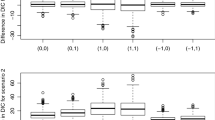
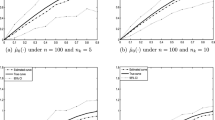
Abstract
Panel count data are frequently encountered when study subjects are under discrete observations. However, limited literature has been found on variable selection for panel count data. In this paper, without considering the model assumption of observation process, a more general semiparametric transformation model for panel count data with informative observation process is developed. A penalized estimation procedure based on the quantile regression function is proposed for variable selection and parameter estimation simultaneously. The consistency and oracle properties of the estimators are established under some mild conditions. Some simulations and an application are reported to evaluate the proposed approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thall P F, Mixed Poisson likelihood regression models for longitudinal interval count data, Biometrics, 1988, 44: 197–209.
Sun J and Kalbfleisch J D, Estimation of the mean function of point processes based on panel count data, Statistica Sinica, 1995, 5: 279–290.
Wellner J A and Zhang Y, Two estimators of the mean of a counting process with panel count data, The Annals of Statistics, 2000, 28: 779–814.
Zhang Y, A semiparametric pseudolikelihood estimation method for panel count data, Biometrika, 2002, 89: 39–48.
Sun J and Wei L J, Regression analysis of panel count data with covariate-dependent observation and censoring times, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 2000, 62: 293–302.
Lin D Y, Wei L J, and Ying Z, Semiparametric transformation models for point processes, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2001, 96: 620–628.
He X, Tong X, and Sun J, Semiparametric analysis of panel count data with correlated observation and follow-up times, Lifetime Data Analysis, 2009, 15: 177–196.
Li N, Sun L, and Sun J, Semiparametric transformation models for panel count data with dependent observation processes, Statistics in Biosciences, 2010, 2: 191–210.
Li N, Semiparametric transformation models for panel count data. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Missouri, Columbia, 2011.
Li N, Zhao H, and Sun J, Semiparametric transformation models for panel count data with correlated observation and follow-up times, Statistics in Medicine, 2013, 32: 3039–3054.
Ghosh D and Lin D Y, Marginal regression models for recurrent and terminal events, Statistica Sinica, 2002, 12: 663–688.
Luo X H and Huang C Y, A comparison of various rate functions of a recurrent event process in the presence of a terminal event, Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 2010, 19: 167–182.
Sun J and Zhao X, Statistical Analysis of Panel Count Data, Springer, New York, 2013.
Tibshirani R J, Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 1996, 58: 267–288.
Fan J and Li R, Variable selection via non-concave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2001, 96: 1348–1360.
Zou H, The adaptive lasso and its oracle properties, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2006, 101: 1418–1429.
Zhang C H, Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty, The Annals of Statistics, 2010, 38: 894–942.
Tong X, He X, Sun L, et al., Variable selection for panel count data via nonconcave penalized estimating function, Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 2009, 36: 620–635.
Zhang H, Sun J, and Wang D, Variable selection and estimation for multivariate panel count data via the seamless-L0 penalty, The Canadian Journal of Statistics, 2013, 41: 368–385.
Stevens W L, Fiducial limits of the parameter of a discontinuous distribution, Biometrika, 1950, 37: 117–129.
Machado J and Santos Silva J, Quantiles for counts, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2005, 100: 1226–1237.
Lee D and Neocleous T, Bayesian quantile regression for count data with application to environmental epidemiology, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series C, 2010, 59: 905–920.
Jiang X, Jiang J, and Song X, Oracle model selection for nonlinear models based on weighted composite quantile regression, Statistica Sinica, 2012, 22: 1479–1506.
Guo J, Tang M, Tian M, et al., Variable selection in high-dimensional partially linear additive models for composite quantile regression, Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2013, 65: 56–67.
Koenker R and Machado J A, Goodness of fit and related inference processes for quantile regression, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1999, 94: 1296–1310.
Li K C, Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1991, 86: 316–342.
Xia Y, Tong H, Li W K, et al., An adaptive estimation of dimension reduction space, Journal of Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 2002, 64: 363–410.
Knight K, Limiting distributions for L1 regression estimators under general conditions, The Annals of Statistics, 1998, 26: 755–770.
Knight K and Fu W J, Asymptotics for lasso-type estimators, The Annals of Statistics, 2000, 28: 1356–1378.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Editor, an associate editor, and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments that have significantly improved the paper. We thank Professor Zhao Xiaobing and Zhou Xian to help improve the English presentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 12001485, the National Bureau of Statistics of China under Grant No. 2020LY073, and the First Class Discipline of Zhejiang-A (Zhejiang University of Finance and Economics- Statistics) under Grant No. Z0111119010/024.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor ZHU Liping.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, W. et al. Robust Estimation of Semiparametric Transformation Model for Panel Count Data. J Syst Sci Complex 34, 2334–2356 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-0099-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-0099-4