions for an SIS model with pulse vaccination, Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2003, 38: 229–308.
C. A. De Quadros, J. K. Andrus, and J. M. Olive, Eradication of poliomyelitis: Progress in the Americas, The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 1991, 10(3): 222–229.
A. B. Sabin, Measlles: Killer of millions in developing countries: Strategies of elimination and continuing control, European Journal of Epidemiology, 1991, 7(1): 1–22.
M. Ramsay, N. Gay, E. Miller, et al., The epidemiology of measles in England and Wales: Rationale for the 1994 national vaccination campaign, Communicable Disease Report, 1997, 4(12): 141–146.
H. Liu, H. Xu, Y. Yu, and G. Zhu, Global asymptotic stability for the SIV epidemic model with impulsive vaccination and infection age, Journal of Biological Systems, 2006, 14(1): 43–51.
H. Liu, J. Yu, and G. Zhu, Analysis of a vector-host malaria model with impulsive, Advances in Complex Systems, 2006, 9(3): 237–248.
H. Inaba, Endemic threshold results in an age-duration-structured population model for HIV infection, Mathematical Biosciences, 2006, 201(1–2): 15–47.
Y. Cha, M. Iannelli, and F. A. Milner, Existence and uniqueness of endemic states for the age-structured SIR epidemic model, Mathematical Biosciences, 1998, 150(2): 177–190.
Z. Ma, Mathematical Modeling and Research of Population Ecology, Anhui Education Publishing House, Hefei, 1996.
H. R. Thieme, Semiflows generated by Lipschitz perturbations of non-densely defined operators, Differential Integral Equations, 1990, 3(6): 1035–1066.
M. Martcheva and H. R. Thieme, Progression age enhanced backward bifurcation in an epidemic model with suoer-infection, Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2003, 46(5): 385–424.
K. Dietz and D. Schenzle, Proportionate mixing for age-dependent infection transmission, J. Math. Biol., 1985, 22: 116–120.
J. Müller, Optimal vaccination patterns in age structured populations, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1998, 59(1): 222–241.
J. Müller, Optimal Vaccination Patterns in Age Structured Populations, Dissertation, Fakultät für Mathematik, Tübingen, 1994.
K. P. Hadeler, J. Müller, Optimal harvesting and optimal vaccination, Mathematical Biosciences, 2007, 206(2): 249–272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province under Grant No. 092300410206, and Science and Technology Program of Educational Department of Henan Province under Grant No. 2009A110015.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor Dexing FENG.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Yu, J. & Zhu, G. Global stability of an age-structured sir epidemic model with pulse vaccination strategy. J Syst Sci Complex 25, 417–429 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-011-9177-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-011-9177-y